New X-ray System Smoothens Radiographic Exams
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 26 Jan 2022 |
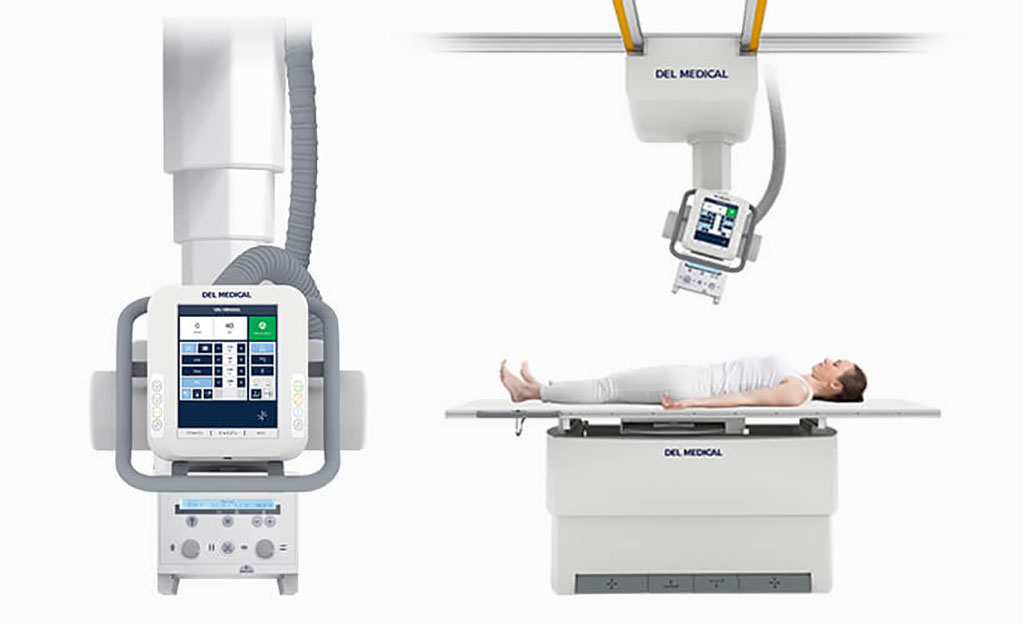
Image: The OTC18S overhead tube crane (OTC) system (Photo courtesy of UMG/Del Medical)
A new X-ray system features enhanced vertical tracking, manual positioning, vertical and horizontal auto-centering and tracking, and fully motorized multi-image stitching capabilities.
The UMG/Del Medical (Harrison, NY, USA) OTC18S is an overhead tube crane (OTC) system that uses sophisticated motorization on overhead horizontal and transverse ceiling-mounted rails and both vertical and horizontal tracking , with effortless movement controlled by an electromagnetic braking system that enables fast and secure readjustments of the tube head. A five-tier telescoping column delivers vertical movement of 180 cm, allowing complete head-to-toe radiographic procedures, including upright weight-bearing and recumbent tabletop exams.
A large 10.4 in touchscreen LCD touchscreen interface enabling the technologist to view, adjust, and control tube angulation, SID values, generator control options, and other system settings without leaving the patient’s side. Color-coded movement identification buttons provide optimal precision when setting up views. An all-lock release sensor located just above the bottom section of the tube head handle enables rapid manual positioning by allowing the user to grab the bottom handle to unlock the system and make swift adjustments.
In addition, it also guides technologists intuitively through an automated stitching exam set up procedure for long length examinations, and helps adjust generator technique factors without leaving the patient’s side. Accelerated patient positioning and reduced radiation exposure are provided by automatically selecting the proper field-of-view for each body part and automated tracking to selected image receptors. The system includes a mobile universal positioning and alignment stand (with optional ruler).
The durable EV800 elevating table features a four-way lift system, with a smooth, scratch-resistant surface that lowers to a height of just 50 cm to ensure stress-free patient transfers and adjustments through conveniently placed recessed foot treadles and table-side controls. The table can handle a patient weight capacity of up to 363 kg. In addition, the system comes with the VT300 wall stand that holds a tilting image receptor, promoting comfort and precision for both standing or seated examinations.
Related Links:
UMG/Del Medical
The UMG/Del Medical (Harrison, NY, USA) OTC18S is an overhead tube crane (OTC) system that uses sophisticated motorization on overhead horizontal and transverse ceiling-mounted rails and both vertical and horizontal tracking , with effortless movement controlled by an electromagnetic braking system that enables fast and secure readjustments of the tube head. A five-tier telescoping column delivers vertical movement of 180 cm, allowing complete head-to-toe radiographic procedures, including upright weight-bearing and recumbent tabletop exams.
A large 10.4 in touchscreen LCD touchscreen interface enabling the technologist to view, adjust, and control tube angulation, SID values, generator control options, and other system settings without leaving the patient’s side. Color-coded movement identification buttons provide optimal precision when setting up views. An all-lock release sensor located just above the bottom section of the tube head handle enables rapid manual positioning by allowing the user to grab the bottom handle to unlock the system and make swift adjustments.
In addition, it also guides technologists intuitively through an automated stitching exam set up procedure for long length examinations, and helps adjust generator technique factors without leaving the patient’s side. Accelerated patient positioning and reduced radiation exposure are provided by automatically selecting the proper field-of-view for each body part and automated tracking to selected image receptors. The system includes a mobile universal positioning and alignment stand (with optional ruler).
The durable EV800 elevating table features a four-way lift system, with a smooth, scratch-resistant surface that lowers to a height of just 50 cm to ensure stress-free patient transfers and adjustments through conveniently placed recessed foot treadles and table-side controls. The table can handle a patient weight capacity of up to 363 kg. In addition, the system comes with the VT300 wall stand that holds a tilting image receptor, promoting comfort and precision for both standing or seated examinations.
Related Links:
UMG/Del Medical
Latest Radiography News
- Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
- AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
- X-Ray Breakthrough Captures Three Image-Contrast Types in Single Shot
- AI Generates Future Knee X-Rays to Predict Osteoarthritis Progression Risk
- AI Algorithm Uses Mammograms to Accurately Predict Cardiovascular Risk in Women
- AI Hybrid Strategy Improves Mammogram Interpretation
- AI Technology Predicts Personalized Five-Year Risk of Developing Breast Cancer
- RSNA AI Challenge Models Can Independently Interpret Mammograms
- New Technique Combines X-Ray Imaging and Radar for Safer Cancer Diagnosis
- New AI Tool Helps Doctors Read Chest X‑Rays Better
- Wearable X-Ray Imaging Detecting Fabric to Provide On-The-Go Diagnostic Scanning
- AI Helps Radiologists Spot More Lesions in Mammograms
- AI Detects Fatty Liver Disease from Chest X-Rays
- AI Detects Hidden Heart Disease in Existing CT Chest Scans
- Ultra-Lightweight AI Model Runs Without GPU to Break Barriers in Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- AI Radiology Tool Identifies Life-Threatening Conditions in Milliseconds

Channels
MRI
view channel
MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
Recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies widely, with some patients regaining full function while others are left with lasting disabilities. Prognosis is especially difficult to assess in patients... Read more
Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
Vascular dysfunction in the spinal cord contributes to multiple neurological conditions, including traumatic injuries and degenerative cervical myelopathy, where reduced blood flow can lead to progressive... Read more
AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
A cardiac MRI can reveal critical information about the heart’s function and any abnormalities, but traditional scans take 30 to 90 minutes and often suffer from poor image quality due to patient movement.... Read more
AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is one of the most common inherited heart conditions and a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young individuals and athletes. While many patients live normal lives, some... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Wearable Ultrasound Imaging System to Enable Real-Time Disease Monitoring
Chronic conditions such as hypertension and heart failure require close monitoring, yet today’s ultrasound imaging is largely confined to hospitals and short, episodic scans. This reactive model limits... Read more
Ultrasound Technique Visualizes Deep Blood Vessels in 3D Without Contrast Agents
Producing clear 3D images of deep blood vessels has long been difficult without relying on contrast agents, CT scans, or MRI. Standard ultrasound typically provides only 2D cross-sections, limiting clinicians’... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
Targeted cancer therapies only work when tumor cells express the specific molecular structures they are designed to attack. In urothelial carcinoma, a common form of bladder cancer, the cell surface protein... Read more
Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
Targeted cancer therapies can be highly effective, but only when a patient’s tumor expresses the specific protein the treatment is designed to attack. Determining this usually requires biopsies or advanced... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer is a form of head and neck cancer that can spread through lymph nodes, significantly affecting survival and treatment decisions. Current therapies often involve combinations of surgery,... Read more
New 3D Imaging System Addresses MRI, CT and Ultrasound Limitations
Medical imaging is central to diagnosing and managing injuries, cancer, infections, and chronic diseases, yet existing tools each come with trade-offs. Ultrasound, X-ray, CT, and MRI can be costly, time-consuming,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more



















