AI Detects Fatty Liver Disease from Chest X-Rays
Posted on 01 Jul 2025
Fatty liver disease, which results from excess fat accumulation in the liver, is believed to impact approximately one in four individuals globally. If not addressed in time, it can progress to severe conditions such as cirrhosis and liver cancer, underscoring the importance of early detection and treatment. The current standard diagnostic tools for fatty liver disease include ultrasounds, CT scans, and MRIs, all of which require expensive, specialized equipment and dedicated facilities.
By contrast, chest X-rays are more commonly used, cost-effective, and involve minimal radiation. Although primarily employed to assess the lungs and heart, chest X-rays also partially image the liver, making it possible to identify signs of fatty liver disease. Despite this potential, the link between chest X-rays and the condition has rarely been studied in depth. Now, researchers have created an AI model capable of identifying fatty liver disease using chest X-ray images.
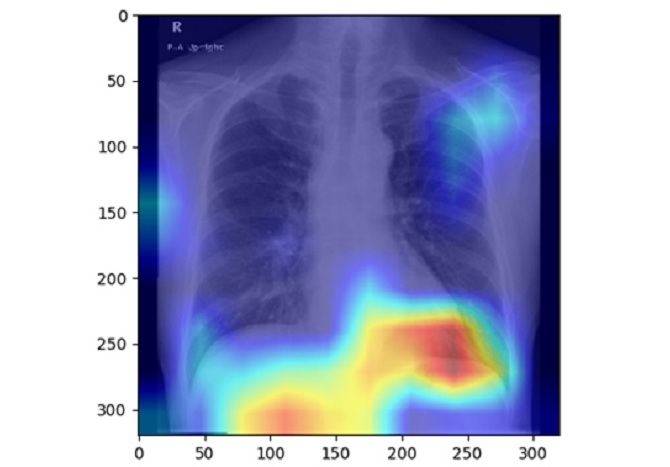
In a retrospective study, a research team from Osaka Metropolitan University (Osaka, Japan) used 6,599 chest X-ray images from 4,414 patients to develop their AI model based on controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) scores. Their results, published in Radiology Cardiothoracic Imaging, demonstrated that the AI model achieved high accuracy, with the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) ranging from 0.82 to 0.83.
“The development of diagnostic methods using easily obtainable and inexpensive chest X-rays has the potential to improve fatty liver detection. We hope it can be put into practical use in the future,” said Associate Professor Sawako Uchida-Kobayashi who led the research.
Related Links:
Osaka Metropolitan University