Generative AI Model Significantly Reduces Chest X-Ray Reading Time
Posted on 20 Mar 2025
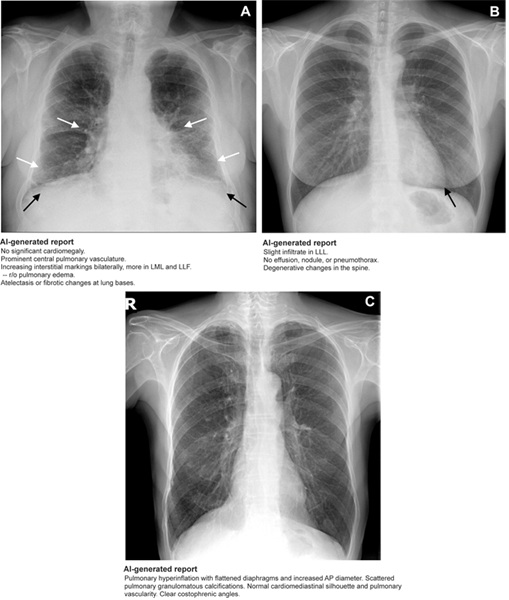
The prompt and accurate interpretation of radiologic images is critical due to its significant impact on patient outcomes, as errors in interpretation can lead to changes in clinical management. Chest radiography is one of the most frequently performed radiologic exams, but its interpretation requires a high level of expertise and considerable time. Although radiologists are highly accurate, their interpretations often face scalability challenges due to the growing volume of imaging studies. This results in an increased workload, delays in diagnosis, disruptions in clinical workflows, and an increased risk of misinterpretation. Multimodal generative artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, which are capable of processing and generating diverse data types, including both images and text, hold the potential to advance radiology. A new study has evaluated the clinical value of a domain-specific multimodal generative AI model for interpreting chest radiographs, with the aim of improving the radiology workflow.
Researchers at Mass General Brigham (Boston, MA, USA), along with their collaborators, carried out a retrospective, sequential, multireader, multicase reader study. They used 758 chest radiographs from a publicly available dataset (2009-2017) to assess the effectiveness of AI-generated reports. Five radiologists interpreted the chest radiographs in two sessions: one without AI-generated reports and the other with AI-generated preliminary reports. Various factors, including reading times, reporting agreement (RADPEER), and quality scores (on a five-point scale), were assessed by two experienced thoracic radiologists. These metrics were compared between the two sessions conducted from October to December 2023. A generalized linear mixed model was employed to analyze the reading times, report agreement, and quality scores. Additionally, a subset of 258 chest radiographs was examined to evaluate the factual correctness of the reports, comparing the sensitivities and specificities between the two sessions using the McNemar test.
The study, published in Radiology, revealed that AI-generated reports reduced the average reading time for chest X-rays (CXRs) by 42% compared to radiologists' unassisted evaluation (19.8 seconds vs. 34.2 seconds). In the subset analysis of 258 cases, the researchers found that AI-generated reports resulted in nearly a 10% increase in sensitivity for detecting pleural lesions (87.4% vs. 77.7%) and a more than 6% increase in sensitivity for identifying a widened mediastinum (90.8% vs. 84.3%). Without AI assistance, the researchers observed a wide range of sensitivities (54.2% to 80.7%) and specificities (84.9% to 93.4%) among the five radiologists for detecting abnormalities on CXRs. However, when AI-generated reports were used, the range for sensitivity and specificity was narrower. The sensitivity rates ranged from 71.1% to 80.8%, while specificity ranged from 85.2% to 87.3%. The researchers concluded that the use of a domain-specific multimodal generative AI model enhanced both the efficiency and quality of radiology report generation.














