Artificial Intelligence Accurately Detects Fractures on X-Rays
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 23 Dec 2021 |
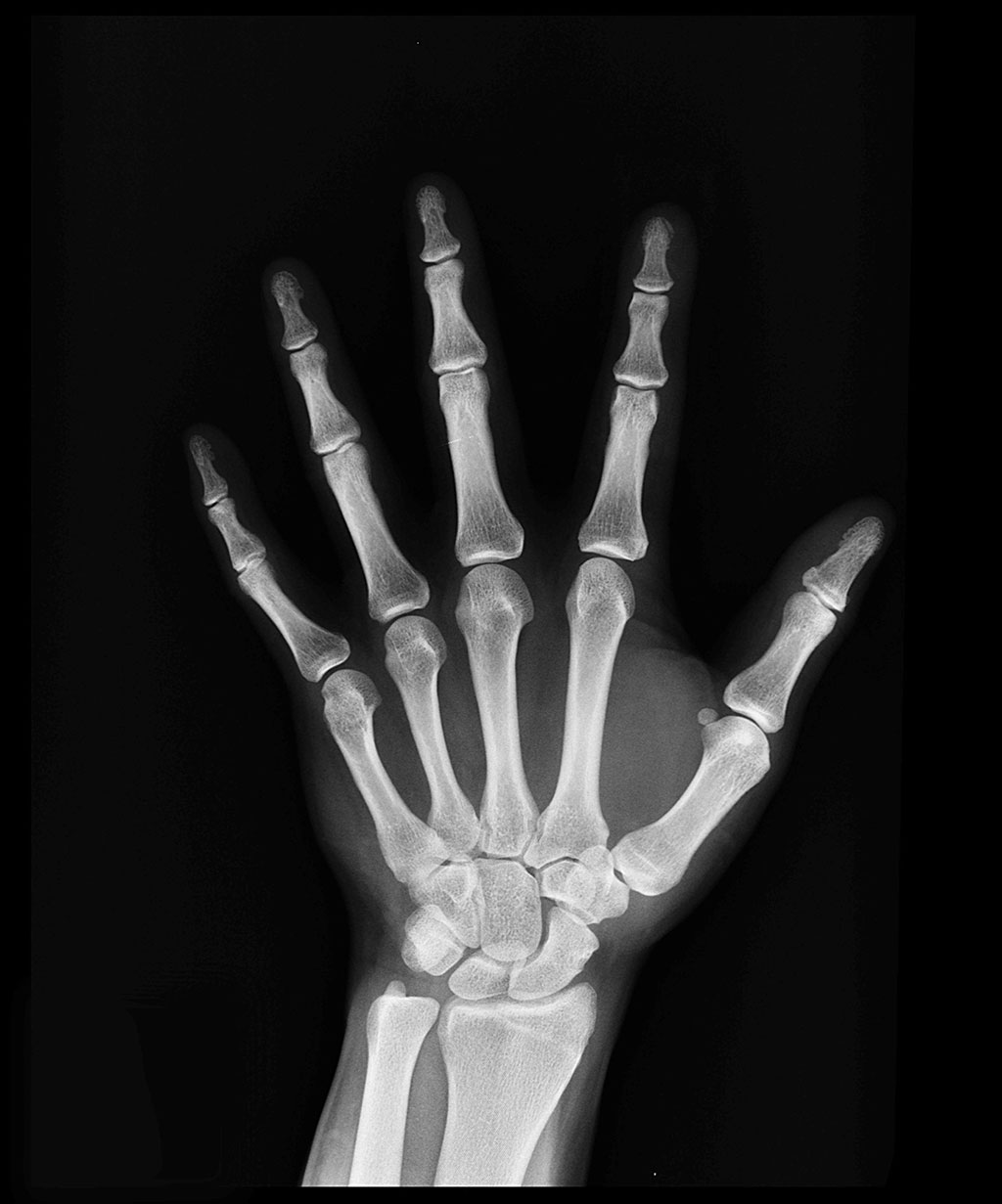
A new study has found that artificial intelligence (AI) can help physicians in interpreting X-rays after an injury and suspected fracture.
The AI algorithm (AI BoneView) developed by researchers at the Boston University School of Medicine (Boston, MA, USA) was trained on a very large number of X-rays from multiple institutions to detect fractures of the limbs, pelvis, torso and lumbar spine and rib cage. Expert human readers (musculoskeletal radiologists, who are sub-specialized radiology doctors after receiving focused training on reading bone X-rays) defined the gold standard in this study and compared the performance of human readers with and without AI assistance.
Emergency room and urgent care clinics are typically busy and patients often have to wait many hours before they can be seen, evaluated and receive treatment. Waiting for X-rays to be interpreted by radiologists can contribute to this long wait time because radiologists often read X-rays for a large number of patients. Fracture interpretation errors represents up to 24% of harmful diagnostic errors seen in the emergency department. Furthermore, inconsistencies in radiographic diagnosis of fractures are more common during the evening and overnight hours (5 p.m. to 3 a.m.), likely related to non-expert reading and fatigue.
In the study, a variety of readers were used to simulate real life scenario, including radiologists, orthopedic surgeons, emergency physicians and physician assistants, rheumatologists, and family physicians, all of whom read X-rays in real clinical practice to diagnose fractures in their patients. Each reader’s diagnostic accuracy of fractures, with and without AI assistance, were compared against the gold standard. They also assessed the diagnostic performance of AI alone against the gold standard. AI assistance helped reduce missed fractures by 29% and increased readers’ sensitivity by 16%, and by 30% for exams with more than one fracture, while improving specificity by 5%. The researchers believe that AI can be a powerful tool to help radiologists and other physicians to improve diagnostic performance and increase efficiency, while potentially improving patient experience at the time of hospital or clinic visit.
“Our AI algorithm can quickly and automatically detect X-rays that are positive for fractures and flag those studies in the system so that radiologists can prioritize reading X-rays with positive fractures. The system also highlights regions of interest with bounding boxes around areas where fractures are suspected. This can potentially contribute to less waiting time at the time of hospital or clinic visit before patients can get a positive diagnosis of fracture,” explained corresponding Ali Guermazi, MD, PhD, chief of radiology at VA Boston Healthcare System and Professor of Radiology & Medicine at BUSM.
“Our study was focused on fracture diagnosis, but similar concept can be applied to other diseases and disorders. Our ongoing research interest is to how best to utilize AI to help human healthcare providers to improve patient care, rather than making AI replace human healthcare providers. Our study showed one such example,” he added.
Related Links:
Boston University School of Medicine
Latest Radiography News
- AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
- X-Ray Breakthrough Captures Three Image-Contrast Types in Single Shot
- AI Generates Future Knee X-Rays to Predict Osteoarthritis Progression Risk
- AI Algorithm Uses Mammograms to Accurately Predict Cardiovascular Risk in Women
- AI Hybrid Strategy Improves Mammogram Interpretation
- AI Technology Predicts Personalized Five-Year Risk of Developing Breast Cancer
- RSNA AI Challenge Models Can Independently Interpret Mammograms
- New Technique Combines X-Ray Imaging and Radar for Safer Cancer Diagnosis
- New AI Tool Helps Doctors Read Chest X‑Rays Better
- Wearable X-Ray Imaging Detecting Fabric to Provide On-The-Go Diagnostic Scanning
- AI Helps Radiologists Spot More Lesions in Mammograms
- AI Detects Fatty Liver Disease from Chest X-Rays
- AI Detects Hidden Heart Disease in Existing CT Chest Scans
- Ultra-Lightweight AI Model Runs Without GPU to Break Barriers in Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- AI Radiology Tool Identifies Life-Threatening Conditions in Milliseconds

- Machine Learning Algorithm Identifies Cardiovascular Risk from Routine Bone Density Scans
Channels
MRI
view channel
Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
Vascular dysfunction in the spinal cord contributes to multiple neurological conditions, including traumatic injuries and degenerative cervical myelopathy, where reduced blood flow can lead to progressive... Read more
AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
A cardiac MRI can reveal critical information about the heart’s function and any abnormalities, but traditional scans take 30 to 90 minutes and often suffer from poor image quality due to patient movement.... Read more
AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is one of the most common inherited heart conditions and a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young individuals and athletes. While many patients live normal lives, some... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Wearable Ultrasound Imaging System to Enable Real-Time Disease Monitoring
Chronic conditions such as hypertension and heart failure require close monitoring, yet today’s ultrasound imaging is largely confined to hospitals and short, episodic scans. This reactive model limits... Read more
Ultrasound Technique Visualizes Deep Blood Vessels in 3D Without Contrast Agents
Producing clear 3D images of deep blood vessels has long been difficult without relying on contrast agents, CT scans, or MRI. Standard ultrasound typically provides only 2D cross-sections, limiting clinicians’... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
PET Imaging of Inflammation Predicts Recovery and Guides Therapy After Heart Attack
Acute myocardial infarction can trigger lasting heart damage, yet clinicians still lack reliable tools to identify which patients will regain function and which may develop heart failure.... Read more
Radiotheranostic Approach Detects, Kills and Reprograms Aggressive Cancers
Aggressive cancers such as osteosarcoma and glioblastoma often resist standard therapies, thrive in hostile tumor environments, and recur despite surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy. These tumors also... Read more
New Imaging Solution Improves Survival for Patients with Recurring Prostate Cancer
Detecting recurrent prostate cancer remains one of the most difficult challenges in oncology, as standard imaging methods such as bone scans and CT scans often fail to accurately locate small or early-stage tumors.... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
New Algorithm Dramatically Speeds Up Stroke Detection Scans
When patients arrive at emergency rooms with stroke symptoms, clinicians must rapidly determine whether the cause is a blood clot or a brain bleed, as treatment decisions depend on this distinction.... Read more
3D Scanning Approach Enables Ultra-Precise Brain Surgery
Precise navigation is critical in neurosurgery, yet even small alignment errors can affect outcomes when operating deep within the brain. A new 3D surface-scanning approach now provides a radiation-free... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more