Automated AI Fat Measurement on Abdominal CT Images Predicts Future Heart Attack or Stroke Risk Better Than BMI
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 07 Jan 2021 |
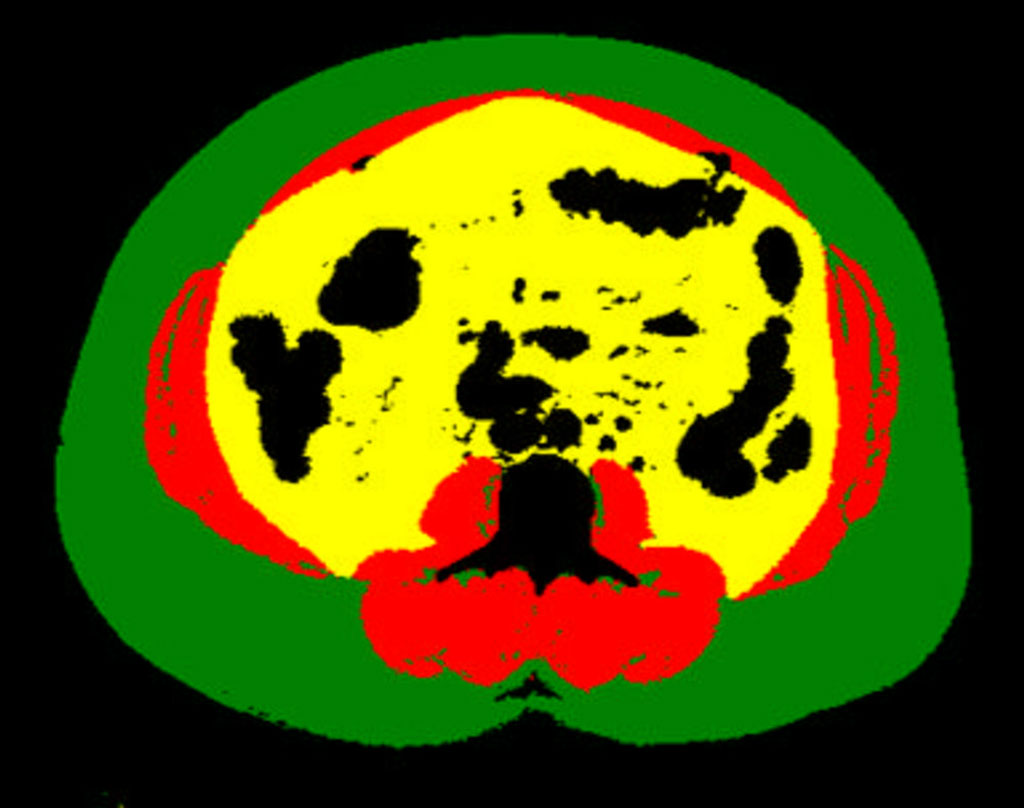
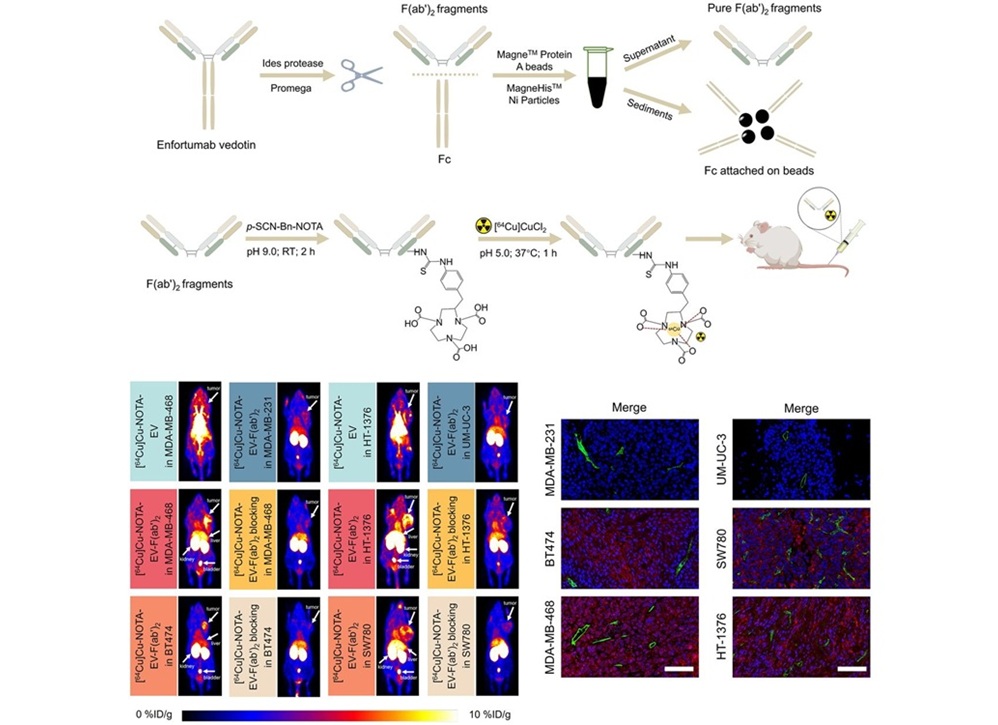
Image: Example of body composition analysis of an abdominal CT slice with subcutaneous fat in green, skeletal muscle in red, and visceral fat in yellow (Photo courtesy of UCSF)
An automated artificial intelligence (AI) measurement of visceral fat area on abdominal CT images predicts future heart attack or stroke risk better than overall weight or body mass index (BMI).
In a study presented at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), researchers from the University of California San Francisco (San Francisco, CA, USA) have suggested that automated deep learning analysis of abdominal CT images produces a more precise measurement of body composition and predicts major cardiovascular events, such as heart attack and stroke, better than overall weight or BMI. Unlike BMI, which is based on height and weight, a single axial CT slice of the abdomen visualizes the volume of subcutaneous fat area, visceral fat area and skeletal muscle area. However, manually measuring these individual areas is time intensive and costly.
A multidisciplinary team of researchers, including radiologists, a data scientist and biostatistician, developed a fully automated method using deep learning - a type of AI - to determine body composition metrics from abdominal CT images. The study cohort was derived from the 33,182 abdominal CT outpatient exams performed on 23,136 patients in 2012. The researchers identified 12,128 patients who were free of major cardiovascular and cancer diagnoses at the time of imaging. Mean age of the patients was 52 years, and 57% of patients were women. The researchers selected the L3 CT slice (from the third lumbar spine vertebra) and calculated body composition areas for each patient. Patients were then divided into four quartiles based on the normalized values of subcutaneous fat area, visceral fat area and skeletal muscle area.
In this retrospective study, it was determined which of these 12,128 patients had a myocardial infarction (heart attack) or stroke within five years after their index abdominal CT scan. The researchers found 1,560 myocardial infarctions and 938 strokes occurred in this study group. Statistical analysis demonstrated that visceral fat area was independently associated with future heart attack and stroke. BMI was not associated with heart attack or stroke. The researchers believe that this work demonstrates that fully automated and normalized body composition analysis could now be applied to large-scale research projects.
“This work shows the promise of AI systems to add value to clinical care by extracting new information from existing imaging data,” said Kirti Magudia, M.D., Ph.D., an abdominal imaging and ultrasound fellow at the University of California San Francisco. “The deployment of AI systems would allow radiologists, cardiologists and primary care doctors to provide better care to patients at minimal incremental cost to the health care system.”
Related Links:
University of California San Francisco
In a study presented at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), researchers from the University of California San Francisco (San Francisco, CA, USA) have suggested that automated deep learning analysis of abdominal CT images produces a more precise measurement of body composition and predicts major cardiovascular events, such as heart attack and stroke, better than overall weight or BMI. Unlike BMI, which is based on height and weight, a single axial CT slice of the abdomen visualizes the volume of subcutaneous fat area, visceral fat area and skeletal muscle area. However, manually measuring these individual areas is time intensive and costly.
A multidisciplinary team of researchers, including radiologists, a data scientist and biostatistician, developed a fully automated method using deep learning - a type of AI - to determine body composition metrics from abdominal CT images. The study cohort was derived from the 33,182 abdominal CT outpatient exams performed on 23,136 patients in 2012. The researchers identified 12,128 patients who were free of major cardiovascular and cancer diagnoses at the time of imaging. Mean age of the patients was 52 years, and 57% of patients were women. The researchers selected the L3 CT slice (from the third lumbar spine vertebra) and calculated body composition areas for each patient. Patients were then divided into four quartiles based on the normalized values of subcutaneous fat area, visceral fat area and skeletal muscle area.
In this retrospective study, it was determined which of these 12,128 patients had a myocardial infarction (heart attack) or stroke within five years after their index abdominal CT scan. The researchers found 1,560 myocardial infarctions and 938 strokes occurred in this study group. Statistical analysis demonstrated that visceral fat area was independently associated with future heart attack and stroke. BMI was not associated with heart attack or stroke. The researchers believe that this work demonstrates that fully automated and normalized body composition analysis could now be applied to large-scale research projects.
“This work shows the promise of AI systems to add value to clinical care by extracting new information from existing imaging data,” said Kirti Magudia, M.D., Ph.D., an abdominal imaging and ultrasound fellow at the University of California San Francisco. “The deployment of AI systems would allow radiologists, cardiologists and primary care doctors to provide better care to patients at minimal incremental cost to the health care system.”
Related Links:
University of California San Francisco
Latest Imaging IT News
- New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI-Based Technology for Ultrasound Image Analysis Receives FDA Approval
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Digital Pathology Software Improves Workflow Efficiency
- Patient-Centric Portal Facilitates Direct Imaging Access
- New Workstation Supports Customer-Driven Imaging Workflow
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read more
AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
Chronological age does not always reflect how fast the body is truly aging, and current biological age tests often rely on DNA-based markers that may miss early organ-level decline. Detecting subtle, age-related... Read moreMRI
view channel
Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
Vascular dysfunction in the spinal cord contributes to multiple neurological conditions, including traumatic injuries and degenerative cervical myelopathy, where reduced blood flow can lead to progressive... Read more
AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
A cardiac MRI can reveal critical information about the heart’s function and any abnormalities, but traditional scans take 30 to 90 minutes and often suffer from poor image quality due to patient movement.... Read more
AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is one of the most common inherited heart conditions and a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young individuals and athletes. While many patients live normal lives, some... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Wearable Ultrasound Imaging System to Enable Real-Time Disease Monitoring
Chronic conditions such as hypertension and heart failure require close monitoring, yet today’s ultrasound imaging is largely confined to hospitals and short, episodic scans. This reactive model limits... Read more
Ultrasound Technique Visualizes Deep Blood Vessels in 3D Without Contrast Agents
Producing clear 3D images of deep blood vessels has long been difficult without relying on contrast agents, CT scans, or MRI. Standard ultrasound typically provides only 2D cross-sections, limiting clinicians’... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
PET Imaging of Inflammation Predicts Recovery and Guides Therapy After Heart Attack
Acute myocardial infarction can trigger lasting heart damage, yet clinicians still lack reliable tools to identify which patients will regain function and which may develop heart failure.... Read more
Radiotheranostic Approach Detects, Kills and Reprograms Aggressive Cancers
Aggressive cancers such as osteosarcoma and glioblastoma often resist standard therapies, thrive in hostile tumor environments, and recur despite surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy. These tumors also... Read more
New Imaging Solution Improves Survival for Patients with Recurring Prostate Cancer
Detecting recurrent prostate cancer remains one of the most difficult challenges in oncology, as standard imaging methods such as bone scans and CT scans often fail to accurately locate small or early-stage tumors.... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI-Based Tool Accelerates Detection of Kidney Cancer
Diagnosing kidney cancer depends on computed tomography scans, often using contrast agents to reveal abnormalities in kidney structure. Tumors are not always searched for deliberately, as many scans are... Read more
New Algorithm Dramatically Speeds Up Stroke Detection Scans
When patients arrive at emergency rooms with stroke symptoms, clinicians must rapidly determine whether the cause is a blood clot or a brain bleed, as treatment decisions depend on this distinction.... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more