VR Tool Increases Efficiency of Brain Scan Analysis
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 06 Sep 2018 |
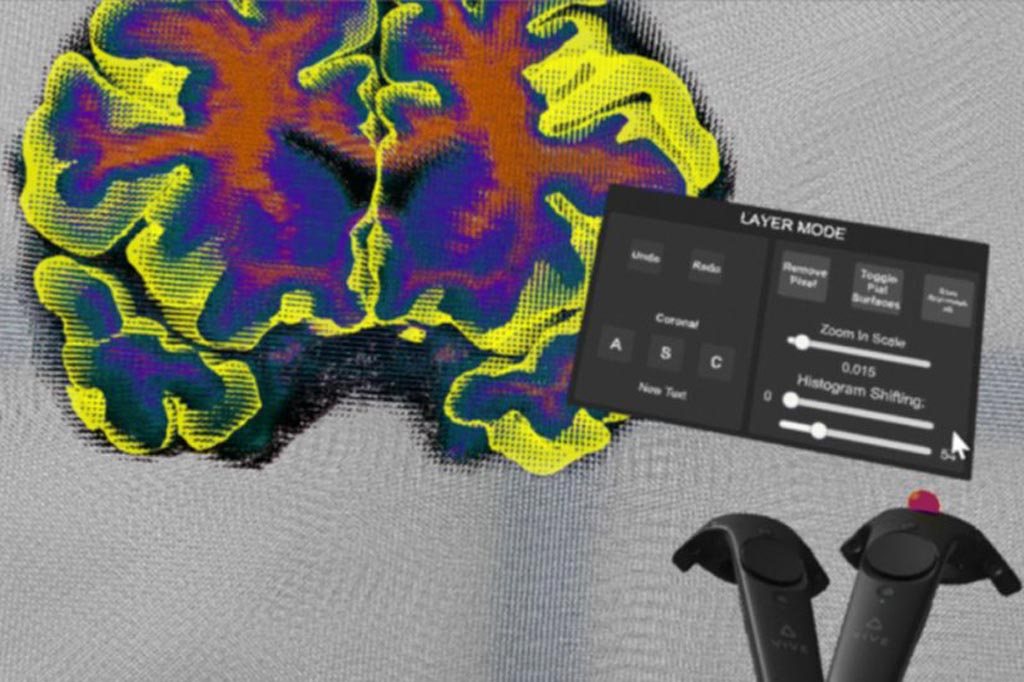
Image: The Virtual Brain Segmenter could increase the efficiency of brain scan analysis (Photo courtesy of Dominique Duncan).
Researchers at the Mark and Mary Stevens Neuroimaging and Informatics Institute at the Keck School of Medicine of University of Southern California {(USC), Los Angeles, CA, USA} have designed a virtual reality (VR) tool for correcting errors in brain scan data. The tool named Virtual Brain Segmenter (VBS) transforms a tedious step in the scientific process into an immersive experience and significantly increases the efficiency of brain scan analysis.
During automatic processing of the MRI data collected from study participants by the researchers, the segmentation step separates the brain into labeled regions to allow for close examination of the different structures. However, the automation has some drawbacks and researchers are required to manually correct the errors before proceeding with the analysis. This can be time consuming work and requires labs to hire undergraduate research assistants to correct the segmentation errors, leading to wasted time and resources spent on training.
In order to make the process more efficient and intuitive, and correct the segmentation errors with less training, the researchers launched an experimental trial to test the efficacy of VR in brain segmentation. The researchers tested 30 participants who were completely new to brain segmentation on using a MacBook to perform a minor error correction with a data cleanup program and completing the same task in VBS with a VR headset and two controllers.
They found that the participants who used VBS as compared to those using the data cleanup program finished the correction 68 seconds faster, translating into significant time savings as the task usually requires less than three minutes to be completed.
“This project is particularly exciting because not much has been done with VR in the field of neuroscience,” said Arthur Toga, provost professor and director of the neuroimaging and informatics institute. “Our main goal is to put this tool in the hands of researchers around the world. We see that as a way to continue driving discovery in the field.”
Related Links:
University of Southern California
During automatic processing of the MRI data collected from study participants by the researchers, the segmentation step separates the brain into labeled regions to allow for close examination of the different structures. However, the automation has some drawbacks and researchers are required to manually correct the errors before proceeding with the analysis. This can be time consuming work and requires labs to hire undergraduate research assistants to correct the segmentation errors, leading to wasted time and resources spent on training.
In order to make the process more efficient and intuitive, and correct the segmentation errors with less training, the researchers launched an experimental trial to test the efficacy of VR in brain segmentation. The researchers tested 30 participants who were completely new to brain segmentation on using a MacBook to perform a minor error correction with a data cleanup program and completing the same task in VBS with a VR headset and two controllers.
They found that the participants who used VBS as compared to those using the data cleanup program finished the correction 68 seconds faster, translating into significant time savings as the task usually requires less than three minutes to be completed.
“This project is particularly exciting because not much has been done with VR in the field of neuroscience,” said Arthur Toga, provost professor and director of the neuroimaging and informatics institute. “Our main goal is to put this tool in the hands of researchers around the world. We see that as a way to continue driving discovery in the field.”
Related Links:
University of Southern California
Latest Industry News News
- GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
- Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
- Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
- Bracco Diagnostics and ColoWatch Partner to Expand Availability CRC Screening Tests Using Virtual Colonoscopy
- Mindray Partners with TeleRay to Streamline Ultrasound Delivery
- Philips and Medtronic Partner on Stroke Care
- Siemens and Medtronic Enter into Global Partnership for Advancing Spine Care Imaging Technologies
- RSNA 2024 Technical Exhibits to Showcase Latest Advances in Radiology
- Bracco Collaborates with Arrayus on Microbubble-Assisted Focused Ultrasound Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer
- Innovative Collaboration to Enhance Ischemic Stroke Detection and Elevate Standards in Diagnostic Imaging
- RSNA 2024 Registration Opens
- Microsoft collaborates with Leading Academic Medical Systems to Advance AI in Medical Imaging
- GE HealthCare Acquires Intelligent Ultrasound Group’s Clinical Artificial Intelligence Business
- Bayer and Rad AI Collaborate on Expanding Use of Cutting Edge AI Radiology Operational Solutions
- Polish Med-Tech Company BrainScan to Expand Extensively into Foreign Markets
- Hologic Acquires UK-Based Breast Surgical Guidance Company Endomagnetics Ltd.
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read more
AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
Chronological age does not always reflect how fast the body is truly aging, and current biological age tests often rely on DNA-based markers that may miss early organ-level decline. Detecting subtle, age-related... Read moreMRI
view channel
MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
Recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies widely, with some patients regaining full function while others are left with lasting disabilities. Prognosis is especially difficult to assess in patients... Read more
Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
Vascular dysfunction in the spinal cord contributes to multiple neurological conditions, including traumatic injuries and degenerative cervical myelopathy, where reduced blood flow can lead to progressive... Read more
AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
A cardiac MRI can reveal critical information about the heart’s function and any abnormalities, but traditional scans take 30 to 90 minutes and often suffer from poor image quality due to patient movement.... Read more
AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is one of the most common inherited heart conditions and a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young individuals and athletes. While many patients live normal lives, some... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Wearable Ultrasound Imaging System to Enable Real-Time Disease Monitoring
Chronic conditions such as hypertension and heart failure require close monitoring, yet today’s ultrasound imaging is largely confined to hospitals and short, episodic scans. This reactive model limits... Read more
Ultrasound Technique Visualizes Deep Blood Vessels in 3D Without Contrast Agents
Producing clear 3D images of deep blood vessels has long been difficult without relying on contrast agents, CT scans, or MRI. Standard ultrasound typically provides only 2D cross-sections, limiting clinicians’... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
Targeted cancer therapies only work when tumor cells express the specific molecular structures they are designed to attack. In urothelial carcinoma, a common form of bladder cancer, the cell surface protein... Read more
Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
Targeted cancer therapies can be highly effective, but only when a patient’s tumor expresses the specific protein the treatment is designed to attack. Determining this usually requires biopsies or advanced... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI-Based Tool Predicts Future Cardiovascular Events in Angina Patients
Stable coronary artery disease is a common cause of chest pain, yet accurately identifying patients at the highest risk of future heart attacks or death remains difficult. Standard coronary CT scans show... Read more
AI-Based Tool Accelerates Detection of Kidney Cancer
Diagnosing kidney cancer depends on computed tomography scans, often using contrast agents to reveal abnormalities in kidney structure. Tumors are not always searched for deliberately, as many scans are... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more