Next-Generation PACS Software Is Faster, with More Powerful Measurement, Communication Tools
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 29 Oct 2013 |
A new version of a picture archiving and communication system (PACS) software has been designed to improve diagnostic speed and accuracy, and integrates effective tools for measuring, monitoring, and comparing measurements over time. The software also provides optimized support for collaborative working through the effective and secure transmission and sharing of digital medical images.
Launched at the Journées Françaises de Radiologie (JFR) Technical Exhibition and Congress, held in Paris (France), October 2013, Telemis Medical PACS version 4.5, developed by Telemis (Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium), a specialist in medical imaging solutions, provides new tools for monitoring and comparing lesion measurements, including improved techniques for the co-registration of multiple images. The company, at the same time, has made database access and image streaming much faster. The latest version of the platform also introduces a new concept of simple, integrated image exchange between Telemis PACS-equipped institutions.
Speed and performance are very important for hospitals, clinics, and medical practices that are trying to improve efficiency and diagnostic accuracy through the use of a PACS platform. With Telemis-Medical PACS version 4.5, Telemis has substantially improved system speed and response by focusing on improvements to its database and content indexing. Visualization of large volumes of image data is now faster thanks to a new volume imaging server-streaming technology, while a TM- Prefetcher module allows pre-loading of images to a console from a regional PACS archive.
Version 4.5 also integrates improvements to the TM-Publisher Web regional image distribution system that supports secure Internet access of images and data. New Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) functionalities and re-publication features support rapid access of archived images and data and eliminate the need for general practitioners (GPs) and other offsite medical personnel to make specific requests for older data. TM-Publisher Web is compatible with regional networks such as Réseau de Santé Wallon-Walloon Health Network (RSW).
To facilitate pathology progression measurement Telemis-Medical PACS version 4.5 features an improved solution for tracking and comparing radiology findings. Simple and rapid comparison with earlier reviews and the measurement of new lesions are accomplished through an intuitive interface in only a few clicks. Multimodal comparison capabilities ensure precision diagnosis, while the new graphic user interface (GUI) is enhanced to the requirements of radiology specialists.
In its latest release, Telemis has also enhanced communication between different collaborating medical facilities. With this PACS, users can communicate with nearly 200 hospitals and medical facilities currently use a Telemis PACS platform in which digital images can be sent rapidly and securely to another site with as few as three clicks. This eliminates the costs, time, and hassle of burning images to CD- ROMs and then sending them by overnight courier when seeking second opinions or transferring patients between facilities.
Telemis CEO, Stephane Ketelaer, said, “As well as offering new PACS users the very latest in image archiving, retrieval and sharing, the latest version of Telemis-Medical PACS is also a way to thank existing customers who have trusted us for many years. Telemis-Medical PACS version 4.5 provides those customers with a simple and secure way of communicating between different sites, together with faster, more powerful software that supports major advances in aiding diagnostic accuracy.”
Related Links:
Telemis
Launched at the Journées Françaises de Radiologie (JFR) Technical Exhibition and Congress, held in Paris (France), October 2013, Telemis Medical PACS version 4.5, developed by Telemis (Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium), a specialist in medical imaging solutions, provides new tools for monitoring and comparing lesion measurements, including improved techniques for the co-registration of multiple images. The company, at the same time, has made database access and image streaming much faster. The latest version of the platform also introduces a new concept of simple, integrated image exchange between Telemis PACS-equipped institutions.
Speed and performance are very important for hospitals, clinics, and medical practices that are trying to improve efficiency and diagnostic accuracy through the use of a PACS platform. With Telemis-Medical PACS version 4.5, Telemis has substantially improved system speed and response by focusing on improvements to its database and content indexing. Visualization of large volumes of image data is now faster thanks to a new volume imaging server-streaming technology, while a TM- Prefetcher module allows pre-loading of images to a console from a regional PACS archive.
Version 4.5 also integrates improvements to the TM-Publisher Web regional image distribution system that supports secure Internet access of images and data. New Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) functionalities and re-publication features support rapid access of archived images and data and eliminate the need for general practitioners (GPs) and other offsite medical personnel to make specific requests for older data. TM-Publisher Web is compatible with regional networks such as Réseau de Santé Wallon-Walloon Health Network (RSW).
To facilitate pathology progression measurement Telemis-Medical PACS version 4.5 features an improved solution for tracking and comparing radiology findings. Simple and rapid comparison with earlier reviews and the measurement of new lesions are accomplished through an intuitive interface in only a few clicks. Multimodal comparison capabilities ensure precision diagnosis, while the new graphic user interface (GUI) is enhanced to the requirements of radiology specialists.
In its latest release, Telemis has also enhanced communication between different collaborating medical facilities. With this PACS, users can communicate with nearly 200 hospitals and medical facilities currently use a Telemis PACS platform in which digital images can be sent rapidly and securely to another site with as few as three clicks. This eliminates the costs, time, and hassle of burning images to CD- ROMs and then sending them by overnight courier when seeking second opinions or transferring patients between facilities.
Telemis CEO, Stephane Ketelaer, said, “As well as offering new PACS users the very latest in image archiving, retrieval and sharing, the latest version of Telemis-Medical PACS is also a way to thank existing customers who have trusted us for many years. Telemis-Medical PACS version 4.5 provides those customers with a simple and secure way of communicating between different sites, together with faster, more powerful software that supports major advances in aiding diagnostic accuracy.”
Related Links:
Telemis
Latest Imaging IT News
- New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI-Based Technology for Ultrasound Image Analysis Receives FDA Approval
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Digital Pathology Software Improves Workflow Efficiency
- Patient-Centric Portal Facilitates Direct Imaging Access
- New Workstation Supports Customer-Driven Imaging Workflow
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Machine Learning Algorithm Identifies Cardiovascular Risk from Routine Bone Density Scans
A new study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research reveals that an automated machine learning program can predict the risk of cardiovascular events and falls or fractures by analyzing bone... Read more
AI Improves Early Detection of Interval Breast Cancers
Interval breast cancers, which occur between routine screenings, are easier to treat when detected earlier. Early detection can reduce the need for aggressive treatments and improve the chances of better outcomes.... Read more
World's Largest Class Single Crystal Diamond Radiation Detector Opens New Possibilities for Diagnostic Imaging
Diamonds possess ideal physical properties for radiation detection, such as exceptional thermal and chemical stability along with a quick response time. Made of carbon with an atomic number of six, diamonds... Read moreMRI
view channel
New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
Traditional exercise stress tests conducted within an MRI machine require patients to lie flat, a position that artificially improves heart function by increasing stroke volume due to gravity-driven blood... Read more
Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
Women with extremely dense breasts face a higher risk of missed breast cancer diagnoses, as dense glandular and fibrous tissue can obscure tumors on mammograms. While breast MRI is recommended for supplemental... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
New Incision-Free Technique Halts Growth of Debilitating Brain Lesions
Cerebral cavernous malformations (CCMs), also known as cavernomas, are abnormal clusters of blood vessels that can grow in the brain, spinal cord, or other parts of the body. While most cases remain asymptomatic,... Read more.jpeg)
AI-Powered Lung Ultrasound Outperforms Human Experts in Tuberculosis Diagnosis
Despite global declines in tuberculosis (TB) rates in previous years, the incidence of TB rose by 4.6% from 2020 to 2023. Early screening and rapid diagnosis are essential elements of the World Health... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related death among men in the United States. However, the majority of older men diagnosed with prostate cancer have slow-growing, low-risk forms of... Read more
Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
Interleukin-13 receptor α-2 (IL13Rα2) is a cell surface receptor commonly found in solid tumors such as glioblastoma, melanoma, and breast cancer. It is minimally expressed in normal tissues, making it... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel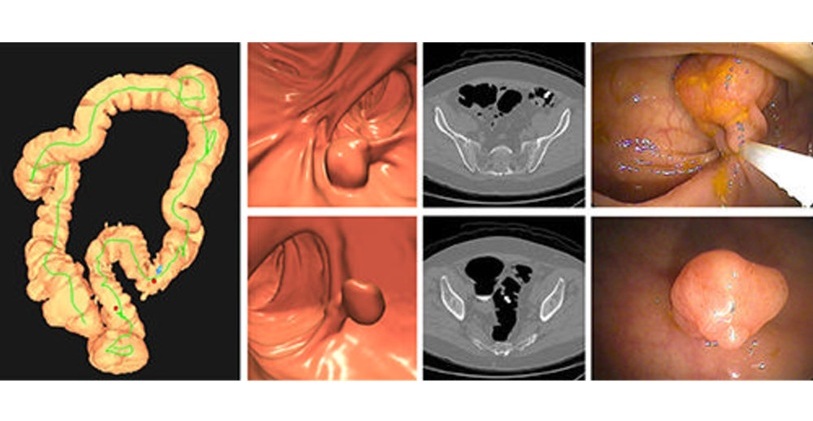
CT Colonography Beats Stool DNA Testing for Colon Cancer Screening
As colorectal cancer remains the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, early detection through screening is vital to reduce advanced-stage treatments and associated costs.... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
Currently, patients with conditions such as heart failure, pneumonia, or respiratory distress often require multiple imaging procedures that are intermittent, disruptive, and involve high levels of radiation.... Read more
AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
Radioligand therapy, a form of targeted nuclear medicine, has recently gained attention for its potential in treating specific types of tumors. However, one of the potential side effects of this therapy... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more