AI Can Flag Mammograms for Supplemental MRI
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 11 Feb 2025 |
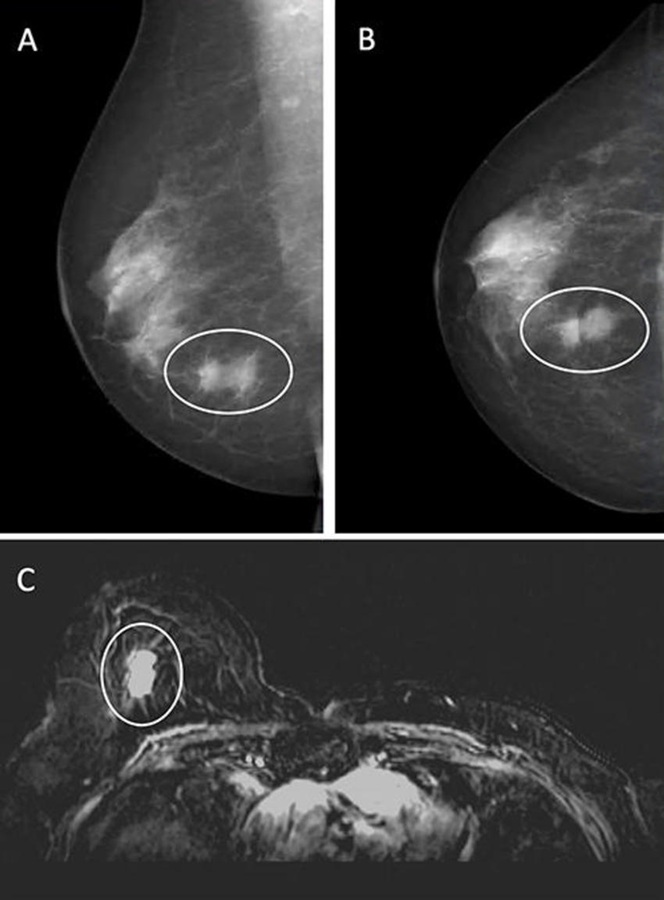
To achieve the highest detection accuracy, international guidelines recommend combining mammography and MRI screening for women with a lifetime breast cancer risk of 20% or higher based on family history. However, in the Netherlands, women with a breast cancer risk ranging from 20% to 50% typically do not have access to additional MRI screening due to limited MRI capacity, high costs of implementation, and inconsistent application of eligibility criteria in clinical practice. Several recent studies have shown the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance cancer detection in mammography screenings, including detecting cancers that may not be visible through standard mammogram interpretations by radiologists. AI could therefore be used to triage mammograms and identify women who might benefit from supplemental MRI after a negative result according to radiologist interpretation. A new study indicates that AI can effectively identify women at higher breast cancer risk within a select Dutch population. The study, published in Radiology, suggests that using AI in mammogram analysis could improve breast cancer detection by identifying patients who are most likely to benefit from breast MRI scans.
In this retrospective study, conducted by researchers at Radboud University Medical Center (Radboudumc, Nijmegen, Netherlands), women with a personal history of breast cancer, dense breasts, a history of high-risk lesions at biopsy, or those with an increased risk due to family history (but no genetic mutations) were classified as "intermediate risk." The researchers utilized a commercially available AI system to analyze the 2D screening mammograms of women they identified as intermediate risk to detect patients most likely to have cancers that were not visible on mammograms (mammographically occult cancers), indicating the need for supplemental MRI. The study cohort included 1,833 consecutive women who underwent at least one screening MRI in combination or alternated with a mammogram between 2003 and 2020, sourced from the patient breast MRI database at Radboudumc. Women with a lifetime breast cancer risk greater than 50% were excluded.
A total of 3,358 mammography exams were performed on 875 women. Of these, 2,819 (84%) exams from 760 women (with an average age of 48.9 years) were processed by the AI system and assigned a case-based suspicion score (ranging from 0 to 10) that ranked the likelihood of malignancy. Combined screening detected 37 (1.3%) breast cancers. In 19 (51%) of these cases, the cancer was not visible on mammography. Using a threshold score of 5 (which allowed supplemental MRI screening for 50% of the women), the AI system selected 31 (84%) of the breast cancer-positive exams for additional MRI screening, including 68% of exams with occult breast cancer that had been missed in the radiologists' initial reading.
"AI could potentially triage mammograms performed in the subgroup and select women that could potentially benefit from supplemental MRI after a negative mammogram," said the study's lead author, Suzanne van Winkel, R.N., M.Sc. "Using AI to triage the mammograms of populations who are not yet eligible for MRI may improve screening results while simultaneously reducing unnecessary costs."
Related Links:
Radboud University Medical Center
Latest Radiography News
- AI Detects Hidden Heart Disease in Existing CT Chest Scans
- Ultra-Lightweight AI Model Runs Without GPU to Break Barriers in Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- AI Radiology Tool Identifies Life-Threatening Conditions in Milliseconds

- Machine Learning Algorithm Identifies Cardiovascular Risk from Routine Bone Density Scans
- AI Improves Early Detection of Interval Breast Cancers
- World's Largest Class Single Crystal Diamond Radiation Detector Opens New Possibilities for Diagnostic Imaging
- AI-Powered Imaging Technique Shows Promise in Evaluating Patients for PCI
- Higher Chest X-Ray Usage Catches Lung Cancer Earlier and Improves Survival
- AI-Powered Mammograms Predict Cardiovascular Risk
- Generative AI Model Significantly Reduces Chest X-Ray Reading Time
- AI-Powered Mammography Screening Boosts Cancer Detection in Single-Reader Settings
- Photon Counting Detectors Promise Fast Color X-Ray Images
- 3D CT Imaging from Single X-Ray Projection Reduces Radiation Exposure
- AI Method Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Risk by Analyzing Multiple Mammograms
- Printable Organic X-Ray Sensors Could Transform Treatment for Cancer Patients
- Highly Sensitive, Foldable Detector to Make X-Rays Safer
Channels
MRI
view channel
New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
Traditional exercise stress tests conducted within an MRI machine require patients to lie flat, a position that artificially improves heart function by increasing stroke volume due to gravity-driven blood... Read more
Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
Women with extremely dense breasts face a higher risk of missed breast cancer diagnoses, as dense glandular and fibrous tissue can obscure tumors on mammograms. While breast MRI is recommended for supplemental... Read moreUltrasound
view channel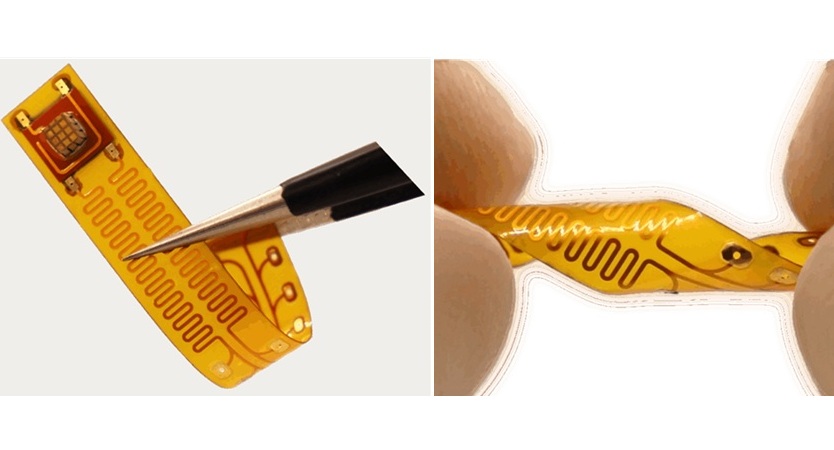
Wireless Chronic Pain Management Device to Reduce Need for Painkillers and Surgery
Chronic pain affects millions of people globally, often leading to long-term disability and dependence on opioid medications, which carry significant risks of side effects and addiction.... Read more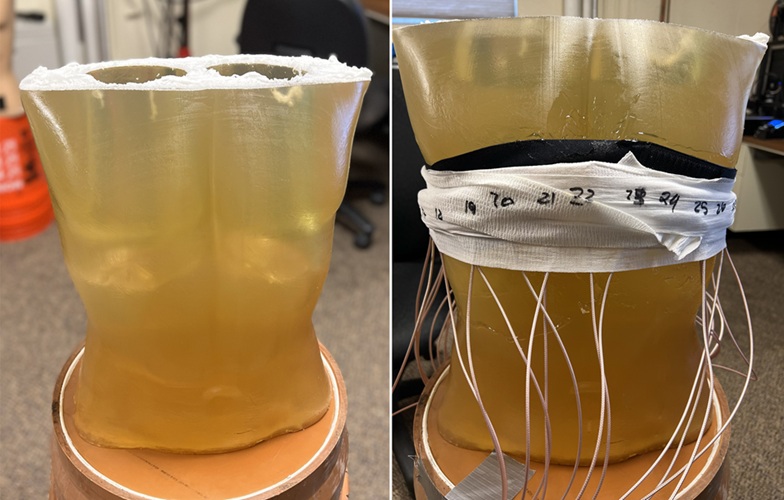
New Medical Ultrasound Imaging Technique Enables ICU Bedside Monitoring
Ultrasound computed tomography (USCT) presents a safer alternative to imaging techniques like X-ray computed tomography (commonly known as CT or “CAT” scans) because it does not produce ionizing radiation.... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel Bacteria-Specific PET Imaging Approach Detects Hard-To-Diagnose Lung Infections
Mycobacteroides abscessus is a rapidly growing mycobacteria that primarily affects immunocompromised patients and those with underlying lung diseases, such as cystic fibrosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary... Read more
New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related death among men in the United States. However, the majority of older men diagnosed with prostate cancer have slow-growing, low-risk forms of... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
CT Colonography Beats Stool DNA Testing for Colon Cancer Screening
As colorectal cancer remains the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, early detection through screening is vital to reduce advanced-stage treatments and associated costs.... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
Currently, patients with conditions such as heart failure, pneumonia, or respiratory distress often require multiple imaging procedures that are intermittent, disruptive, and involve high levels of radiation.... Read more
AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
Radioligand therapy, a form of targeted nuclear medicine, has recently gained attention for its potential in treating specific types of tumors. However, one of the potential side effects of this therapy... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more













.jpeg)




