AI Model Reconstructs Sparse-View 3D CT Scan With Much Lower X-Ray Dose
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 20 Dec 2024 |
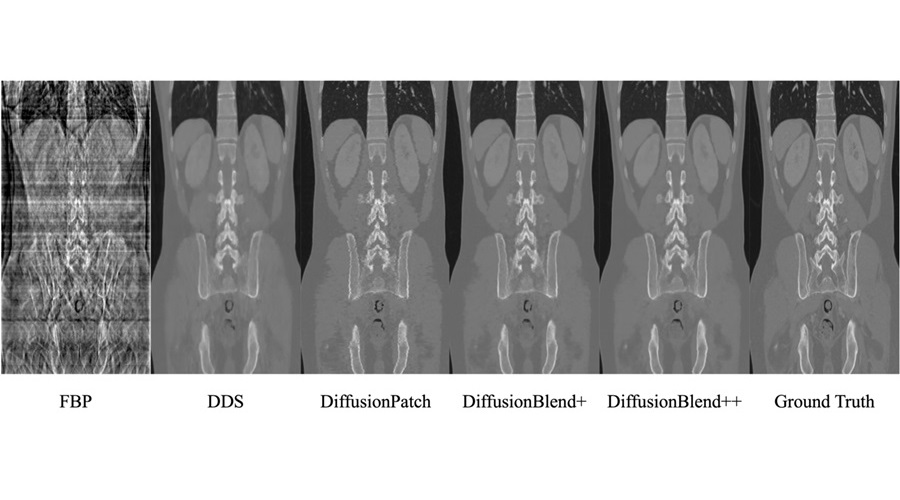
While 3D CT scans provide detailed images of internal structures, the 1,000 to 2,000 X-rays captured from different angles during scanning can increase cancer risk, especially for vulnerable patients. Sparse-view CT scans, which use fewer X-ray projections (as few as 100), significantly reduce radiation exposure but present challenges for accurate image reconstruction. Recently, supervised learning techniques, a form of machine learning that trains algorithms with labeled data, have enhanced the speed and resolution of under-sampled MRI and sparse-view CT image reconstructions. However, labeling large training datasets is both time-consuming and costly. Now, researchers have developed a new framework that works efficiently with 3D images, making the method more applicable to CT and MRI.
This new framework, called DiffusionBlend, was developed by researchers at the University of Michigan Engineering (Ann Arbor, MI, USA). It employs a diffusion model, a self-supervised learning technique that learns a data distribution prior, to enable sparse-view 3D CT reconstruction through posterior sampling. DiffusionBlend learns spatial correlations among nearby 2D image slices, referred to as a 3D-patch diffusion prior, and then blends the scores of these multi-slice patches to create the full 3D CT image volume. When tested on a public dataset of sparse-view 3D CT scans, DiffusionBlend outperformed several baseline methods, including four diffusion approaches at eight, six, and four views, achieving comparable or better computational image quality.
To further enhance its practicality, acceleration methods were applied, reducing DiffusionBlend's CT reconstruction time to one hour, compared to the 24 hours required by previous methods. While deep learning methods can sometimes introduce visual artifacts—AI-generated images of non-existent features—this can be problematic for patient diagnosis. To mitigate this issue, the researchers employed data consistency optimization, specifically using the conjugate gradient method, and evaluated how well the generated images matched the actual measurements using metrics like signal-to-noise ratio.
“We’re still in the early days of this, but there’s a lot of potential here. I think the principles of this method can extend to four dimensions, three spatial dimensions plus time, for applications like imaging the beating heart or stomach contractions,” said Jeff Fessler, the William L. Root Distinguished University Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at U-M and co-corresponding author of the study.
Related Links:
University of Michigan Engineering
Latest General/Advanced Imaging News
- CT Colonography Beats Stool DNA Testing for Colon Cancer Screening
- First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
- AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
- CT-Based Deep Learning-Driven Tool to Enhance Liver Cancer Diagnosis
- AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
- Ultra-Low Dose CT Aids Pneumonia Diagnosis in Immunocompromised Patients
- AI Reduces CT Lung Cancer Screening Workload by Almost 80%
- Cutting-Edge Technology Combines Light and Sound for Real-Time Stroke Monitoring
- AI System Detects Subtle Changes in Series of Medical Images Over Time
- New CT Scan Technique to Improve Prognosis and Treatments for Head and Neck Cancers
- World’s First Mobile Whole-Body CT Scanner to Provide Diagnostics at POC
- Comprehensive CT Scans Could Identify Atherosclerosis Among Lung Cancer Patients
- AI Improves Detection of Colorectal Cancer on Routine Abdominopelvic CT Scans
- Super-Resolution Technology Enhances Clinical Bone Imaging to Predict Osteoporotic Fracture Risk
- AI-Powered Abdomen Map Enables Early Cancer Detection
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI Detects Fatty Liver Disease from Chest X-Rays
Fatty liver disease, which results from excess fat accumulation in the liver, is believed to impact approximately one in four individuals globally. If not addressed in time, it can progress to severe conditions... Read more
AI Detects Hidden Heart Disease in Existing CT Chest Scans
Coronary artery calcium (CAC) is a major indicator of cardiovascular risk, but its assessment typically requires a specialized “gated” CT scan that synchronizes with the heartbeat. In contrast, most chest... Read moreMRI
view channel
New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
Traditional exercise stress tests conducted within an MRI machine require patients to lie flat, a position that artificially improves heart function by increasing stroke volume due to gravity-driven blood... Read more
Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
Women with extremely dense breasts face a higher risk of missed breast cancer diagnoses, as dense glandular and fibrous tissue can obscure tumors on mammograms. While breast MRI is recommended for supplemental... Read moreUltrasound
view channel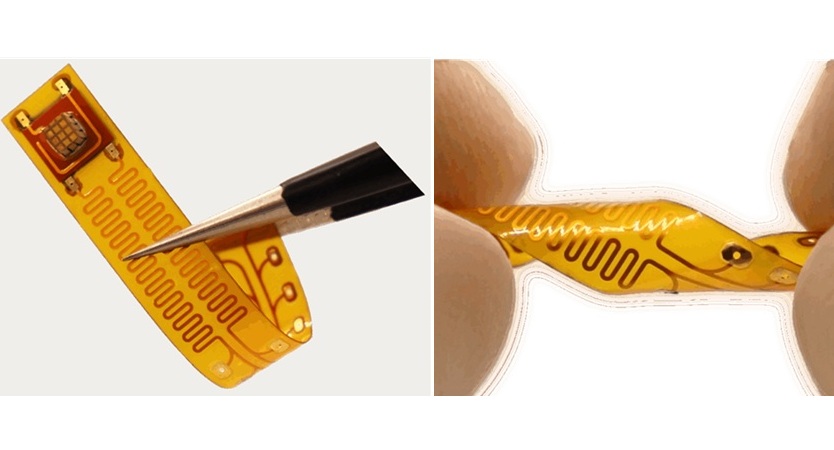
Wireless Chronic Pain Management Device to Reduce Need for Painkillers and Surgery
Chronic pain affects millions of people globally, often leading to long-term disability and dependence on opioid medications, which carry significant risks of side effects and addiction.... Read more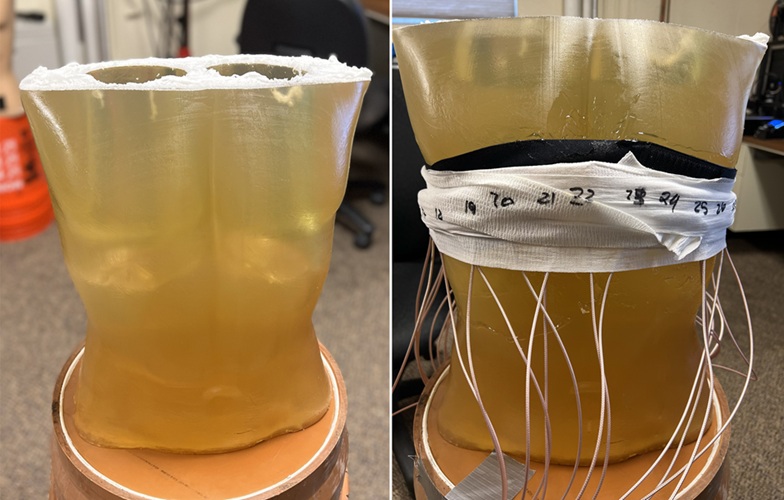
New Medical Ultrasound Imaging Technique Enables ICU Bedside Monitoring
Ultrasound computed tomography (USCT) presents a safer alternative to imaging techniques like X-ray computed tomography (commonly known as CT or “CAT” scans) because it does not produce ionizing radiation.... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel Bacteria-Specific PET Imaging Approach Detects Hard-To-Diagnose Lung Infections
Mycobacteroides abscessus is a rapidly growing mycobacteria that primarily affects immunocompromised patients and those with underlying lung diseases, such as cystic fibrosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary... Read more
New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related death among men in the United States. However, the majority of older men diagnosed with prostate cancer have slow-growing, low-risk forms of... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more













.jpeg)



