AI Uncovers Hidden Heart Disease and Predicts Woman’s Risk for Developing Breast Cancer
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 12 Dec 2023 |
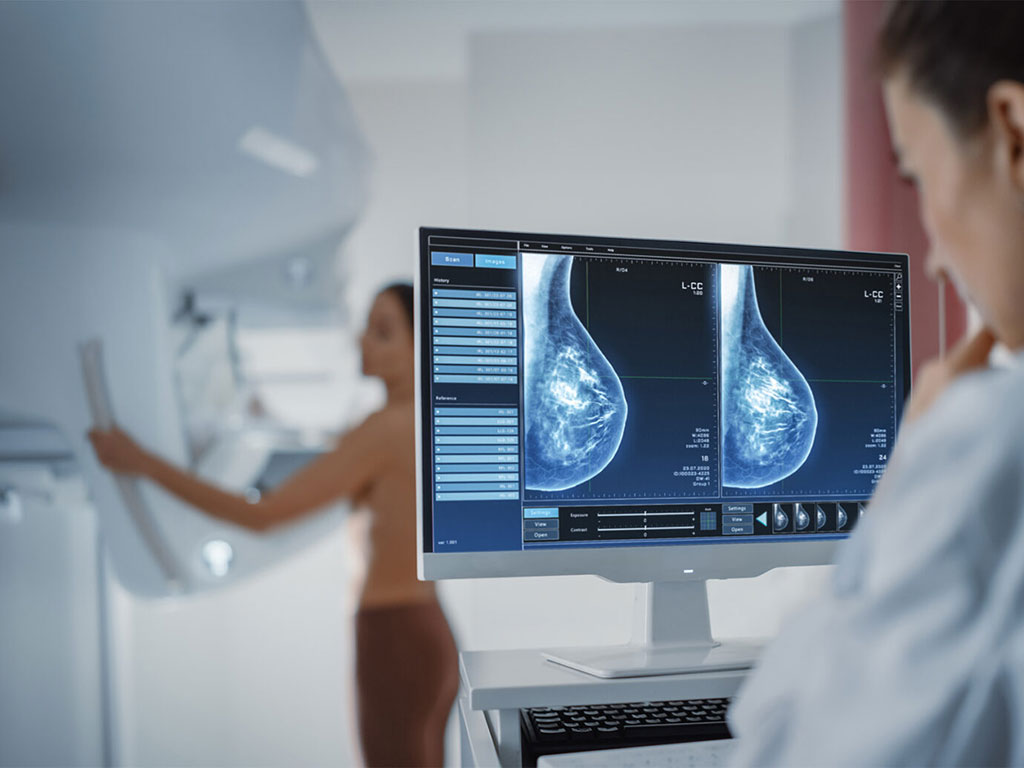
Recent research has revealed that calcium deposits in the breast's blood vessels are linked to the hardening of cardiovascular arteries. Studies have shown that women with breast arterial calcifications (BAC) face a 51% increased risk of heart disease. Now, new studies have validated the ability of an artificial intelligence (AI) powered solution to uncover hidden heart or vascular diseases as well as predict a woman’s risk for developing breast cancer in the next one- or two years from a single mammogram.
iCAD, Inc. (Nashua, NH, USA) has combined AI with computer-aided detection (AI CAD) in its ProFound Breast Health Suite. This software platform is capable of analyzing a single mammogram to screen for both breast cancer and heart disease, the two leading causes of death in women. ProFound AI not only enhances accuracy and clinical workflow efficiency but also expedites the delivery of results to patients. The software's ability to report on arterial calcification, accompanied by easy-to-comprehend visuals illustrating calcification levels, empowers women to consult with their physicians about their cardiovascular health and any necessary interventions.
A 15-site prospective study, which examined 2D screening mammograms from 15,785 asymptomatic women aged between 20 and 97, found that the ProFound Heart Health AI algorithm accurately detected BAC in mammograms. As anticipated, the prevalence and extent of calcium deposits were found to increase with age. Additionally, in a retrospective study, the ProFound Risk for 2D Mammography tool was evaluated for its effectiveness in identifying women at an elevated risk of developing breast cancer within the following two years, based on subtle changes in their mammograms.
In the second study, ProFound Risk analyzed mammograms of 53,453 women who had received normal results from their radiologists two years earlier. The software identified 42.8% of these women, amounting to 22,878 patients, as being at a higher risk for breast cancer. The predictions made by ProFound Risk were subsequently validated. Women who developed breast cancer within two years of their mammogram were found to have an average risk 2.4 times higher than those who did not develop cancer. Furthermore, the average risk for invasive cancers was higher than for ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), a less aggressive cancer form developing in the milk ducts.
“Radiologists currently rely on visual detection of breast arterial calcifications, which is time-consuming and leads to a national underreporting of BAC results in mammography reports,” explained Dr. Chirag Parghi, M.D., chief medical officer of Solis Mammography, and a pioneer in the use of mammography to assess BAC. “Our study suggests that AI can standardize BAC detection on a large scale, speeding up the measurement process and reducing variations between reviewers. By standardizing BAC reporting, AI increases the ease of identifying women that may benefit from additional cardiovascular screening.”
“Our findings suggest AI enables radiologists to identify women who would benefit from more frequent screenings, or suggest supplemental screenings, without leading to overdiagnosis,” said Dr. Axel Gräwingholt, M.D., head of mammography screening at Radiologie am Theater in Germany. “ProFound Risk accurately pinpoints women at high risk for breast cancer while helping us discover small, subtle and aggressive cancers that often go undetected by the naked eye. We believe this technology could greatly enhance the effectiveness of breast cancer screening strategies worldwide.”
Related Links:
iCAD, Inc.
Latest Radiography News
- Machine Learning Algorithm Identifies Cardiovascular Risk from Routine Bone Density Scans
- AI Improves Early Detection of Interval Breast Cancers
- World's Largest Class Single Crystal Diamond Radiation Detector Opens New Possibilities for Diagnostic Imaging
- AI-Powered Imaging Technique Shows Promise in Evaluating Patients for PCI
- Higher Chest X-Ray Usage Catches Lung Cancer Earlier and Improves Survival
- AI-Powered Mammograms Predict Cardiovascular Risk
- Generative AI Model Significantly Reduces Chest X-Ray Reading Time
- AI-Powered Mammography Screening Boosts Cancer Detection in Single-Reader Settings
- Photon Counting Detectors Promise Fast Color X-Ray Images
- AI Can Flag Mammograms for Supplemental MRI
- 3D CT Imaging from Single X-Ray Projection Reduces Radiation Exposure
- AI Method Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Risk by Analyzing Multiple Mammograms
- Printable Organic X-Ray Sensors Could Transform Treatment for Cancer Patients
- Highly Sensitive, Foldable Detector to Make X-Rays Safer
- Novel Breast Cancer Screening Technology Could Offer Superior Alternative to Mammogram
- Artificial Intelligence Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Years Before Diagnosis
Channels
MRI
view channel
New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
Traditional exercise stress tests conducted within an MRI machine require patients to lie flat, a position that artificially improves heart function by increasing stroke volume due to gravity-driven blood... Read more
Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
Women with extremely dense breasts face a higher risk of missed breast cancer diagnoses, as dense glandular and fibrous tissue can obscure tumors on mammograms. While breast MRI is recommended for supplemental... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
New Incision-Free Technique Halts Growth of Debilitating Brain Lesions
Cerebral cavernous malformations (CCMs), also known as cavernomas, are abnormal clusters of blood vessels that can grow in the brain, spinal cord, or other parts of the body. While most cases remain asymptomatic,... Read more.jpeg)
AI-Powered Lung Ultrasound Outperforms Human Experts in Tuberculosis Diagnosis
Despite global declines in tuberculosis (TB) rates in previous years, the incidence of TB rose by 4.6% from 2020 to 2023. Early screening and rapid diagnosis are essential elements of the World Health... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related death among men in the United States. However, the majority of older men diagnosed with prostate cancer have slow-growing, low-risk forms of... Read more
Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
Interleukin-13 receptor α-2 (IL13Rα2) is a cell surface receptor commonly found in solid tumors such as glioblastoma, melanoma, and breast cancer. It is minimally expressed in normal tissues, making it... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
Currently, patients with conditions such as heart failure, pneumonia, or respiratory distress often require multiple imaging procedures that are intermittent, disruptive, and involve high levels of radiation.... Read more
AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
Radioligand therapy, a form of targeted nuclear medicine, has recently gained attention for its potential in treating specific types of tumors. However, one of the potential side effects of this therapy... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more