New Reporting Style Improves Accuracy and Speed of Reading Radiology Scans
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 06 Dec 2023 |
Certain health issues, such as calcified arteries, infections, minor bone fractures, or cancerous tumors, often remain hidden within our bodies. Special imaging techniques like X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans are crucial for detecting these issues. Interpreting the bluish, black and white images produced by these scans requires the expert eye of a radiologist, who is adept at identifying anomalies in images of our brains, lungs, arteries, bones, and muscles. Radiologists specialize in spotting irregularities and generate detailed reports for physicians to confirm diagnoses and inform treatment plans. Radiologists typically review a vast range of images, from about 200 in simpler cases like X-rays to 20,000 in more intricate MRI scans, leading to an average of 50 to 60 reports each day.
Technological advancements such as AI-powered speech-to-text conversion tools, can assist radiologists in dictating and completing important reports for the patient’s healthcare team, although there can be mistakes in the transcription that can have ripple effects. A research team at Florida International University (Miami, FL, USA) explored the effectiveness of a new reporting style that is more concise yet remains structured and easy to comprehend. This style leverages voice command technology for dictation, focusing solely on documenting abnormal findings that radiologists are trained to identify and that are critical for doctors' awareness. Essentially, the radiologists verbalize only the irregularities they observe. This approach was found to be more efficient than the traditional checklist-style reporting commonly utilized in radiology.
The standard checklist reporting style often requires radiologists to divide their attention between two screens - one showing the diagnostic images and the other displaying the transcribed spoken findings. This process can be cumbersome and distracting, particularly when correcting errors arising from voice recognition software misinterpreting spoken words. In contrast, the new method allows radiologists to concentrate fully on the images, mentally going through the checklist based on their training. They only dictate the abnormal findings, reviewing the report for accuracy after completing their interpretation of the images.
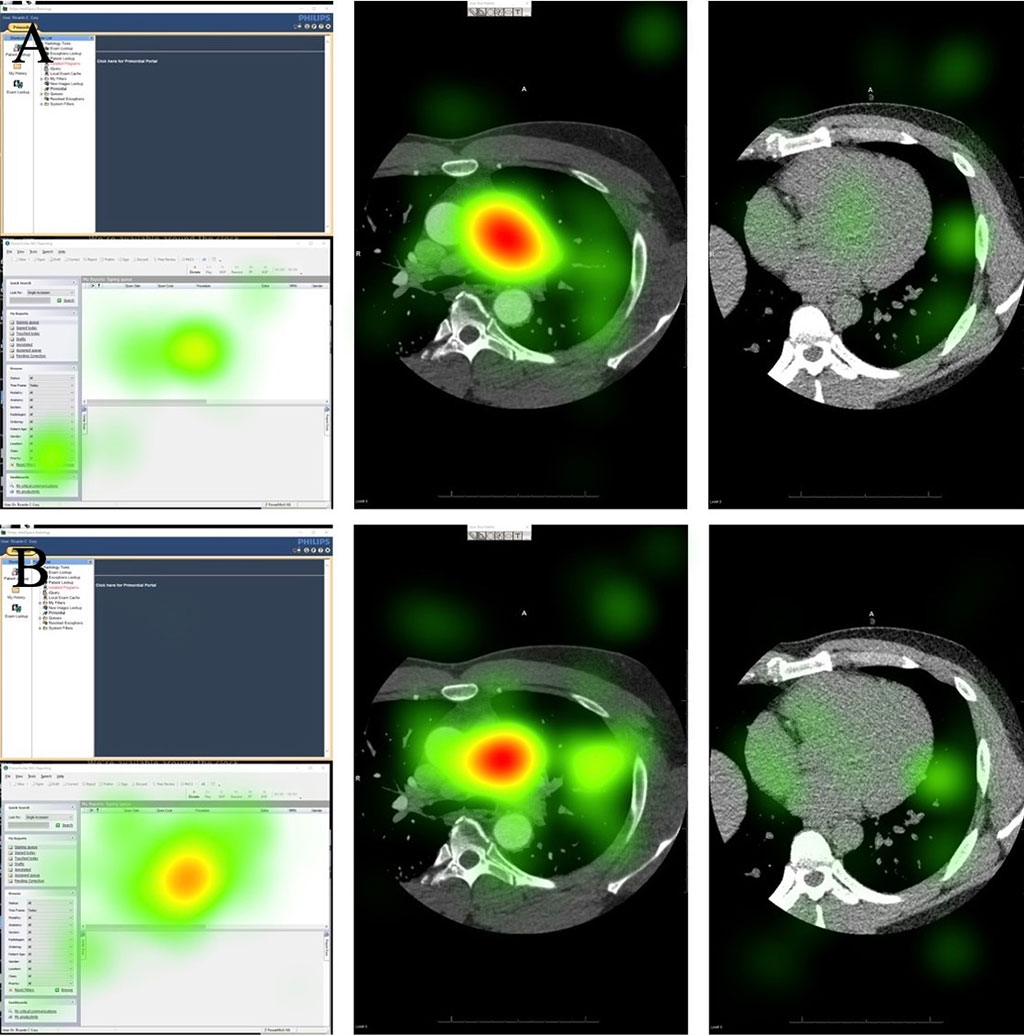
In the new study, experienced, board-certified radiologists used eye-tracking goggles to review a variety of X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, totaling over 150 studies — 76 with the new dictation style and 81 with the standard checklist. This new approach not only enhanced the radiologists' focus on the diagnostic images but also reduced inaccuracies and dictation time, benefiting both patients, who rely on accurate reports for their treatment, and overburdened radiologists. The new dictation method, using voice commands, cut the average dictation time by about half without affecting the total time taken for interpretation or examination. The researchers view this study as a foundation for future advancements, anticipating that evolving conversational and generative AI technologies could further enhance the efficiency and accuracy of radiology reporting.
“I saw firsthand how this new dictation process significantly enhanced radiologists’ focus on the diagnostic images,” said Mona Roshan, an FIU third-year medical student and the study’s first author. “The eye-tracking software validated our results, because it allowed us to create heatmaps showing that radiologists were directing their attention to the imaging. This is better for the patient, as a heightened focus on the images means that radiologists are dedicating more time to interpreting potential abnormal findings, ultimately improving patient care.”
Related Links:
Florida International University
Latest Radiography News
- X-Ray Breakthrough Captures Three Image-Contrast Types in Single Shot
- AI Generates Future Knee X-Rays to Predict Osteoarthritis Progression Risk
- AI Algorithm Uses Mammograms to Accurately Predict Cardiovascular Risk in Women
- AI Hybrid Strategy Improves Mammogram Interpretation
- AI Technology Predicts Personalized Five-Year Risk of Developing Breast Cancer
- RSNA AI Challenge Models Can Independently Interpret Mammograms
- New Technique Combines X-Ray Imaging and Radar for Safer Cancer Diagnosis
- New AI Tool Helps Doctors Read Chest X‑Rays Better
- Wearable X-Ray Imaging Detecting Fabric to Provide On-The-Go Diagnostic Scanning
- AI Helps Radiologists Spot More Lesions in Mammograms
- AI Detects Fatty Liver Disease from Chest X-Rays
- AI Detects Hidden Heart Disease in Existing CT Chest Scans
- Ultra-Lightweight AI Model Runs Without GPU to Break Barriers in Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- AI Radiology Tool Identifies Life-Threatening Conditions in Milliseconds

- Machine Learning Algorithm Identifies Cardiovascular Risk from Routine Bone Density Scans
- AI Improves Early Detection of Interval Breast Cancers
Channels
MRI
view channel
Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
Vascular dysfunction in the spinal cord contributes to multiple neurological conditions, including traumatic injuries and degenerative cervical myelopathy, where reduced blood flow can lead to progressive... Read more
AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
A cardiac MRI can reveal critical information about the heart’s function and any abnormalities, but traditional scans take 30 to 90 minutes and often suffer from poor image quality due to patient movement.... Read more
AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is one of the most common inherited heart conditions and a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young individuals and athletes. While many patients live normal lives, some... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Wearable Ultrasound Imaging System to Enable Real-Time Disease Monitoring
Chronic conditions such as hypertension and heart failure require close monitoring, yet today’s ultrasound imaging is largely confined to hospitals and short, episodic scans. This reactive model limits... Read more
Ultrasound Technique Visualizes Deep Blood Vessels in 3D Without Contrast Agents
Producing clear 3D images of deep blood vessels has long been difficult without relying on contrast agents, CT scans, or MRI. Standard ultrasound typically provides only 2D cross-sections, limiting clinicians’... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
PET Imaging of Inflammation Predicts Recovery and Guides Therapy After Heart Attack
Acute myocardial infarction can trigger lasting heart damage, yet clinicians still lack reliable tools to identify which patients will regain function and which may develop heart failure.... Read more
Radiotheranostic Approach Detects, Kills and Reprograms Aggressive Cancers
Aggressive cancers such as osteosarcoma and glioblastoma often resist standard therapies, thrive in hostile tumor environments, and recur despite surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy. These tumors also... Read more
New Imaging Solution Improves Survival for Patients with Recurring Prostate Cancer
Detecting recurrent prostate cancer remains one of the most difficult challenges in oncology, as standard imaging methods such as bone scans and CT scans often fail to accurately locate small or early-stage tumors.... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
3D Scanning Approach Enables Ultra-Precise Brain Surgery
Precise navigation is critical in neurosurgery, yet even small alignment errors can affect outcomes when operating deep within the brain. A new 3D surface-scanning approach now provides a radiation-free... Read more
AI Tool Improves Medical Imaging Process by 90%
Accurately labeling different regions within medical scans, a process known as medical image segmentation, is critical for diagnosis, surgery planning, and research. Traditionally, this has been a manual... Read more
New Ultrasmall, Light-Sensitive Nanoparticles Could Serve as Contrast Agents
Medical imaging technologies face ongoing challenges in capturing accurate, detailed views of internal processes, especially in conditions like cancer, where tracking disease development and treatment... Read more
AI Algorithm Accurately Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis Using Routine CT Images
In pancreatic cancer, detecting whether the disease has spread to other organs is critical for determining whether surgery is appropriate. If metastasis is present, surgery is not recommended, yet current... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more