Machine Learning Outperforms Clinical Experts in Classifying Hip Fractures from X-Rays
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 14 Feb 2022 |
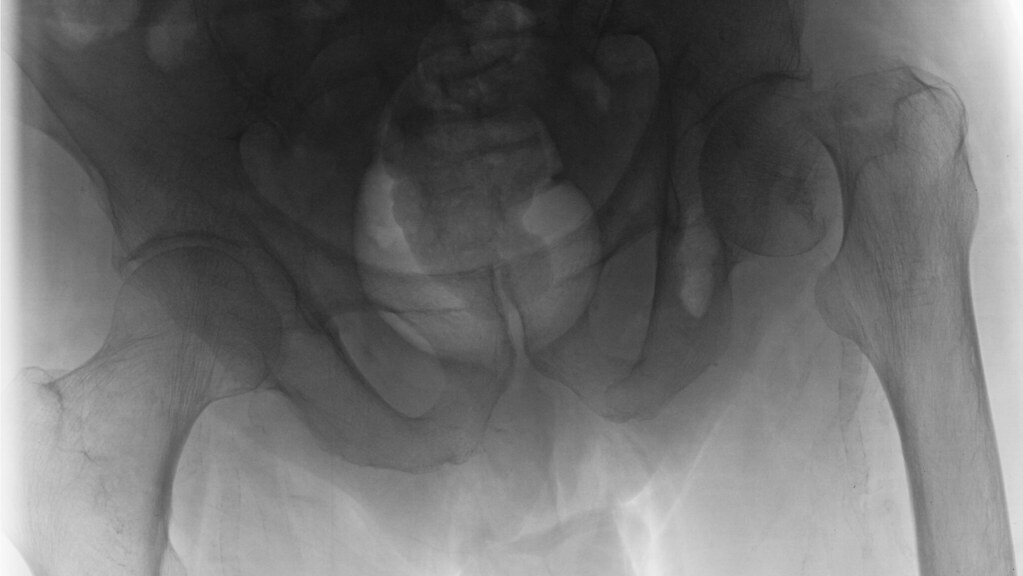
A new machine learning process designed to identify and classify hip fractures has been shown to outperform human clinicians.
Two convolutional neural networks (CNNs) developed at the University of Bath (Somerset, UK) were able to identify and classify hip fractures from X-rays with a 19% greater degree of accuracy and confidence than hospital-based clinicians. The research team set about creating the new process to help clinicians make hip fracture care more efficient and to support better patient outcomes. They used a total of 3,659 hip X-rays, classified by at least two experts, to train and test the neural networks, which achieved an overall accuracy of 92%, and 19% greater accuracy than hospital-based clinicians.
Hip fractures are a major cause of morbidity and mortality in the elderly, incurring high costs to health and social care. Classifying a fracture prior to surgery is crucial to help surgeons select the right interventions to treat the fracture and restore mobility and improve patient outcomes. The ability to swiftly, accurately, and reliably classify a fracture is key: delays to surgery of more than 48 hours can increase the risk of adverse outcomes and mortality. Fractures are divided into three classes – intracapsular, trochanteric, or subtrochanteric – depending on the part of the joint they occur in. Some treatments, which are determined by the fracture classification, can cost up to 4.5 times as much as others.
As important are longer-term patient outcomes: people who sustain a hip fracture have in the following year twice the age-specific mortality of the general population. So, the team says, the development of strategies to improve hip fracture management and their impact of morbidity, mortality and healthcare provision costs is a high priority. One critical issue affecting the use of diagnostic imaging is the mismatch between demand and resource. Rising demand on radiology departments often means they cannot report results in a timely manner.
“Machine learning methods and neural networks offer a new and powerful approach to automate diagnostics and outcome prediction, so this new technique we’ve shared has great potential,” said Prof Richie Gill, lead author of the paper and Co-Director of the Center for Therapeutic Innovation, says. “Despite fracture classification so strongly determining surgical treatment and hence patient outcomes, there is currently no standardized process as to who determines this classification in the UK – whether this is done by orthopedic surgeons or radiologists specializing in musculoskeletal disorders.”
Related Links:
University of Bath
Latest Radiography News
- AI Hybrid Strategy Improves Mammogram Interpretation
- AI Technology Predicts Personalized Five-Year Risk of Developing Breast Cancer
- RSNA AI Challenge Models Can Independently Interpret Mammograms
- New Technique Combines X-Ray Imaging and Radar for Safer Cancer Diagnosis
- New AI Tool Helps Doctors Read Chest X‑Rays Better
- Wearable X-Ray Imaging Detecting Fabric to Provide On-The-Go Diagnostic Scanning
- AI Helps Radiologists Spot More Lesions in Mammograms
- AI Detects Fatty Liver Disease from Chest X-Rays
- AI Detects Hidden Heart Disease in Existing CT Chest Scans
- Ultra-Lightweight AI Model Runs Without GPU to Break Barriers in Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- AI Radiology Tool Identifies Life-Threatening Conditions in Milliseconds

- Machine Learning Algorithm Identifies Cardiovascular Risk from Routine Bone Density Scans
- AI Improves Early Detection of Interval Breast Cancers
- World's Largest Class Single Crystal Diamond Radiation Detector Opens New Possibilities for Diagnostic Imaging
- AI-Powered Imaging Technique Shows Promise in Evaluating Patients for PCI
- Higher Chest X-Ray Usage Catches Lung Cancer Earlier and Improves Survival
Channels
MRI
view channel
AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
A cardiac MRI can reveal critical information about the heart’s function and any abnormalities, but traditional scans take 30 to 90 minutes and often suffer from poor image quality due to patient movement.... Read more
AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is one of the most common inherited heart conditions and a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young individuals and athletes. While many patients live normal lives, some... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Non-Invasive Ultrasound-Based Tool Accurately Detects Infant Meningitis
Meningitis, an inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord, can be fatal in infants if not diagnosed and treated early. Even when treated, it may leave lasting damage, such as cognitive... Read more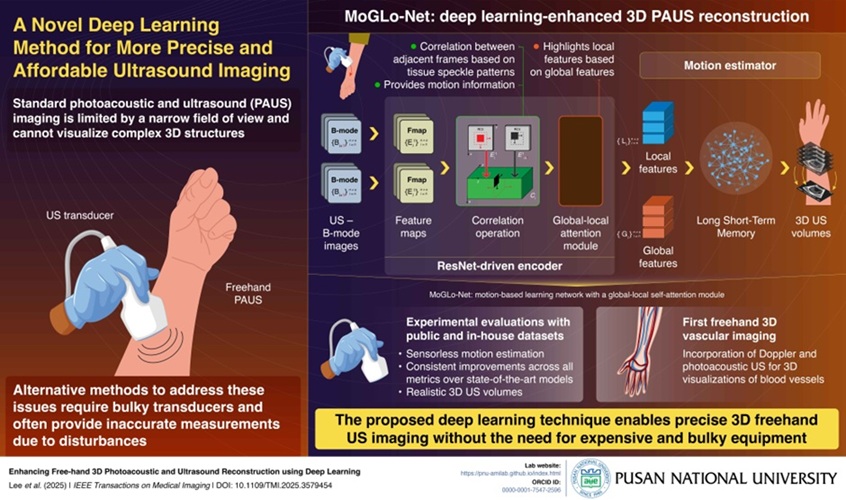
Breakthrough Deep Learning Model Enhances Handheld 3D Medical Imaging
Ultrasound imaging is a vital diagnostic technique used to visualize internal organs and tissues in real time and to guide procedures such as biopsies and injections. When paired with photoacoustic imaging... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
New Camera Sees Inside Human Body for Enhanced Scanning and Diagnosis
Nuclear medicine scans like single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) allow doctors to observe heart function, track blood flow, and detect hidden diseases. However, current detectors are either... Read more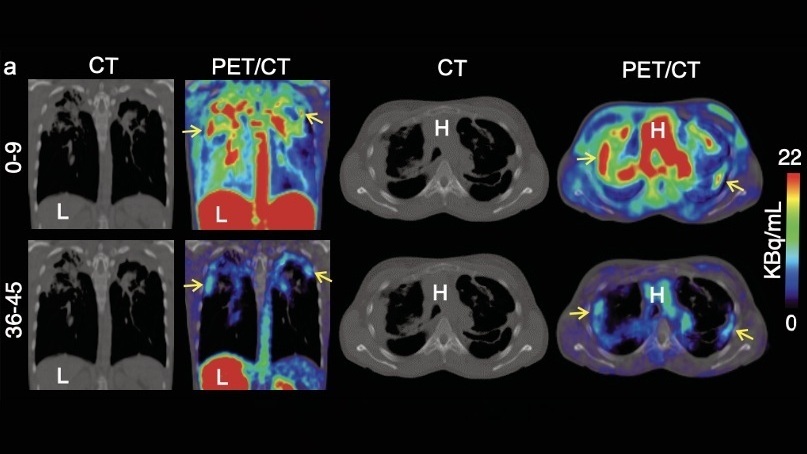
Novel Bacteria-Specific PET Imaging Approach Detects Hard-To-Diagnose Lung Infections
Mycobacteroides abscessus is a rapidly growing mycobacteria that primarily affects immunocompromised patients and those with underlying lung diseases, such as cystic fibrosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Algorithm Accurately Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis Using Routine CT Images
In pancreatic cancer, detecting whether the disease has spread to other organs is critical for determining whether surgery is appropriate. If metastasis is present, surgery is not recommended, yet current... Read more
Cutting-Edge Angio-CT Solution Offers New Therapeutic Possibilities
Maintaining accuracy and safety in interventional radiology is a constant challenge, especially as complex procedures require both high precision and efficiency. Traditional setups often involve multiple... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more





















