Curved Detector Concept Brings Clearer and Safer X-Rays Closer to Reality
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 21 Dec 2021 |
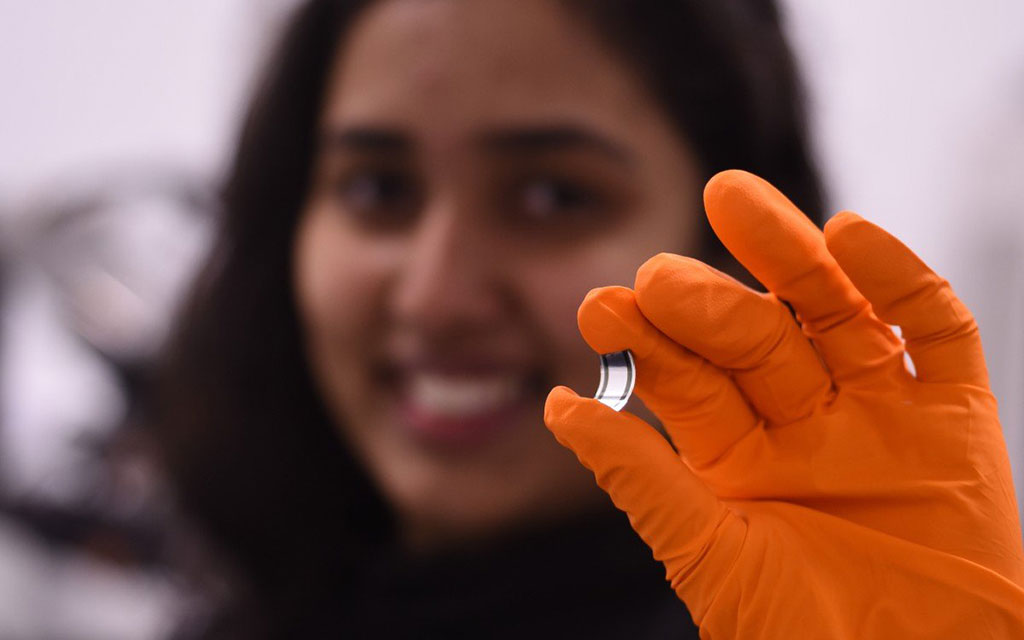

Researchers have identified key design rules for making curved X-ray detectors, bringing clearer and safer X-rays a step closer to reality.
Researchers at the University of Surrey (Guildford, Surrey, UK) have identified the design rules for a special class of “inorganic in organic” semiconductors. By tuning the molecular weight of the bismuth oxide nanoparticle sensitized organic semiconductors to lengthen the polymer chains, the researchers are paving the way towards making more robust, curved digital detectors with high sensitivity, or digital film.
Although the use of digital flat panel detectors has enabled radiographers to examine X-rays much more quickly compared with old-fashioned X-ray sensitive photographic films and to make quicker diagnoses, flat panels are ill-suited to the complex shape and geometry of the human body. The reliance purely on flat panels means there is unavoidable distortion around the edges of images. Flat panels also prevent an accurate registration of the X-ray dose delivered, a key feature towards enabling safer radiation therapy and minimizing secondary tumors. Efforts to create flexible detectors have so far been unsuccessful owing to the brittle characteristics of the rigid inorganic semiconductors used to make them. Some curvature has been achieved through using a thinner layer of semiconductor, but this has compromised performance levels and resulted in poor quality images.
“Our curved detector concept has shown exceptional mechanical robustness and enables bending radii as small as 1.3mm,” said Prabodhi Nanayakkara, lead author of the study and PhD student at the University of Surrey. “The use of organic or ‘inorganic in organic’ semiconductors is also far more cost effective than conventional inorganic semiconductors made from silicon or germanium, which require expensive crystal growth methods. Our approach potentially offers a significant commercial advantage.”
“The technology we’re demonstrating will help create a revolutionary new high sensitivity X-ray detector that is scalable, due to the design and materials adopted,” said Professor Ravi Silva, Director of Surrey’s Advanced Technology Institute. “This technology has huge potential in medical applications and other X-ray uses, so we’re working with a spinout company, SilverRay, and hope to turn this technology into the X-ray detector of choice for high sensitivity, high resolution, flexible large area detectors.”
Related Links:
University of Surrey
Latest Radiography News
- AI Tool Predicts Breast Cancer Risk Years Ahead Using Routine Mammograms
- Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
- AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
- X-Ray Breakthrough Captures Three Image-Contrast Types in Single Shot
- AI Generates Future Knee X-Rays to Predict Osteoarthritis Progression Risk
- AI Algorithm Uses Mammograms to Accurately Predict Cardiovascular Risk in Women
- AI Hybrid Strategy Improves Mammogram Interpretation
- AI Technology Predicts Personalized Five-Year Risk of Developing Breast Cancer
- RSNA AI Challenge Models Can Independently Interpret Mammograms
- New Technique Combines X-Ray Imaging and Radar for Safer Cancer Diagnosis
- New AI Tool Helps Doctors Read Chest X‑Rays Better
- Wearable X-Ray Imaging Detecting Fabric to Provide On-The-Go Diagnostic Scanning
- AI Helps Radiologists Spot More Lesions in Mammograms
- AI Detects Fatty Liver Disease from Chest X-Rays
- AI Detects Hidden Heart Disease in Existing CT Chest Scans
- Ultra-Lightweight AI Model Runs Without GPU to Break Barriers in Lung Cancer Diagnosis
Channels
MRI
view channel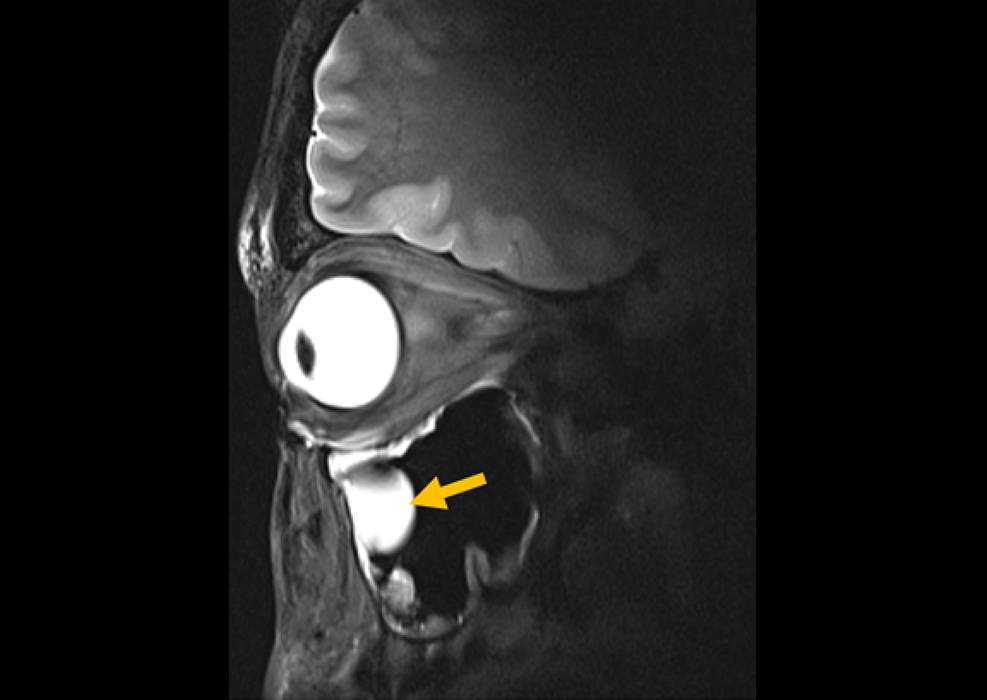
New Material Boosts MRI Image Quality
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a cornerstone of modern diagnostics, yet certain deep or anatomically complex tissues, including delicate structures of the eye and orbit, remain difficult to visualize clearly.... Read more
AI Model Reads and Diagnoses Brain MRI in Seconds
Brain MRI scans are critical for diagnosing strokes, hemorrhages, and other neurological disorders, but interpreting them can take hours or even days due to growing demand and limited specialist availability.... Read moreMRI Scan Breakthrough to Help Avoid Risky Invasive Tests for Heart Patients
Heart failure patients often require right heart catheterization to assess how severely their heart is struggling to pump blood, a procedure that involves inserting a tube into the heart to measure blood... Read more
MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
Recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies widely, with some patients regaining full function while others are left with lasting disabilities. Prognosis is especially difficult to assess in patients... Read moreUltrasound
view channel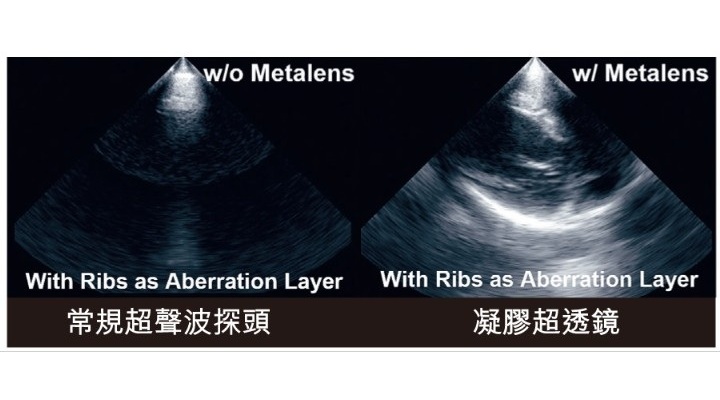
Groundbreaking Technology to Enhance Precision in Emergency and Critical Care
Rapid and accurate imaging is essential for diagnosing life-threatening conditions such as myocardial infarction, heart failure, and pulmonary embolism. However, conventional ultrasound imaging of the... Read more
Reusable Gel Pad Made from Tamarind Seed Could Transform Ultrasound Examinations
Ultrasound imaging depends on a conductive gel to eliminate air between the probe and the skin so sound waves can pass clearly into the body. While the imaging technology is fast, safe, and noninvasive,... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
Targeted cancer therapies only work when tumor cells express the specific molecular structures they are designed to attack. In urothelial carcinoma, a common form of bladder cancer, the cell surface protein... Read more
Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
Targeted cancer therapies can be highly effective, but only when a patient’s tumor expresses the specific protein the treatment is designed to attack. Determining this usually requires biopsies or advanced... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Tool Predicts Side Effects from Lung Cancer Treatment
Radiation therapy is a central treatment for lung cancer, but even carefully targeted radiation can affect surrounding healthy tissue. Patients may develop side effects such as lung inflammation, coughing,... Read more
AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer is a form of head and neck cancer that can spread through lymph nodes, significantly affecting survival and treatment decisions. Current therapies often involve combinations of surgery,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Nuclear Medicine Set for Continued Growth Driven by Demand for Precision Diagnostics
Clinical imaging services face rising demand for precise molecular diagnostics and targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy as cancer and chronic disease rates climb. A new market analysis projects rapid expansion... Read more





















