Novel CT System Provides Spatial Breast Imaging 
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 18 Oct 2021 |
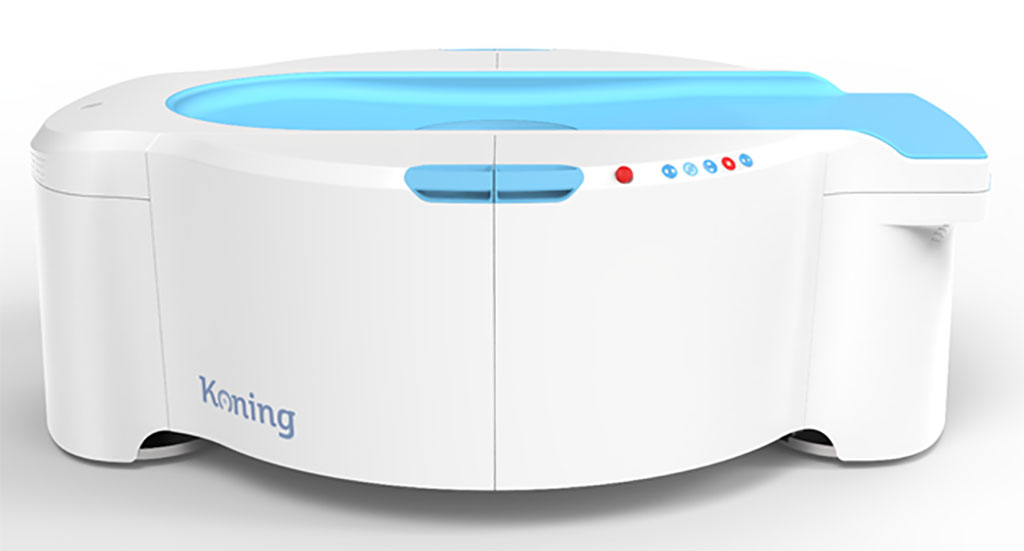

Image: The KBCT 3D breast imaging system (Photo courtesy of Koning)
An advanced cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) system dramatically improves the way clinicians can visualize, evaluate, and biopsy breast tissue.
The Koning (Norcross, GA, USA) Koning Breast CT (KBCT) system is a new breast imaging platform that produces true three-dimensional (3D) images of the breast, without painful compression, in a simple, rapid 10-second procedure at the same radiation levels used during mammography. KBCT images are also less distorted than mammography, and are optimized so as to differentiate between normal and cancerous breast tissue. The KBCT acquires the entire volume of the breast, allowing radiologists to spatially scroll through the slices (up and down, left and right).
The system consists of a horizontal patient table, the CBCT scanner mounted on a rotating assembly, an operator’s console, a reconstruction software engine, and a 3D visualization/temporary DICOM storage package. Data acquisition is achieved via a flat panel detector (FPD), an X-ray tube, and a 480 VAC high frequency generator. The tube/detector assembly rotates around the breast (which is located at the rotation axis), acquiring 300 projection images. Radiologists can also co-register data in multiple planes, similar to whole body CT imaging.
“Current breast imaging modalities have been lacking in their ability to confidently recognize breast cancer at earlier stages in its development,” said David Georges, President of Konig. “The Koning Breast CT can find lesions as small as 2mm and calcifications as small as 200 microns without breast compression.”
“Koning Breast CT is a true 3D dimensional image of the breast,’ said Professor Etta Pisano, MD, of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC; Boston, MA, USA). “The detector is surrounding the woman’s breast, and so the cancers have nowhere to hide in the breast. There’s no way for over lapping tissue to be in the way from every angle.”
During CBCT, the region of interest is centered in the field of view. A single 200 degree rotation acquires a volumetric data set which is used to produce a digital volume composed of 3D voxels of anatomical data that can then be manipulated and visualized. CBCT has only recently become practical with the introduction of large-area high-speed digital X-ray imagers, such as hydrogenated amorphous silicon (a-Si:H) based FPDs.
Related Links:
Koning
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
The Koning (Norcross, GA, USA) Koning Breast CT (KBCT) system is a new breast imaging platform that produces true three-dimensional (3D) images of the breast, without painful compression, in a simple, rapid 10-second procedure at the same radiation levels used during mammography. KBCT images are also less distorted than mammography, and are optimized so as to differentiate between normal and cancerous breast tissue. The KBCT acquires the entire volume of the breast, allowing radiologists to spatially scroll through the slices (up and down, left and right).
The system consists of a horizontal patient table, the CBCT scanner mounted on a rotating assembly, an operator’s console, a reconstruction software engine, and a 3D visualization/temporary DICOM storage package. Data acquisition is achieved via a flat panel detector (FPD), an X-ray tube, and a 480 VAC high frequency generator. The tube/detector assembly rotates around the breast (which is located at the rotation axis), acquiring 300 projection images. Radiologists can also co-register data in multiple planes, similar to whole body CT imaging.
“Current breast imaging modalities have been lacking in their ability to confidently recognize breast cancer at earlier stages in its development,” said David Georges, President of Konig. “The Koning Breast CT can find lesions as small as 2mm and calcifications as small as 200 microns without breast compression.”
“Koning Breast CT is a true 3D dimensional image of the breast,’ said Professor Etta Pisano, MD, of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC; Boston, MA, USA). “The detector is surrounding the woman’s breast, and so the cancers have nowhere to hide in the breast. There’s no way for over lapping tissue to be in the way from every angle.”
During CBCT, the region of interest is centered in the field of view. A single 200 degree rotation acquires a volumetric data set which is used to produce a digital volume composed of 3D voxels of anatomical data that can then be manipulated and visualized. CBCT has only recently become practical with the introduction of large-area high-speed digital X-ray imagers, such as hydrogenated amorphous silicon (a-Si:H) based FPDs.
Related Links:
Koning
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Latest Radiography News
- Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
- AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
- X-Ray Breakthrough Captures Three Image-Contrast Types in Single Shot
- AI Generates Future Knee X-Rays to Predict Osteoarthritis Progression Risk
- AI Algorithm Uses Mammograms to Accurately Predict Cardiovascular Risk in Women
- AI Hybrid Strategy Improves Mammogram Interpretation
- AI Technology Predicts Personalized Five-Year Risk of Developing Breast Cancer
- RSNA AI Challenge Models Can Independently Interpret Mammograms
- New Technique Combines X-Ray Imaging and Radar for Safer Cancer Diagnosis
- New AI Tool Helps Doctors Read Chest X‑Rays Better
- Wearable X-Ray Imaging Detecting Fabric to Provide On-The-Go Diagnostic Scanning
- AI Helps Radiologists Spot More Lesions in Mammograms
- AI Detects Fatty Liver Disease from Chest X-Rays
- AI Detects Hidden Heart Disease in Existing CT Chest Scans
- Ultra-Lightweight AI Model Runs Without GPU to Break Barriers in Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- AI Radiology Tool Identifies Life-Threatening Conditions in Milliseconds

Channels
MRI
view channel
MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
Recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies widely, with some patients regaining full function while others are left with lasting disabilities. Prognosis is especially difficult to assess in patients... Read more
Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
Vascular dysfunction in the spinal cord contributes to multiple neurological conditions, including traumatic injuries and degenerative cervical myelopathy, where reduced blood flow can lead to progressive... Read more
AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
A cardiac MRI can reveal critical information about the heart’s function and any abnormalities, but traditional scans take 30 to 90 minutes and often suffer from poor image quality due to patient movement.... Read more
AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is one of the most common inherited heart conditions and a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young individuals and athletes. While many patients live normal lives, some... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Portable Ultrasound Sensor to Enable Earlier Breast Cancer Detection
Breast cancer screening relies heavily on annual mammograms, but aggressive tumors can develop between scans, accounting for up to 30 percent of cases. These interval cancers are often diagnosed later,... Read more
Portable Imaging Scanner to Diagnose Lymphatic Disease in Real Time
Lymphatic disorders affect hundreds of millions of people worldwide and are linked to conditions ranging from limb swelling and organ dysfunction to birth defects and cancer-related complications.... Read more
Imaging Technique Generates Simultaneous 3D Color Images of Soft-Tissue Structure and Vasculature
Medical imaging tools often force clinicians to choose between speed, structural detail, and functional insight. Ultrasound is fast and affordable but typically limited to two-dimensional anatomy, while... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
Targeted cancer therapies only work when tumor cells express the specific molecular structures they are designed to attack. In urothelial carcinoma, a common form of bladder cancer, the cell surface protein... Read more
Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
Targeted cancer therapies can be highly effective, but only when a patient’s tumor expresses the specific protein the treatment is designed to attack. Determining this usually requires biopsies or advanced... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer is a form of head and neck cancer that can spread through lymph nodes, significantly affecting survival and treatment decisions. Current therapies often involve combinations of surgery,... Read more
New 3D Imaging System Addresses MRI, CT and Ultrasound Limitations
Medical imaging is central to diagnosing and managing injuries, cancer, infections, and chronic diseases, yet existing tools each come with trade-offs. Ultrasound, X-ray, CT, and MRI can be costly, time-consuming,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Nuclear Medicine Set for Continued Growth Driven by Demand for Precision Diagnostics
Clinical imaging services face rising demand for precise molecular diagnostics and targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy as cancer and chronic disease rates climb. A new market analysis projects rapid expansion... Read more



















