Singing Supports Ultrasound Screening for Thyroid Cancer
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 28 Jan 2021 |
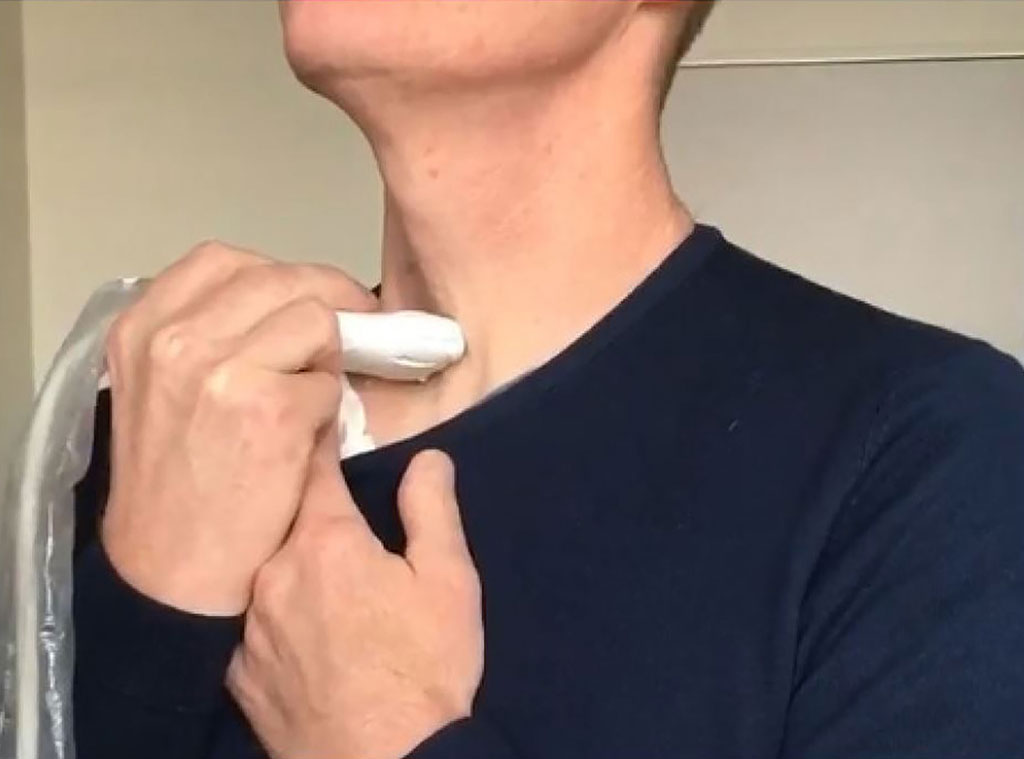
Image: A volunteer sings while holding a linear ultrasound probe to measure VP-E (Photo courtesy of Steve Beuve/ Tours University)
A new study suggests that a shear wave acoustic field generated naturally by the human voice can be used to measure the elasticity of thyroid tissue.
Developed by researchers at Université de Tours (France), Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Dijon-Bourgogne (France), and Université Bourgogne Franche-Comté (France), vocal passive elastography (V-PE) is designed to measure tissue elasticity from physiological noise generated by body vibrations. In the thyroid, this is mainly due to carotid pulsation, which is in the 1–10 Hz bandwidth and is located right next to the gland. To decrease shear wavelength and increase signal to noise ratio (SNR), a complex shear wave field can be created by using vocal tract vibrations.
The nature of the sound can be modified by changing pitch. Thus, singing and maintain an “eeee” note (approximately the frequency of D3, or 150 hertz), shear wave is generated that can be used to identify abnormally stiff thyroid gland areas that can be indicative of cancer. A correlation-based algorithm then computes a shear wave velocity map that is then super-positioned onto a B-mode ultrasound image of the thyroid, with a pixel resolution of 150 × 150 μm2. The values obtained are in good agreement with comparative shear wave elastography (SWE) ultrasound measurements. The study was published on January 12, 2021, in Applied Physics Letters.
“The singing vibrates the patient's trachea, which in turn produces vibrations throughout the thyroid, allowing the clinician to use an ultrafast frame rate to track changes in shear-wave velocity, giving us information about mechanical properties of soft tissues,” said lead author Steve Beuve, PhD, of the Université de Tours. “Developing noninvasive methods would reduce the stress of patients during their medical exams. Having to sing during a medical exam can perhaps help release some of the nervous tension even more.”
Thyroid nodular disease is one of the most widespread endocrine disorders, but although fine needle aspiration guided with ultrasound examination is commonly used to detect malignant tumors, only 5% of thyroid cancers are detectable with this technique. As a result elastography has been proposed to detect cancerous nodules, with a nodule whose Young's modulus exceeds 65 kPa usually considered suspicious. But one of the problems with such an approach is that the thyroid SNR is drowned out by natural background noise from nearby organs.
Related Links:
Université de Tours
Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Dijon-Bourgogne
Université Bourgogne Franche-Comté
Developed by researchers at Université de Tours (France), Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Dijon-Bourgogne (France), and Université Bourgogne Franche-Comté (France), vocal passive elastography (V-PE) is designed to measure tissue elasticity from physiological noise generated by body vibrations. In the thyroid, this is mainly due to carotid pulsation, which is in the 1–10 Hz bandwidth and is located right next to the gland. To decrease shear wavelength and increase signal to noise ratio (SNR), a complex shear wave field can be created by using vocal tract vibrations.
The nature of the sound can be modified by changing pitch. Thus, singing and maintain an “eeee” note (approximately the frequency of D3, or 150 hertz), shear wave is generated that can be used to identify abnormally stiff thyroid gland areas that can be indicative of cancer. A correlation-based algorithm then computes a shear wave velocity map that is then super-positioned onto a B-mode ultrasound image of the thyroid, with a pixel resolution of 150 × 150 μm2. The values obtained are in good agreement with comparative shear wave elastography (SWE) ultrasound measurements. The study was published on January 12, 2021, in Applied Physics Letters.
“The singing vibrates the patient's trachea, which in turn produces vibrations throughout the thyroid, allowing the clinician to use an ultrafast frame rate to track changes in shear-wave velocity, giving us information about mechanical properties of soft tissues,” said lead author Steve Beuve, PhD, of the Université de Tours. “Developing noninvasive methods would reduce the stress of patients during their medical exams. Having to sing during a medical exam can perhaps help release some of the nervous tension even more.”
Thyroid nodular disease is one of the most widespread endocrine disorders, but although fine needle aspiration guided with ultrasound examination is commonly used to detect malignant tumors, only 5% of thyroid cancers are detectable with this technique. As a result elastography has been proposed to detect cancerous nodules, with a nodule whose Young's modulus exceeds 65 kPa usually considered suspicious. But one of the problems with such an approach is that the thyroid SNR is drowned out by natural background noise from nearby organs.
Related Links:
Université de Tours
Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Dijon-Bourgogne
Université Bourgogne Franche-Comté
Latest Ultrasound News
- Reusable Gel Pad Made from Tamarind Seed Could Transform Ultrasound Examinations
- AI Model Accurately Detects Placenta Accreta in Pregnancy Before Delivery
- Portable Ultrasound Sensor to Enable Earlier Breast Cancer Detection
- Portable Imaging Scanner to Diagnose Lymphatic Disease in Real Time
- Imaging Technique Generates Simultaneous 3D Color Images of Soft-Tissue Structure and Vasculature
- Wearable Ultrasound Imaging System to Enable Real-Time Disease Monitoring
- Ultrasound Technique Visualizes Deep Blood Vessels in 3D Without Contrast Agents
- Ultrasound Probe Images Entire Organ in 4D

- Disposable Ultrasound Patch Performs Better Than Existing Devices
- Non-Invasive Ultrasound-Based Tool Accurately Detects Infant Meningitis
- Breakthrough Deep Learning Model Enhances Handheld 3D Medical Imaging
- Pain-Free Breast Imaging System Performs One Minute Cancer Scan
- Wireless Chronic Pain Management Device to Reduce Need for Painkillers and Surgery
- New Medical Ultrasound Imaging Technique Enables ICU Bedside Monitoring
- New Incision-Free Technique Halts Growth of Debilitating Brain Lesions
- AI-Powered Lung Ultrasound Outperforms Human Experts in Tuberculosis Diagnosis
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read more
AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
Chronological age does not always reflect how fast the body is truly aging, and current biological age tests often rely on DNA-based markers that may miss early organ-level decline. Detecting subtle, age-related... Read moreMRI
view channel
New Material Boosts MRI Image Quality
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a cornerstone of modern diagnostics, yet certain deep or anatomically complex tissues, including delicate structures of the eye and orbit, remain difficult to visualize clearly.... Read more
AI Model Reads and Diagnoses Brain MRI in Seconds
Brain MRI scans are critical for diagnosing strokes, hemorrhages, and other neurological disorders, but interpreting them can take hours or even days due to growing demand and limited specialist availability.... Read moreMRI Scan Breakthrough to Help Avoid Risky Invasive Tests for Heart Patients
Heart failure patients often require right heart catheterization to assess how severely their heart is struggling to pump blood, a procedure that involves inserting a tube into the heart to measure blood... Read more
MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
Recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies widely, with some patients regaining full function while others are left with lasting disabilities. Prognosis is especially difficult to assess in patients... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
Targeted cancer therapies only work when tumor cells express the specific molecular structures they are designed to attack. In urothelial carcinoma, a common form of bladder cancer, the cell surface protein... Read more
Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
Targeted cancer therapies can be highly effective, but only when a patient’s tumor expresses the specific protein the treatment is designed to attack. Determining this usually requires biopsies or advanced... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Tool Predicts Side Effects from Lung Cancer Treatment
Radiation therapy is a central treatment for lung cancer, but even carefully targeted radiation can affect surrounding healthy tissue. Patients may develop side effects such as lung inflammation, coughing,... Read more
AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer is a form of head and neck cancer that can spread through lymph nodes, significantly affecting survival and treatment decisions. Current therapies often involve combinations of surgery,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Nuclear Medicine Set for Continued Growth Driven by Demand for Precision Diagnostics
Clinical imaging services face rising demand for precise molecular diagnostics and targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy as cancer and chronic disease rates climb. A new market analysis projects rapid expansion... Read more




















