Power Assist Technology Positions X-Ray Tubes Effortlessly
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 14 Jan 2021 |
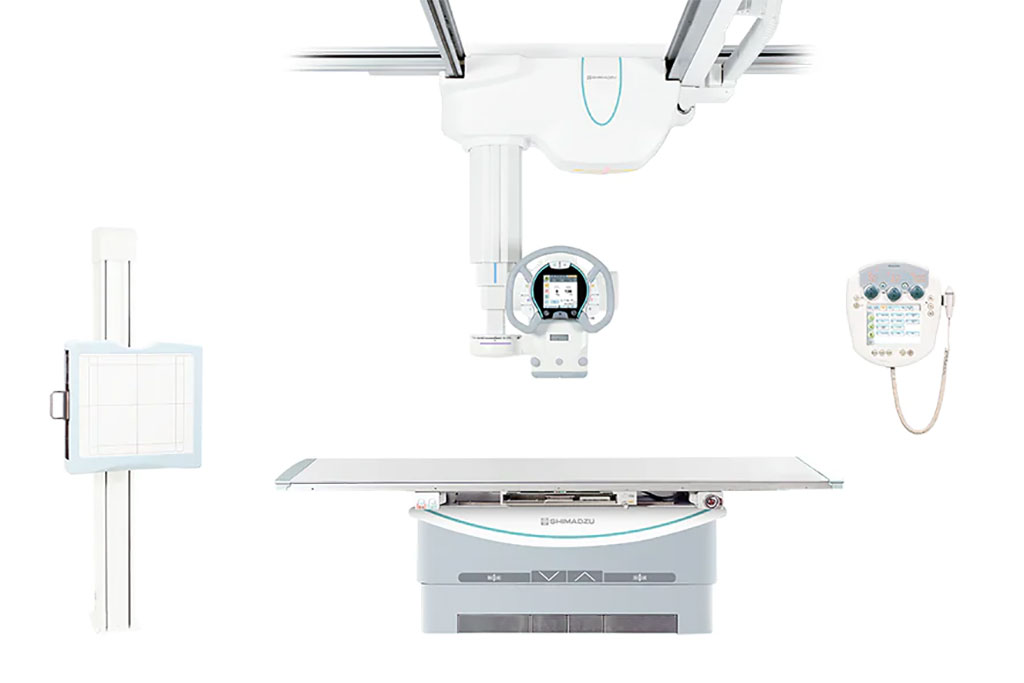

Image: The RADspeed Pro style edition with Power Glide (Photo courtesy of Shimadzu Medical Systems)
Brand-new power assist technology designed for high-end Shimadzu Medical Systems (SMS; Kyoto, Japan) general radiography systems provides an effortless operating assistance experience, improving radiographic examination environments. The assist-level can be selected among three levels on the X-ray tube support touch panel.
The technology, called Power Glide, is designed to instantaneously sense the amount of force applied by an operator during each operation, calculate the amount of assist-force required, and activate the motors accordingly to provide smooth and comfortable control when positioning the X-ray tube. As the forces applied to the handle during operation vary from person to person, the amount of power assist that each operator feels is optimal for operations, such as for large movements or detailed positioning adjustments, differs as well.
Power Glide is available in the SMS RADspeed Pro style edition, which provides up to 800 anatomical programs that can be registered; auto-positioning can move the position and angle of the X-ray tube to the programmed position. An auto-collimator selects a proper filter according to the program selected to optimize exposure dose and image quality. For dose management, the system can automatically calculate the dose area product (DAP) value from the X-ray conditions and display at each exposure. The LCD screen and illumination color can change according to the Bucky table or X-ray tube settings selected.
The ceiling X-ray tube support ensures wide-range vertical stroke of 1600 mm to examine the whole body (up to the lower extremities) in standing position. This support also rotates on the vertical and horizontal axis in addition to fixed positioning at any desired angle, enabling fast positioning at complex angles for orthopedic applications. Options include automatic imaging stitching; gridless scatter noise removal and improved image contrast; an image processing function that helps to confirm the absence of residual instruments, like gauze and needles, and reconfirmation of catheter tip location in PICC insertion procedures.
“Shimadzu has remained committed to developing innovative technologies that minimize radiation dose, improve image quality, and ensure excellent operability, in order to supply diagnostic imaging systems for supporting those working at the front lines of healthcare throughout the world,” said the company in a press release. “This new product can help increase the productivity of busy healthcare operations and improve the working environment of medical professionals, whether at small clinics or large hospitals, while maintaining the cumulative excellences offered by previous models.”
As general radiography examinations require fine operability to position the X-ray exposure area to within a few millimeters, it requires moving the entire assembly along ceiling rails from large distances, and as result the physical burden on operators is high. Reducing operating loads by improving system ergonomics enables a smoother workflow, and also shortens the time that patients must maintain a particular body position during examinations.
The technology, called Power Glide, is designed to instantaneously sense the amount of force applied by an operator during each operation, calculate the amount of assist-force required, and activate the motors accordingly to provide smooth and comfortable control when positioning the X-ray tube. As the forces applied to the handle during operation vary from person to person, the amount of power assist that each operator feels is optimal for operations, such as for large movements or detailed positioning adjustments, differs as well.
Power Glide is available in the SMS RADspeed Pro style edition, which provides up to 800 anatomical programs that can be registered; auto-positioning can move the position and angle of the X-ray tube to the programmed position. An auto-collimator selects a proper filter according to the program selected to optimize exposure dose and image quality. For dose management, the system can automatically calculate the dose area product (DAP) value from the X-ray conditions and display at each exposure. The LCD screen and illumination color can change according to the Bucky table or X-ray tube settings selected.
The ceiling X-ray tube support ensures wide-range vertical stroke of 1600 mm to examine the whole body (up to the lower extremities) in standing position. This support also rotates on the vertical and horizontal axis in addition to fixed positioning at any desired angle, enabling fast positioning at complex angles for orthopedic applications. Options include automatic imaging stitching; gridless scatter noise removal and improved image contrast; an image processing function that helps to confirm the absence of residual instruments, like gauze and needles, and reconfirmation of catheter tip location in PICC insertion procedures.
“Shimadzu has remained committed to developing innovative technologies that minimize radiation dose, improve image quality, and ensure excellent operability, in order to supply diagnostic imaging systems for supporting those working at the front lines of healthcare throughout the world,” said the company in a press release. “This new product can help increase the productivity of busy healthcare operations and improve the working environment of medical professionals, whether at small clinics or large hospitals, while maintaining the cumulative excellences offered by previous models.”
As general radiography examinations require fine operability to position the X-ray exposure area to within a few millimeters, it requires moving the entire assembly along ceiling rails from large distances, and as result the physical burden on operators is high. Reducing operating loads by improving system ergonomics enables a smoother workflow, and also shortens the time that patients must maintain a particular body position during examinations.
Latest Radiography News
- AI Tool Predicts Breast Cancer Risk Years Ahead Using Routine Mammograms
- Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
- AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
- X-Ray Breakthrough Captures Three Image-Contrast Types in Single Shot
- AI Generates Future Knee X-Rays to Predict Osteoarthritis Progression Risk
- AI Algorithm Uses Mammograms to Accurately Predict Cardiovascular Risk in Women
- AI Hybrid Strategy Improves Mammogram Interpretation
- AI Technology Predicts Personalized Five-Year Risk of Developing Breast Cancer
- RSNA AI Challenge Models Can Independently Interpret Mammograms
- New Technique Combines X-Ray Imaging and Radar for Safer Cancer Diagnosis
- New AI Tool Helps Doctors Read Chest X‑Rays Better
- Wearable X-Ray Imaging Detecting Fabric to Provide On-The-Go Diagnostic Scanning
- AI Helps Radiologists Spot More Lesions in Mammograms
- AI Detects Fatty Liver Disease from Chest X-Rays
- AI Detects Hidden Heart Disease in Existing CT Chest Scans
- Ultra-Lightweight AI Model Runs Without GPU to Break Barriers in Lung Cancer Diagnosis
Channels
MRI
view channel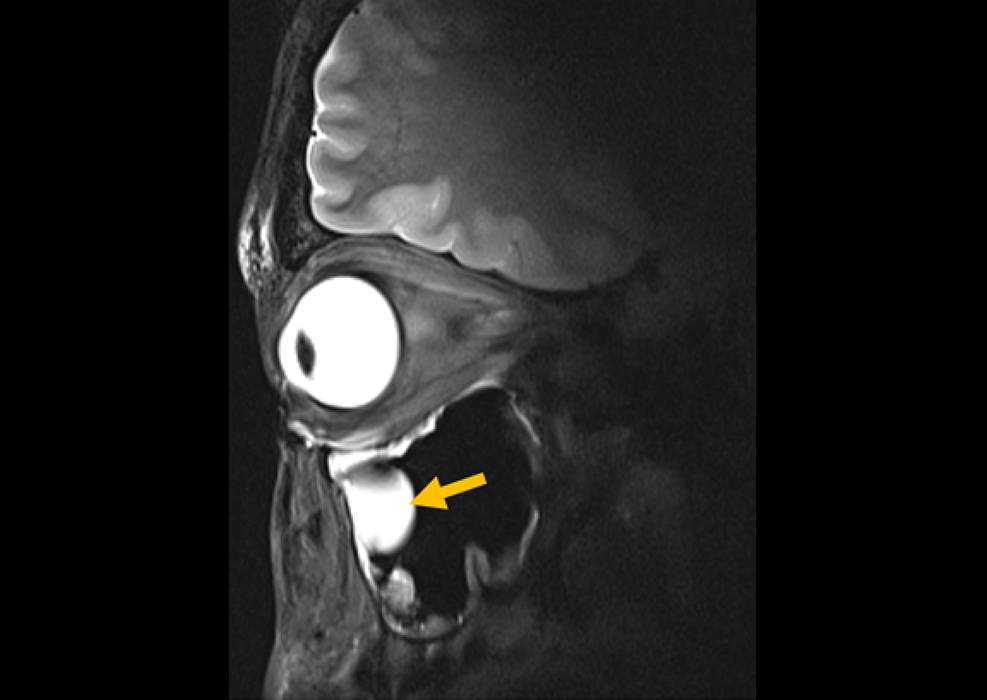
New Material Boosts MRI Image Quality
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a cornerstone of modern diagnostics, yet certain deep or anatomically complex tissues, including delicate structures of the eye and orbit, remain difficult to visualize clearly.... Read more
AI Model Reads and Diagnoses Brain MRI in Seconds
Brain MRI scans are critical for diagnosing strokes, hemorrhages, and other neurological disorders, but interpreting them can take hours or even days due to growing demand and limited specialist availability.... Read moreMRI Scan Breakthrough to Help Avoid Risky Invasive Tests for Heart Patients
Heart failure patients often require right heart catheterization to assess how severely their heart is struggling to pump blood, a procedure that involves inserting a tube into the heart to measure blood... Read more
MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
Recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies widely, with some patients regaining full function while others are left with lasting disabilities. Prognosis is especially difficult to assess in patients... Read moreUltrasound
view channel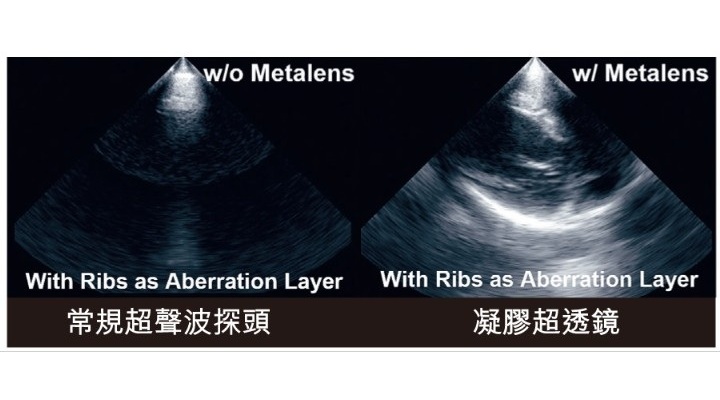
Groundbreaking Technology to Enhance Precision in Emergency and Critical Care
Rapid and accurate imaging is essential for diagnosing life-threatening conditions such as myocardial infarction, heart failure, and pulmonary embolism. However, conventional ultrasound imaging of the... Read more
Reusable Gel Pad Made from Tamarind Seed Could Transform Ultrasound Examinations
Ultrasound imaging depends on a conductive gel to eliminate air between the probe and the skin so sound waves can pass clearly into the body. While the imaging technology is fast, safe, and noninvasive,... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
Targeted cancer therapies only work when tumor cells express the specific molecular structures they are designed to attack. In urothelial carcinoma, a common form of bladder cancer, the cell surface protein... Read more
Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
Targeted cancer therapies can be highly effective, but only when a patient’s tumor expresses the specific protein the treatment is designed to attack. Determining this usually requires biopsies or advanced... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Tool Predicts Side Effects from Lung Cancer Treatment
Radiation therapy is a central treatment for lung cancer, but even carefully targeted radiation can affect surrounding healthy tissue. Patients may develop side effects such as lung inflammation, coughing,... Read more
AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer is a form of head and neck cancer that can spread through lymph nodes, significantly affecting survival and treatment decisions. Current therapies often involve combinations of surgery,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Nuclear Medicine Set for Continued Growth Driven by Demand for Precision Diagnostics
Clinical imaging services face rising demand for precise molecular diagnostics and targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy as cancer and chronic disease rates climb. A new market analysis projects rapid expansion... Read more





















