Single-Dose IORT Offsets COVID-19 Compliance Issues
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 07 Jan 2021 |

Image: The Zeiss Intrabeam 600 IORT system (Photo courtesy of Zeiss)
A long-term study show that targeted intraoperative radiotherapy (IORT) is equivalent to the traditional six-week radiotherapy (RT) regimen for early breast cancer (BC), reducing potential exposure to COVID-19.
Researchers at University College London (UCL; United Kingdom), Centro di Riferimento Oncologico di Aviano (CRO; Italy), and 30 other centers in 10 countries conducted a prospective, open label, randomized study to determine if single dose IORT during lumpectomy can effectively replace postoperative external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) for early BC. In all, 2,298 women with cN0-N1 invasive ductal carcinoma up to 3.5 cm in size were randomized before lumpectomy to risk adapted targeted IORT or EBRT.
The results demonstrated equal BC recurrence and survival rates among recipients of targeted IORT and those receiving multiple weeks of whole breast EBRT following lumpectomy. Long term follow-up of up to 18.9 years showed no significant difference in the five year local recurrence rates and 8.6 year local recurrence-free survival rates, BC survival rate, and overall survival rate. Women receiving targeted IORT also had a significantly lower risk of dying from other causes, such as heart disease or other cancers. The study was published on August 19, 2020, in BMJ.
“The long term results of this trial have shown that risk adapted single dose targeted IORT given during lumpectomy can effectively replace the mandatory use of several weeks of daily postoperative EBRT in patients with BC undergoing breast conservation,” concluded lead author Professor Jayant Vaidya, MD, of UCL, and colleagues. “Crucially, 80% of the patients required no additional radiotherapy; additionally, targeted IORT reduced non-breast cancer mortality. The advantage to the patient of avoiding post-operative radiotherapy could be considered obvious.”
“Unlike EBRT, which requires up to 30 visits to the radiotherapist, targeted IORT achieves the same clinical outcomes with one dose of targeted radiation delivered from inside the breast during surgery immediately following the removal of the tumor,” said Neil Friedman, MD, director of The Hoffberger Breast Center at Mercy Medical Center (Baltimore, MD, USA), who was not involved in the study. “Not only does targeted IORT mitigate the side effects normally associated with irradiating the entire breast multiple times, it may lessen or even eliminate unsafe additional outside trips during the pandemic.”
Related Links:
University College London
Centro di Riferimento Oncologico di Aviano
Researchers at University College London (UCL; United Kingdom), Centro di Riferimento Oncologico di Aviano (CRO; Italy), and 30 other centers in 10 countries conducted a prospective, open label, randomized study to determine if single dose IORT during lumpectomy can effectively replace postoperative external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) for early BC. In all, 2,298 women with cN0-N1 invasive ductal carcinoma up to 3.5 cm in size were randomized before lumpectomy to risk adapted targeted IORT or EBRT.
The results demonstrated equal BC recurrence and survival rates among recipients of targeted IORT and those receiving multiple weeks of whole breast EBRT following lumpectomy. Long term follow-up of up to 18.9 years showed no significant difference in the five year local recurrence rates and 8.6 year local recurrence-free survival rates, BC survival rate, and overall survival rate. Women receiving targeted IORT also had a significantly lower risk of dying from other causes, such as heart disease or other cancers. The study was published on August 19, 2020, in BMJ.
“The long term results of this trial have shown that risk adapted single dose targeted IORT given during lumpectomy can effectively replace the mandatory use of several weeks of daily postoperative EBRT in patients with BC undergoing breast conservation,” concluded lead author Professor Jayant Vaidya, MD, of UCL, and colleagues. “Crucially, 80% of the patients required no additional radiotherapy; additionally, targeted IORT reduced non-breast cancer mortality. The advantage to the patient of avoiding post-operative radiotherapy could be considered obvious.”
“Unlike EBRT, which requires up to 30 visits to the radiotherapist, targeted IORT achieves the same clinical outcomes with one dose of targeted radiation delivered from inside the breast during surgery immediately following the removal of the tumor,” said Neil Friedman, MD, director of The Hoffberger Breast Center at Mercy Medical Center (Baltimore, MD, USA), who was not involved in the study. “Not only does targeted IORT mitigate the side effects normally associated with irradiating the entire breast multiple times, it may lessen or even eliminate unsafe additional outside trips during the pandemic.”
Related Links:
University College London
Centro di Riferimento Oncologico di Aviano
Latest Nuclear Medicine News
- PET Imaging of Inflammation Predicts Recovery and Guides Therapy After Heart Attack
- Radiotheranostic Approach Detects, Kills and Reprograms Aggressive Cancers
- New Imaging Solution Improves Survival for Patients with Recurring Prostate Cancer
- PET Tracer Enables Same-Day Imaging of Triple-Negative Breast and Urothelial Cancers
- New Camera Sees Inside Human Body for Enhanced Scanning and Diagnosis
- Novel Bacteria-Specific PET Imaging Approach Detects Hard-To-Diagnose Lung Infections
- New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
- Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
- Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
- Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
- New Molecular Imaging Test to Improve Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- Novel PET Technique Visualizes Spinal Cord Injuries to Predict Recovery
- Next-Gen Tau Radiotracers Outperform FDA-Approved Imaging Agents in Detecting Alzheimer’s
- Breakthrough Method Detects Inflammation in Body Using PET Imaging
- Advanced Imaging Reveals Hidden Metastases in High-Risk Prostate Cancer Patients
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read more
AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
Chronological age does not always reflect how fast the body is truly aging, and current biological age tests often rely on DNA-based markers that may miss early organ-level decline. Detecting subtle, age-related... Read moreMRI
view channel
MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
Recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies widely, with some patients regaining full function while others are left with lasting disabilities. Prognosis is especially difficult to assess in patients... Read more
Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
Vascular dysfunction in the spinal cord contributes to multiple neurological conditions, including traumatic injuries and degenerative cervical myelopathy, where reduced blood flow can lead to progressive... Read more
AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
A cardiac MRI can reveal critical information about the heart’s function and any abnormalities, but traditional scans take 30 to 90 minutes and often suffer from poor image quality due to patient movement.... Read more
AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is one of the most common inherited heart conditions and a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young individuals and athletes. While many patients live normal lives, some... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Wearable Ultrasound Imaging System to Enable Real-Time Disease Monitoring
Chronic conditions such as hypertension and heart failure require close monitoring, yet today’s ultrasound imaging is largely confined to hospitals and short, episodic scans. This reactive model limits... Read more
Ultrasound Technique Visualizes Deep Blood Vessels in 3D Without Contrast Agents
Producing clear 3D images of deep blood vessels has long been difficult without relying on contrast agents, CT scans, or MRI. Standard ultrasound typically provides only 2D cross-sections, limiting clinicians’... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI-Based Tool Accelerates Detection of Kidney Cancer
Diagnosing kidney cancer depends on computed tomography scans, often using contrast agents to reveal abnormalities in kidney structure. Tumors are not always searched for deliberately, as many scans are... Read more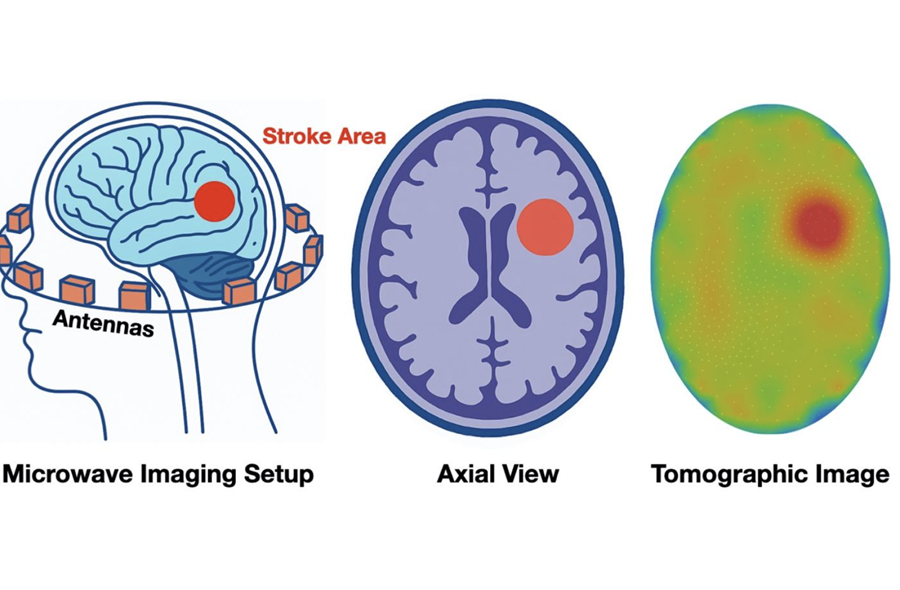
New Algorithm Dramatically Speeds Up Stroke Detection Scans
When patients arrive at emergency rooms with stroke symptoms, clinicians must rapidly determine whether the cause is a blood clot or a brain bleed, as treatment decisions depend on this distinction.... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more



















