Miniature Dosimeters Autonomously Monitor EMR Exposure
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 16 Jan 2020 |
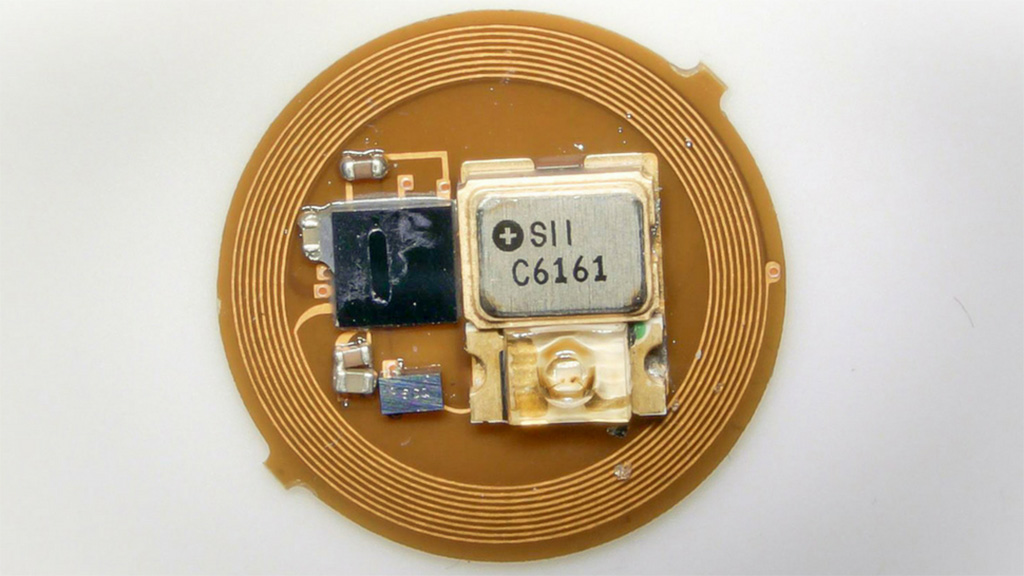
Image: A prototype autonomous EMR dosimeter (Photo courtesy of NU)
A millimeter-scale, ultra-low-power wireless digital platform provides continuous electromagnetic radiation (EMR) dosimetry for time-managed, wireless consumer devices.
Developed at Northwestern University (NU; Evanston, IL, USA) and the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST; Daejeon, Republic of Korea), the miniaturized digital dosimeter provides continuous EMR monitoring in an autonomous mode at one or multiple wavelengths simultaneously, transmitting the data over long-range wireless protocols to standard consumer devices. A single button cell battery powers the unit over a multiyear life span, enabled by the combined use of a light-powered, accumulation mode of detection and a light-adaptive, ultralow-power circuit design.
The dosimeter includes an accumulation detection module (ADM) for dosimetry and a Bluetooth low energy (BLE) system on a chip for wireless communication. A key feature is that the built-in ADM can directly measure continuous dose exposure without power consumption. As a result, it remains in an ultra-low sleep mode in the absence of light while continuously monitoring dosage via the ADM. When the dose exceeded a threshold, the device briefly wakes up to wirelessly transmit exposure data using BLE protocols to a smartphone, and resets the ADM and quickly return to sleep mode.
The ADM also includes a photodiode, supercapacitor, and a metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET). The miniaturized forms of the device have already been tested on sunglass clips, earrings, and wristbands for personalized EMR exposure detection. Field studies have shown that the dosimeter is extremely efficient in monitoring short-wavelength blue light from indoor lighting and display systems, as well as ultraviolet (UV), visible, and infrared (IR) radiation from the sun. The study was published on December 13, 2109, in Science Advances.
“The key feature of the ADM is that it directly measures exposure dose in a continuous fashion, without any power consumption. By contrast, conventional digital approaches approximate dose through computational time integration across a series of brief measurements of intensity, each performed using active, battery-powered electronics,” concluded lead author Kyeongha Kwon, PhD, of NU and KAIST, and colleagues. “Lack of interface ports and mechanical switches and the absence of need for battery replacement allow hermetic sealing of device for waterproof, sweat-resistant, and wear-resistant capabilities.”
Overexposure or underexposure to EMR can accumulate with latent consequences; where excessive exposure to UV and blue light from the sun or emissions of tanning beds and cellphones, can have associated health risks. For instance, repetitive keratinocyte damage from chronic exposure to UV is fundamental to cause skin cancer. The shorter wavelengths of the visible spectrum can generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the skin to cause DNA damage, hyperpigmentation and inflammation, alongside collagen and elastin degradation. Blue light can cause photochemical damage in retinal tissue to accelerate age-related maculopathy and modulate retinal control of the human circadian rhythm to suppress melatonin secretion.
Related Links:
Northwestern University
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology
Developed at Northwestern University (NU; Evanston, IL, USA) and the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST; Daejeon, Republic of Korea), the miniaturized digital dosimeter provides continuous EMR monitoring in an autonomous mode at one or multiple wavelengths simultaneously, transmitting the data over long-range wireless protocols to standard consumer devices. A single button cell battery powers the unit over a multiyear life span, enabled by the combined use of a light-powered, accumulation mode of detection and a light-adaptive, ultralow-power circuit design.
The dosimeter includes an accumulation detection module (ADM) for dosimetry and a Bluetooth low energy (BLE) system on a chip for wireless communication. A key feature is that the built-in ADM can directly measure continuous dose exposure without power consumption. As a result, it remains in an ultra-low sleep mode in the absence of light while continuously monitoring dosage via the ADM. When the dose exceeded a threshold, the device briefly wakes up to wirelessly transmit exposure data using BLE protocols to a smartphone, and resets the ADM and quickly return to sleep mode.
The ADM also includes a photodiode, supercapacitor, and a metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET). The miniaturized forms of the device have already been tested on sunglass clips, earrings, and wristbands for personalized EMR exposure detection. Field studies have shown that the dosimeter is extremely efficient in monitoring short-wavelength blue light from indoor lighting and display systems, as well as ultraviolet (UV), visible, and infrared (IR) radiation from the sun. The study was published on December 13, 2109, in Science Advances.
“The key feature of the ADM is that it directly measures exposure dose in a continuous fashion, without any power consumption. By contrast, conventional digital approaches approximate dose through computational time integration across a series of brief measurements of intensity, each performed using active, battery-powered electronics,” concluded lead author Kyeongha Kwon, PhD, of NU and KAIST, and colleagues. “Lack of interface ports and mechanical switches and the absence of need for battery replacement allow hermetic sealing of device for waterproof, sweat-resistant, and wear-resistant capabilities.”
Overexposure or underexposure to EMR can accumulate with latent consequences; where excessive exposure to UV and blue light from the sun or emissions of tanning beds and cellphones, can have associated health risks. For instance, repetitive keratinocyte damage from chronic exposure to UV is fundamental to cause skin cancer. The shorter wavelengths of the visible spectrum can generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the skin to cause DNA damage, hyperpigmentation and inflammation, alongside collagen and elastin degradation. Blue light can cause photochemical damage in retinal tissue to accelerate age-related maculopathy and modulate retinal control of the human circadian rhythm to suppress melatonin secretion.
Related Links:
Northwestern University
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology
Latest Radiography News
- Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
- AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
- X-Ray Breakthrough Captures Three Image-Contrast Types in Single Shot
- AI Generates Future Knee X-Rays to Predict Osteoarthritis Progression Risk
- AI Algorithm Uses Mammograms to Accurately Predict Cardiovascular Risk in Women
- AI Hybrid Strategy Improves Mammogram Interpretation
- AI Technology Predicts Personalized Five-Year Risk of Developing Breast Cancer
- RSNA AI Challenge Models Can Independently Interpret Mammograms
- New Technique Combines X-Ray Imaging and Radar for Safer Cancer Diagnosis
- New AI Tool Helps Doctors Read Chest X‑Rays Better
- Wearable X-Ray Imaging Detecting Fabric to Provide On-The-Go Diagnostic Scanning
- AI Helps Radiologists Spot More Lesions in Mammograms
- AI Detects Fatty Liver Disease from Chest X-Rays
- AI Detects Hidden Heart Disease in Existing CT Chest Scans
- Ultra-Lightweight AI Model Runs Without GPU to Break Barriers in Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- AI Radiology Tool Identifies Life-Threatening Conditions in Milliseconds

Channels
MRI
view channel
New Material Boosts MRI Image Quality
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a cornerstone of modern diagnostics, yet certain deep or anatomically complex tissues, including delicate structures of the eye and orbit, remain difficult to visualize clearly.... Read more
AI Model Reads and Diagnoses Brain MRI in Seconds
Brain MRI scans are critical for diagnosing strokes, hemorrhages, and other neurological disorders, but interpreting them can take hours or even days due to growing demand and limited specialist availability.... Read moreMRI Scan Breakthrough to Help Avoid Risky Invasive Tests for Heart Patients
Heart failure patients often require right heart catheterization to assess how severely their heart is struggling to pump blood, a procedure that involves inserting a tube into the heart to measure blood... Read more
MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
Recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies widely, with some patients regaining full function while others are left with lasting disabilities. Prognosis is especially difficult to assess in patients... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Reusable Gel Pad Made from Tamarind Seed Could Transform Ultrasound Examinations
Ultrasound imaging depends on a conductive gel to eliminate air between the probe and the skin so sound waves can pass clearly into the body. While the imaging technology is fast, safe, and noninvasive,... Read more
AI Model Accurately Detects Placenta Accreta in Pregnancy Before Delivery
Placenta accreta spectrum (PAS) is a life-threatening pregnancy complication in which the placenta abnormally attaches to the uterine wall. The condition is a leading cause of maternal mortality and morbidity... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
Targeted cancer therapies only work when tumor cells express the specific molecular structures they are designed to attack. In urothelial carcinoma, a common form of bladder cancer, the cell surface protein... Read more
Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
Targeted cancer therapies can be highly effective, but only when a patient’s tumor expresses the specific protein the treatment is designed to attack. Determining this usually requires biopsies or advanced... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Tool Predicts Side Effects from Lung Cancer Treatment
Radiation therapy is a central treatment for lung cancer, but even carefully targeted radiation can affect surrounding healthy tissue. Patients may develop side effects such as lung inflammation, coughing,... Read more
AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer is a form of head and neck cancer that can spread through lymph nodes, significantly affecting survival and treatment decisions. Current therapies often involve combinations of surgery,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Nuclear Medicine Set for Continued Growth Driven by Demand for Precision Diagnostics
Clinical imaging services face rising demand for precise molecular diagnostics and targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy as cancer and chronic disease rates climb. A new market analysis projects rapid expansion... Read more






 Guided Devices.jpg)














