Photoacoustic Radar Identifies Cholesterol in Arterial Plaque
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 26 Jun 2019 |
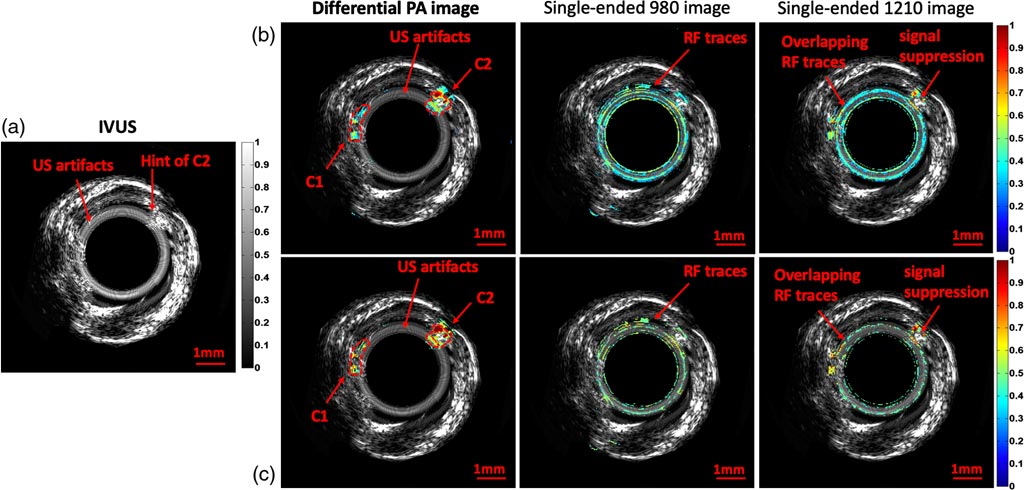
Image: Photoacoustic radar uses two different light sources to identify cholesterol (Photo courtesy of JBO).
A new study shows how a combination of low-power continuous wave laser and frequency-domain signal processing can accurately evaluate plaque-based cholesterol.
Developed by the University of Toronto (UT; Canada), Sunnybrook Research Institute (Toronto, Canada), and Conavi Medical (North York, Canada), differential photoacoustic radar (DPAR) can provide lipid-specific chemical information from an arterial wall with high optical contrast and long acoustic penetration depth. Using two low-power continuous-wave (1210 nm and 970 nm) optical sources in a differential manner, hybrid optical-acoustic DPAR can provide an imaging modality that is only sensitive and specific to the spectroscopically defined imaging target, cholesterol.
According to the researchers, in the near-infrared (NIR) window, the 1210-nm optical source usually used during single-ended systems intravascular photoacoustic (IVPA) lipid applications causes sensitivity issues, as other arterial tissues also show some degree of absorption near that spectral region, thereby generating undesirably interfering PA signals. The introduction of the second, 970 nm optical source, results in a more accurate and molecularly specific evaluation of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques. The study was published in the June 2019 issue of the Journal of Biomedical Optics (JBO).
“Laser photoacoustics is a hybrid optical-acoustic imaging technology in which a subsurface target is excited with near-infrared light and imaged with optically induced ultrasound signals,” wrote lead author Sung Soo Sean Choi, PhD, of the University of Toronto, and colleagues. “Satisfying both high optical contrast and high ultrasonic depth penetration, intravascular photoacoustics is emerging as a competitive modality for plaque detection.”
“Photoacoustic imaging has the best potential for imaging through thick tissues or blood: the high-sensitivity detection of cholesterol described in this paper is made possible with a specifically modified, dual wavelength approach,” commented Professor Brian Pogue, PhD, of Dartmouth College (Hanover, NH, USA), editor-in-chief of JBO. “This is an original direction of imaging research that utilizes an innovative idea of detection based upon differences between wavelengths, and signal analysis based upon radar methods.”
Atherosclerosis is a chronic cardiovascular disease characterized by inflammation and the gradual buildup of lipid-rich plaque in the intima of the arterial walls. Early atherosclerosis is initiated as lipid-carrying low-density lipoproteins (LDLs) get retained beneath the endothelial cells of the vessels. As the LDLs are oxidized, the endothelial cells trigger an immune response by attracting macrophages. The ingested oxidized LDLs in the macrophages increase abnormally, transforming them into foam cells that eventually rupture, causing local damage to the endothelial cells.
Related Links:
University of Toronto
Sunnybrook Research Institute
Conavi Medical
Developed by the University of Toronto (UT; Canada), Sunnybrook Research Institute (Toronto, Canada), and Conavi Medical (North York, Canada), differential photoacoustic radar (DPAR) can provide lipid-specific chemical information from an arterial wall with high optical contrast and long acoustic penetration depth. Using two low-power continuous-wave (1210 nm and 970 nm) optical sources in a differential manner, hybrid optical-acoustic DPAR can provide an imaging modality that is only sensitive and specific to the spectroscopically defined imaging target, cholesterol.
According to the researchers, in the near-infrared (NIR) window, the 1210-nm optical source usually used during single-ended systems intravascular photoacoustic (IVPA) lipid applications causes sensitivity issues, as other arterial tissues also show some degree of absorption near that spectral region, thereby generating undesirably interfering PA signals. The introduction of the second, 970 nm optical source, results in a more accurate and molecularly specific evaluation of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques. The study was published in the June 2019 issue of the Journal of Biomedical Optics (JBO).
“Laser photoacoustics is a hybrid optical-acoustic imaging technology in which a subsurface target is excited with near-infrared light and imaged with optically induced ultrasound signals,” wrote lead author Sung Soo Sean Choi, PhD, of the University of Toronto, and colleagues. “Satisfying both high optical contrast and high ultrasonic depth penetration, intravascular photoacoustics is emerging as a competitive modality for plaque detection.”
“Photoacoustic imaging has the best potential for imaging through thick tissues or blood: the high-sensitivity detection of cholesterol described in this paper is made possible with a specifically modified, dual wavelength approach,” commented Professor Brian Pogue, PhD, of Dartmouth College (Hanover, NH, USA), editor-in-chief of JBO. “This is an original direction of imaging research that utilizes an innovative idea of detection based upon differences between wavelengths, and signal analysis based upon radar methods.”
Atherosclerosis is a chronic cardiovascular disease characterized by inflammation and the gradual buildup of lipid-rich plaque in the intima of the arterial walls. Early atherosclerosis is initiated as lipid-carrying low-density lipoproteins (LDLs) get retained beneath the endothelial cells of the vessels. As the LDLs are oxidized, the endothelial cells trigger an immune response by attracting macrophages. The ingested oxidized LDLs in the macrophages increase abnormally, transforming them into foam cells that eventually rupture, causing local damage to the endothelial cells.
Related Links:
University of Toronto
Sunnybrook Research Institute
Conavi Medical
Latest General/Advanced Imaging News
- AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
- New 3D Imaging System Addresses MRI, CT and Ultrasound Limitations
- AI-Based Tool Predicts Future Cardiovascular Events in Angina Patients
- AI-Based Tool Accelerates Detection of Kidney Cancer
- New Algorithm Dramatically Speeds Up Stroke Detection Scans
- 3D Scanning Approach Enables Ultra-Precise Brain Surgery
- AI Tool Improves Medical Imaging Process by 90%
- New Ultrasmall, Light-Sensitive Nanoparticles Could Serve as Contrast Agents
- AI Algorithm Accurately Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis Using Routine CT Images
- Cutting-Edge Angio-CT Solution Offers New Therapeutic Possibilities
- Extending CT Imaging Detects Hidden Blood Clots in Stroke Patients
- Groundbreaking AI Model Accurately Segments Liver Tumors from CT Scans
- New CT-Based Indicator Helps Predict Life-Threatening Postpartum Bleeding Cases
- CT Colonography Beats Stool DNA Testing for Colon Cancer Screening
- First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
- AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read more
AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
Chronological age does not always reflect how fast the body is truly aging, and current biological age tests often rely on DNA-based markers that may miss early organ-level decline. Detecting subtle, age-related... Read moreMRI
view channel
MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
Recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies widely, with some patients regaining full function while others are left with lasting disabilities. Prognosis is especially difficult to assess in patients... Read more
Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
Vascular dysfunction in the spinal cord contributes to multiple neurological conditions, including traumatic injuries and degenerative cervical myelopathy, where reduced blood flow can lead to progressive... Read more
AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
A cardiac MRI can reveal critical information about the heart’s function and any abnormalities, but traditional scans take 30 to 90 minutes and often suffer from poor image quality due to patient movement.... Read more
AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is one of the most common inherited heart conditions and a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young individuals and athletes. While many patients live normal lives, some... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Wearable Ultrasound Imaging System to Enable Real-Time Disease Monitoring
Chronic conditions such as hypertension and heart failure require close monitoring, yet today’s ultrasound imaging is largely confined to hospitals and short, episodic scans. This reactive model limits... Read more
Ultrasound Technique Visualizes Deep Blood Vessels in 3D Without Contrast Agents
Producing clear 3D images of deep blood vessels has long been difficult without relying on contrast agents, CT scans, or MRI. Standard ultrasound typically provides only 2D cross-sections, limiting clinicians’... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
Targeted cancer therapies only work when tumor cells express the specific molecular structures they are designed to attack. In urothelial carcinoma, a common form of bladder cancer, the cell surface protein... Read more
Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
Targeted cancer therapies can be highly effective, but only when a patient’s tumor expresses the specific protein the treatment is designed to attack. Determining this usually requires biopsies or advanced... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more



















