Real-Time VR Enhances View and Treatment Options in IR
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 05 Apr 2019 |
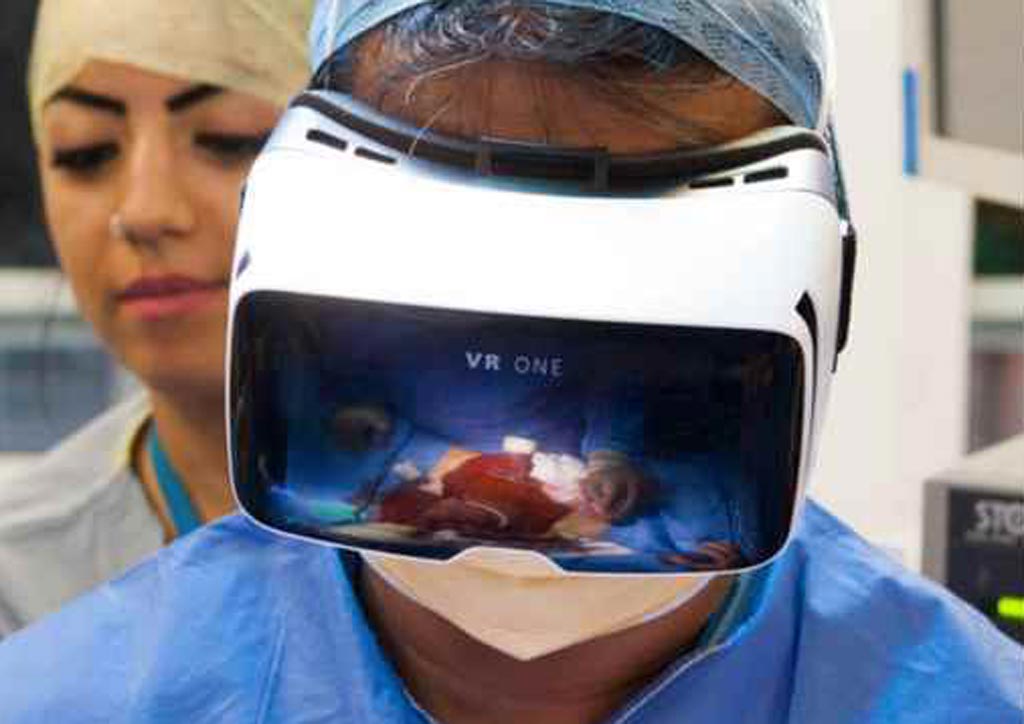
Image: New research suggests virtual reality options could enable interventional radiologists to improve treatments using RT 3D images from inside a patient’s blood vessels (Photo courtesy of Techmaish).
New research presented at the Society of Interventional Radiology’s 2019 Annual Scientific Meeting shows that immersive virtual reality (VR) could enable interventional radiologists to improve treatments using real-time 3D images from inside a patient’s blood vessels. The interactive technology could provide faster, more efficient treatment, with less radiation exposure and greater precision, ease and confidence.
The researchers conducted a study to demonstrate the feasibility of using a catheter with electromagnetic sensors projected onto a VR headset to see and steer the catheter through the anatomy to certain blood vessels. Using a CT angiography scan, they created a 3D printed model and a holographic image of blood vessels in a patient’s abdomen and pelvis. A team of radiologists guided hi-tech catheters through the 3D printed model while the tracking system showed the image from the catheter through the VR headset. They compared the time taken to steer the catheter from the entry point of the femoral artery to three different targeted vessels versus the time the process took using conventional fluoroscopic guidance, as well as the time taken in similar real-life clinical angiographic procedures.
In 18 simulated procedures, the researchers found the mean time to reach the three targeted vessels using VR was much lower than in fluoroscopy, the standard practice that uses an x-ray image. In the first vessel, VR took 17.6 seconds versus 70.3 seconds using the standard practice on the model and 171.2 seconds in the real-life procedure. With the improved efficiency, the researchers believe that VR technology will create safer treatments by reducing the amount of radiation exposure to both patient and physician, as well as increase access to IR treatments. The researchers also surveyed the practitioners who had tried the technology who reported that VR improved the ease, precision and efficiency of the treatment. Additionally, the users said they felt more confident in their abilities.
“Virtual reality will change how we look at a patient’s anatomy during an IR treatment. This technology will allow physicians to travel inside a patient’s body instead of relying solely on 2D, black and white images,” said Wayne Monsky, M.D, PhD, a professor of radiology at the University of Washington and lead author of the study. “Currently, the life-saving potential of IR is limited to hospitals and areas with the resources to invest in image-guided technology. There are three billion people worldwide in rural areas who don't have this access. This technology could allow for portability and accessibility so that these procedures are brought to rural areas using nothing more than a suitcase.”
The researchers conducted a study to demonstrate the feasibility of using a catheter with electromagnetic sensors projected onto a VR headset to see and steer the catheter through the anatomy to certain blood vessels. Using a CT angiography scan, they created a 3D printed model and a holographic image of blood vessels in a patient’s abdomen and pelvis. A team of radiologists guided hi-tech catheters through the 3D printed model while the tracking system showed the image from the catheter through the VR headset. They compared the time taken to steer the catheter from the entry point of the femoral artery to three different targeted vessels versus the time the process took using conventional fluoroscopic guidance, as well as the time taken in similar real-life clinical angiographic procedures.
In 18 simulated procedures, the researchers found the mean time to reach the three targeted vessels using VR was much lower than in fluoroscopy, the standard practice that uses an x-ray image. In the first vessel, VR took 17.6 seconds versus 70.3 seconds using the standard practice on the model and 171.2 seconds in the real-life procedure. With the improved efficiency, the researchers believe that VR technology will create safer treatments by reducing the amount of radiation exposure to both patient and physician, as well as increase access to IR treatments. The researchers also surveyed the practitioners who had tried the technology who reported that VR improved the ease, precision and efficiency of the treatment. Additionally, the users said they felt more confident in their abilities.
“Virtual reality will change how we look at a patient’s anatomy during an IR treatment. This technology will allow physicians to travel inside a patient’s body instead of relying solely on 2D, black and white images,” said Wayne Monsky, M.D, PhD, a professor of radiology at the University of Washington and lead author of the study. “Currently, the life-saving potential of IR is limited to hospitals and areas with the resources to invest in image-guided technology. There are three billion people worldwide in rural areas who don't have this access. This technology could allow for portability and accessibility so that these procedures are brought to rural areas using nothing more than a suitcase.”
Latest Imaging IT News
- New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI-Based Technology for Ultrasound Image Analysis Receives FDA Approval
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Digital Pathology Software Improves Workflow Efficiency
- Patient-Centric Portal Facilitates Direct Imaging Access
- New Workstation Supports Customer-Driven Imaging Workflow
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI Tool Predicts Breast Cancer Risk Years Ahead Using Routine Mammograms
Breast cancer screening saves lives but still relies largely on uniform schedules despite wide differences in individual risk. This one-size-fits-all approach can miss cancers in higher-risk women while... Read more
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read moreMRI
view channel
New Material Boosts MRI Image Quality
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a cornerstone of modern diagnostics, yet certain deep or anatomically complex tissues, including delicate structures of the eye and orbit, remain difficult to visualize clearly.... Read more
AI Model Reads and Diagnoses Brain MRI in Seconds
Brain MRI scans are critical for diagnosing strokes, hemorrhages, and other neurological disorders, but interpreting them can take hours or even days due to growing demand and limited specialist availability.... Read moreMRI Scan Breakthrough to Help Avoid Risky Invasive Tests for Heart Patients
Heart failure patients often require right heart catheterization to assess how severely their heart is struggling to pump blood, a procedure that involves inserting a tube into the heart to measure blood... Read more
MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
Recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies widely, with some patients regaining full function while others are left with lasting disabilities. Prognosis is especially difficult to assess in patients... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Reusable Gel Pad Made from Tamarind Seed Could Transform Ultrasound Examinations
Ultrasound imaging depends on a conductive gel to eliminate air between the probe and the skin so sound waves can pass clearly into the body. While the imaging technology is fast, safe, and noninvasive,... Read more
AI Model Accurately Detects Placenta Accreta in Pregnancy Before Delivery
Placenta accreta spectrum (PAS) is a life-threatening pregnancy complication in which the placenta abnormally attaches to the uterine wall. The condition is a leading cause of maternal mortality and morbidity... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
Targeted cancer therapies only work when tumor cells express the specific molecular structures they are designed to attack. In urothelial carcinoma, a common form of bladder cancer, the cell surface protein... Read more
Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
Targeted cancer therapies can be highly effective, but only when a patient’s tumor expresses the specific protein the treatment is designed to attack. Determining this usually requires biopsies or advanced... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Tool Predicts Side Effects from Lung Cancer Treatment
Radiation therapy is a central treatment for lung cancer, but even carefully targeted radiation can affect surrounding healthy tissue. Patients may develop side effects such as lung inflammation, coughing,... Read more
AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer is a form of head and neck cancer that can spread through lymph nodes, significantly affecting survival and treatment decisions. Current therapies often involve combinations of surgery,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more





















