Digital Pathology Software Improves Workflow Efficiency
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 31 Jan 2019 |
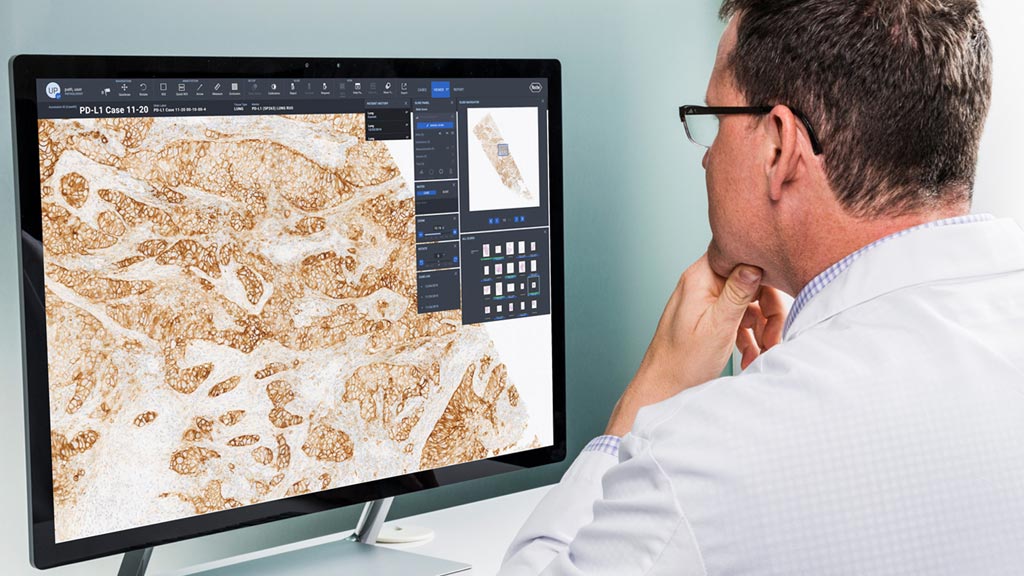
Image: uPath enterprise software provides improved digital pathology tools (Photo courtesy of Roche).
A novel software platform drastically decreases image-rendering times, integrates automated image analysis, and enables improved case sharing between pathologists.
The Roche (Basel, Switzerland) uPath enterprise software for digital pathology can help pathologists diagnose a patient case more quickly by viewing all slides in a single continuous view, as well as viewing all available patient information simultaneously. The multiple slides, which are presented on a canvas-like display, enabling seamless navigation between hematoxylin and eosin (HE), immunohistochemistry (IHC) and special stains in a single view, thanks to Leeds Virtual Microscope (LVM) technology, which is not possible with a standard microscope.
Analyses, both automated and manual, and slide markups are easily managed in the multi-slide viewer, while reporting features allow pathologists to aggregate notes, measurements, and slide scoring into easy-to-share images or PDFs. The customization offered through the uPath configurable interface and scalability allows pathologists to request second opinions and share cases in a fraction of the time that has traditionally been required, with no geographical limitations, unlike glass slides. LVM technology can also scale to display sizes ranging from laptops to high-definition wall screens.
"With this launch, we are able to deliver an improved digital pathology experience. We're excited to offer pathology labs a high-quality solution to help improve workflow efficiencies, accuracy, and precision tools,” said Jill German, Head of Roche Tissue Diagnostics. “This launch is another major milestone in our commitment to the advancement of patient care through digital pathology, empowering pathologists to deliver next-level personalized healthcare solutions.”
Digital pathology is an image-based information environment, which is enabled by computer technology, allowing for management of information generated from a digital slide. It is enabled in part by virtual microscopy, the conversion of glass slides into digital slides that can be viewed, managed, shared, and analyzed on a computer monitor. With the advent of whole-slide imaging, digital pathology is currently regarded as one of the most promising avenues of diagnostic medicine.
The Roche (Basel, Switzerland) uPath enterprise software for digital pathology can help pathologists diagnose a patient case more quickly by viewing all slides in a single continuous view, as well as viewing all available patient information simultaneously. The multiple slides, which are presented on a canvas-like display, enabling seamless navigation between hematoxylin and eosin (HE), immunohistochemistry (IHC) and special stains in a single view, thanks to Leeds Virtual Microscope (LVM) technology, which is not possible with a standard microscope.
Analyses, both automated and manual, and slide markups are easily managed in the multi-slide viewer, while reporting features allow pathologists to aggregate notes, measurements, and slide scoring into easy-to-share images or PDFs. The customization offered through the uPath configurable interface and scalability allows pathologists to request second opinions and share cases in a fraction of the time that has traditionally been required, with no geographical limitations, unlike glass slides. LVM technology can also scale to display sizes ranging from laptops to high-definition wall screens.
"With this launch, we are able to deliver an improved digital pathology experience. We're excited to offer pathology labs a high-quality solution to help improve workflow efficiencies, accuracy, and precision tools,” said Jill German, Head of Roche Tissue Diagnostics. “This launch is another major milestone in our commitment to the advancement of patient care through digital pathology, empowering pathologists to deliver next-level personalized healthcare solutions.”
Digital pathology is an image-based information environment, which is enabled by computer technology, allowing for management of information generated from a digital slide. It is enabled in part by virtual microscopy, the conversion of glass slides into digital slides that can be viewed, managed, shared, and analyzed on a computer monitor. With the advent of whole-slide imaging, digital pathology is currently regarded as one of the most promising avenues of diagnostic medicine.
Latest Imaging IT News
- New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI-Based Technology for Ultrasound Image Analysis Receives FDA Approval
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Patient-Centric Portal Facilitates Direct Imaging Access
- New Workstation Supports Customer-Driven Imaging Workflow
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
Chronological age does not always reflect how fast the body is truly aging, and current biological age tests often rely on DNA-based markers that may miss early organ-level decline. Detecting subtle, age-related... Read more
X-Ray Breakthrough Captures Three Image-Contrast Types in Single Shot
Detecting early-stage cancer or subtle changes deep inside tissues has long challenged conventional X-ray systems, which rely only on how structures absorb radiation. This limitation keeps many microstructural... Read moreMRI
view channel
Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
Vascular dysfunction in the spinal cord contributes to multiple neurological conditions, including traumatic injuries and degenerative cervical myelopathy, where reduced blood flow can lead to progressive... Read more
AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
A cardiac MRI can reveal critical information about the heart’s function and any abnormalities, but traditional scans take 30 to 90 minutes and often suffer from poor image quality due to patient movement.... Read more
AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is one of the most common inherited heart conditions and a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young individuals and athletes. While many patients live normal lives, some... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Wearable Ultrasound Imaging System to Enable Real-Time Disease Monitoring
Chronic conditions such as hypertension and heart failure require close monitoring, yet today’s ultrasound imaging is largely confined to hospitals and short, episodic scans. This reactive model limits... Read more
Ultrasound Technique Visualizes Deep Blood Vessels in 3D Without Contrast Agents
Producing clear 3D images of deep blood vessels has long been difficult without relying on contrast agents, CT scans, or MRI. Standard ultrasound typically provides only 2D cross-sections, limiting clinicians’... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
PET Imaging of Inflammation Predicts Recovery and Guides Therapy After Heart Attack
Acute myocardial infarction can trigger lasting heart damage, yet clinicians still lack reliable tools to identify which patients will regain function and which may develop heart failure.... Read more
Radiotheranostic Approach Detects, Kills and Reprograms Aggressive Cancers
Aggressive cancers such as osteosarcoma and glioblastoma often resist standard therapies, thrive in hostile tumor environments, and recur despite surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy. These tumors also... Read more
New Imaging Solution Improves Survival for Patients with Recurring Prostate Cancer
Detecting recurrent prostate cancer remains one of the most difficult challenges in oncology, as standard imaging methods such as bone scans and CT scans often fail to accurately locate small or early-stage tumors.... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel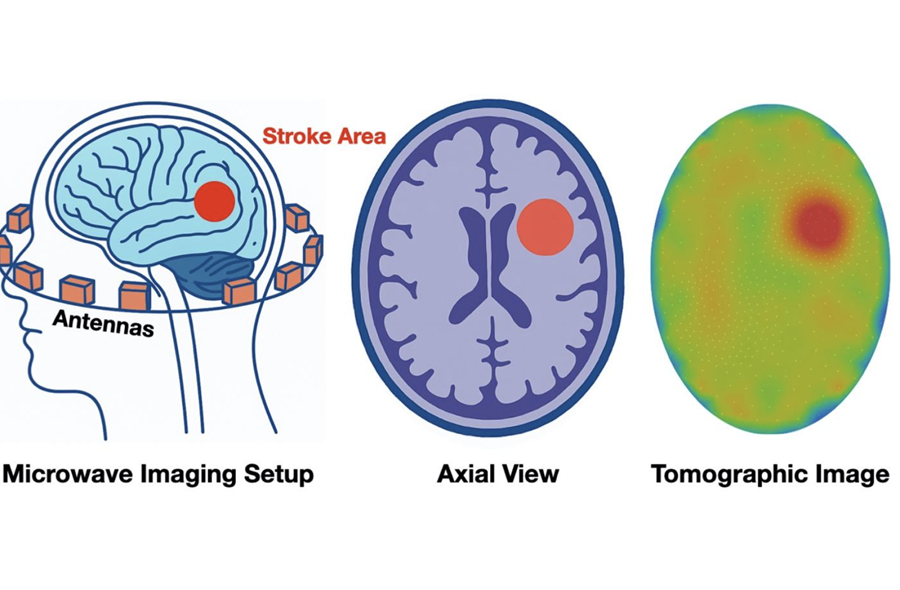
New Algorithm Dramatically Speeds Up Stroke Detection Scans
When patients arrive at emergency rooms with stroke symptoms, clinicians must rapidly determine whether the cause is a blood clot or a brain bleed, as treatment decisions depend on this distinction.... Read more
3D Scanning Approach Enables Ultra-Precise Brain Surgery
Precise navigation is critical in neurosurgery, yet even small alignment errors can affect outcomes when operating deep within the brain. A new 3D surface-scanning approach now provides a radiation-free... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more








 Guided Devices.jpg)