Dedicated System Scans Heart in One Heartbeat
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 18 Sep 2018 |
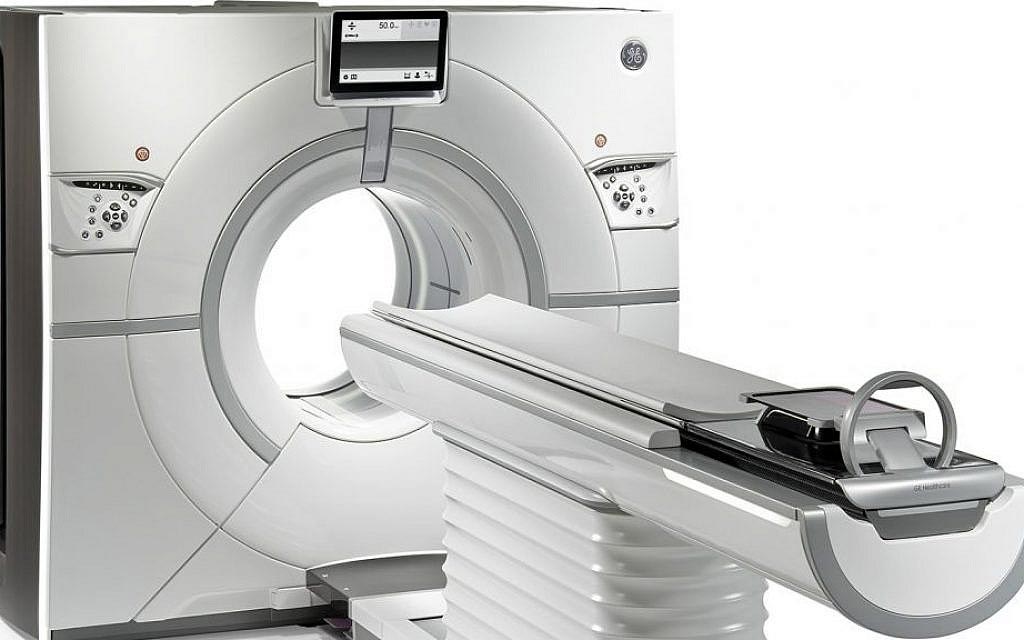
Image: A dedicated cardiovascular CT system targets the heart (Photo courtesy of Arineta).
A dedicated cardiovascular computerized tomography (CT) system creates a three-dimensional (3D) scan of the entire heart in one rotation.
The GE Healthcare (GE, Little Chalfont, United Kingdom) Cardiographe is a proprietary CT scanner optimized for cardiovascular imaging by eliminating aspects required for whole-body imaging, but irrelevant for cardiac scanning, thus optimizing its operation for a range of cardiac imaging parameters. The compact, high performance system provides high resolution, motion-free, artifact-free, volumetric images of the whole heart without stitching, using a gantry rotation speed of 0.24 seconds, enabling very fast scans that freeze cardiac motion.
Several innovative proprietary technologies are combined into the system to provide optimal cardiac imaging. The most important is focused field of view (FFW), which uses full beam intensity in the field of interest, and highly attenuated beam in the periphery. Two detector arrays are used, a high-resolution array in the focused field of view, and peripheral detector arrays optimized for low intensity imaging at the wings. Special algorithms are used to reconstruct the images in the center of the field of view, with GE SnapShot Freeze intelligent motion correction software integrated to suspend coronary motion.
Proprietary Twin Beam technology is also used, which involves two overlapping X-ray beams irradiating the scanned volume and detected both by a single detector. Ultra-fast beam switching technology and unique reconstruction algorithms optimize image quality. Finally, the system uses ultra short geometry (USG), wherein the twin x-ray source is substantially closer to the patient than in a conventional CT design. USG presents several advantages, including lower doses (2 mSv or below), faster rotation, and improved temporal resolution.
The Cardiographe was developed by Arineta (Ceserea, Israel), who partnered with GE Healthcare to commercialize the scanner. GE incorporated into the system features from its Revolution CT system, including advances for dose reduction, iterative reconstruction, metal artifact reduction and others. The Cardiographe was built to be very compact so it can fit into a physician’s office, or utilize a smaller room than a standard 64-slice scanner. The scanner is also optimized for other cardiovascular studies such as the aorta, the carotid, and renal arteries.
“It is more worthwhile for hospitals to buy one CT device at an average price for all the non-cardiac indications and our system for cardiac scans,” said Ehud Dafni, MD, CEO of Arineta. “That way, it can scan twice as many patients as it could by buying the expensive CT designed for all the systems, and which also has improved cardiac scan capabilities.”
The GE Healthcare (GE, Little Chalfont, United Kingdom) Cardiographe is a proprietary CT scanner optimized for cardiovascular imaging by eliminating aspects required for whole-body imaging, but irrelevant for cardiac scanning, thus optimizing its operation for a range of cardiac imaging parameters. The compact, high performance system provides high resolution, motion-free, artifact-free, volumetric images of the whole heart without stitching, using a gantry rotation speed of 0.24 seconds, enabling very fast scans that freeze cardiac motion.
Several innovative proprietary technologies are combined into the system to provide optimal cardiac imaging. The most important is focused field of view (FFW), which uses full beam intensity in the field of interest, and highly attenuated beam in the periphery. Two detector arrays are used, a high-resolution array in the focused field of view, and peripheral detector arrays optimized for low intensity imaging at the wings. Special algorithms are used to reconstruct the images in the center of the field of view, with GE SnapShot Freeze intelligent motion correction software integrated to suspend coronary motion.
Proprietary Twin Beam technology is also used, which involves two overlapping X-ray beams irradiating the scanned volume and detected both by a single detector. Ultra-fast beam switching technology and unique reconstruction algorithms optimize image quality. Finally, the system uses ultra short geometry (USG), wherein the twin x-ray source is substantially closer to the patient than in a conventional CT design. USG presents several advantages, including lower doses (2 mSv or below), faster rotation, and improved temporal resolution.
The Cardiographe was developed by Arineta (Ceserea, Israel), who partnered with GE Healthcare to commercialize the scanner. GE incorporated into the system features from its Revolution CT system, including advances for dose reduction, iterative reconstruction, metal artifact reduction and others. The Cardiographe was built to be very compact so it can fit into a physician’s office, or utilize a smaller room than a standard 64-slice scanner. The scanner is also optimized for other cardiovascular studies such as the aorta, the carotid, and renal arteries.
“It is more worthwhile for hospitals to buy one CT device at an average price for all the non-cardiac indications and our system for cardiac scans,” said Ehud Dafni, MD, CEO of Arineta. “That way, it can scan twice as many patients as it could by buying the expensive CT designed for all the systems, and which also has improved cardiac scan capabilities.”
Latest General/Advanced Imaging News
- CT Colonography Beats Stool DNA Testing for Colon Cancer Screening
- First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
- AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
- CT-Based Deep Learning-Driven Tool to Enhance Liver Cancer Diagnosis
- AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
- Ultra-Low Dose CT Aids Pneumonia Diagnosis in Immunocompromised Patients
- AI Reduces CT Lung Cancer Screening Workload by Almost 80%
- Cutting-Edge Technology Combines Light and Sound for Real-Time Stroke Monitoring
- AI System Detects Subtle Changes in Series of Medical Images Over Time
- New CT Scan Technique to Improve Prognosis and Treatments for Head and Neck Cancers
- World’s First Mobile Whole-Body CT Scanner to Provide Diagnostics at POC
- Comprehensive CT Scans Could Identify Atherosclerosis Among Lung Cancer Patients
- AI Improves Detection of Colorectal Cancer on Routine Abdominopelvic CT Scans
- Super-Resolution Technology Enhances Clinical Bone Imaging to Predict Osteoporotic Fracture Risk
- AI-Powered Abdomen Map Enables Early Cancer Detection
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI Radiology Tool Identifies Life-Threatening Conditions in Milliseconds
Radiology is emerging as one of healthcare’s most pressing bottlenecks. By 2033, the U.S. could face a shortage of up to 42,000 radiologists, even as imaging volumes grow by 5% annually.... Read more
Machine Learning Algorithm Identifies Cardiovascular Risk from Routine Bone Density Scans
A new study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research reveals that an automated machine learning program can predict the risk of cardiovascular events and falls or fractures by analyzing bone... Read more
AI Improves Early Detection of Interval Breast Cancers
Interval breast cancers, which occur between routine screenings, are easier to treat when detected earlier. Early detection can reduce the need for aggressive treatments and improve the chances of better outcomes.... Read more
World's Largest Class Single Crystal Diamond Radiation Detector Opens New Possibilities for Diagnostic Imaging
Diamonds possess ideal physical properties for radiation detection, such as exceptional thermal and chemical stability along with a quick response time. Made of carbon with an atomic number of six, diamonds... Read moreMRI
view channel
New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
Traditional exercise stress tests conducted within an MRI machine require patients to lie flat, a position that artificially improves heart function by increasing stroke volume due to gravity-driven blood... Read more
Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
Women with extremely dense breasts face a higher risk of missed breast cancer diagnoses, as dense glandular and fibrous tissue can obscure tumors on mammograms. While breast MRI is recommended for supplemental... Read moreUltrasound
view channel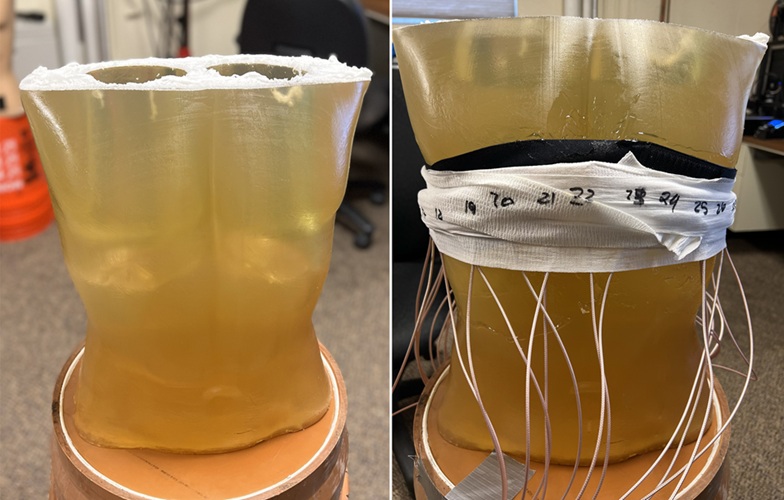
New Medical Ultrasound Imaging Technique Enables ICU Bedside Monitoring
Ultrasound computed tomography (USCT) presents a safer alternative to imaging techniques like X-ray computed tomography (commonly known as CT or “CAT” scans) because it does not produce ionizing radiation.... Read more
New Incision-Free Technique Halts Growth of Debilitating Brain Lesions
Cerebral cavernous malformations (CCMs), also known as cavernomas, are abnormal clusters of blood vessels that can grow in the brain, spinal cord, or other parts of the body. While most cases remain asymptomatic,... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related death among men in the United States. However, the majority of older men diagnosed with prostate cancer have slow-growing, low-risk forms of... Read more
Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
Interleukin-13 receptor α-2 (IL13Rα2) is a cell surface receptor commonly found in solid tumors such as glioblastoma, melanoma, and breast cancer. It is minimally expressed in normal tissues, making it... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more











.jpeg)




