Twice-Daily Radiation Therapy Reduces Cancer Mortality
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 10 Feb 2017 |
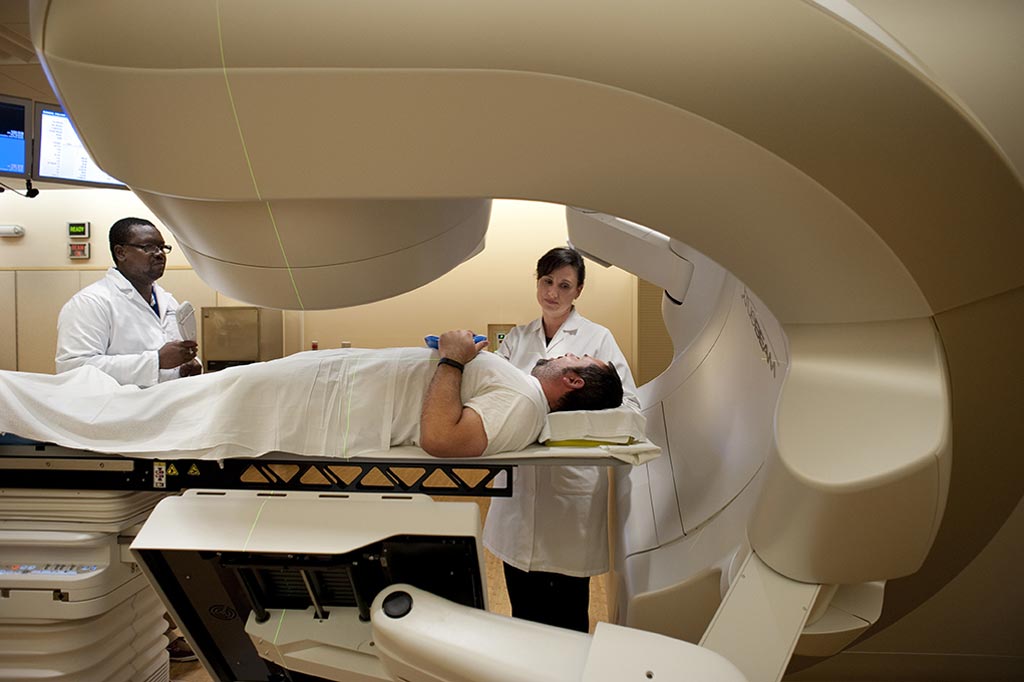
Image: A new study shows hyperfractionated radiotherapy with concomitant chemotherapy provides best results for some cancers (Photo courtesy of NCI).
Splitting daily radiation therapy (RT) treatment into two portions allows more effective treatment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, according to a new study.
Researchers at the Gustave Roussy cancer center, Aarhus University Hospital, and other institutions conducted a literature review based on a relatively new technique called network meta-analysis in order to bring together data from 117 different trials that included 28,804 patients from around the world. The data compilation allowed the researchers to compare 16 different treatment strategies in order to find out which was best at reducing cancer spread and mortality.
The results showed that hyper-fractionated RT, when combined with chemotherapy, cut mortality rates by 20% when compared to the current best standard of treatment, administration of daily RT combined with chemotherapy. In fact, hyperfractionated radiotherapy with concomitant chemotherapy was ranked as the best treatment in all analyses. Hyper-fractionated RT also reduced the risk of the cancer getting worse by 23%. The study was presented at the European Cancer Organization (ECCO) annual congress, held during January 2017 in Amsterdam (The Netherlands).
“There are a number of new treatments that have shown promise in head and neck cancer trials. This large study has enabled us to compare several of these treatments to see which is the best overall in terms of reducing mortality,” concluded lead author and study presenter radiation oncology resident Claire Petit, MD, of Gustave Roussy. “Some of the studies we looked at did not include data on side effects; others did not follow patients long enough to pick up long-term side effects. This will be the focus of more research over the next year.”
Most cancers of the head, mouth, nasal cavity, nasopharynx, throat, and associated structures histologically belong to the squamous cell type, and are the 6th most common cancers worldwide and 3rd most common cancers in developing world, accounting for about 5% of all malignancies worldwide. Risk factors include tobacco consumption (chewing or smoking), alcohol consumption, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection, human papilloma virus (HPV) infection, betel nut chewing, wood dust exposures, consumption of certain slated fish, and others.
Researchers at the Gustave Roussy cancer center, Aarhus University Hospital, and other institutions conducted a literature review based on a relatively new technique called network meta-analysis in order to bring together data from 117 different trials that included 28,804 patients from around the world. The data compilation allowed the researchers to compare 16 different treatment strategies in order to find out which was best at reducing cancer spread and mortality.
The results showed that hyper-fractionated RT, when combined with chemotherapy, cut mortality rates by 20% when compared to the current best standard of treatment, administration of daily RT combined with chemotherapy. In fact, hyperfractionated radiotherapy with concomitant chemotherapy was ranked as the best treatment in all analyses. Hyper-fractionated RT also reduced the risk of the cancer getting worse by 23%. The study was presented at the European Cancer Organization (ECCO) annual congress, held during January 2017 in Amsterdam (The Netherlands).
“There are a number of new treatments that have shown promise in head and neck cancer trials. This large study has enabled us to compare several of these treatments to see which is the best overall in terms of reducing mortality,” concluded lead author and study presenter radiation oncology resident Claire Petit, MD, of Gustave Roussy. “Some of the studies we looked at did not include data on side effects; others did not follow patients long enough to pick up long-term side effects. This will be the focus of more research over the next year.”
Most cancers of the head, mouth, nasal cavity, nasopharynx, throat, and associated structures histologically belong to the squamous cell type, and are the 6th most common cancers worldwide and 3rd most common cancers in developing world, accounting for about 5% of all malignancies worldwide. Risk factors include tobacco consumption (chewing or smoking), alcohol consumption, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection, human papilloma virus (HPV) infection, betel nut chewing, wood dust exposures, consumption of certain slated fish, and others.
Latest Nuclear Medicine News
- PET Imaging of Inflammation Predicts Recovery and Guides Therapy After Heart Attack
- Radiotheranostic Approach Detects, Kills and Reprograms Aggressive Cancers
- New Imaging Solution Improves Survival for Patients with Recurring Prostate Cancer
- PET Tracer Enables Same-Day Imaging of Triple-Negative Breast and Urothelial Cancers
- New Camera Sees Inside Human Body for Enhanced Scanning and Diagnosis
- Novel Bacteria-Specific PET Imaging Approach Detects Hard-To-Diagnose Lung Infections
- New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
- Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
- Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
- Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
- New Molecular Imaging Test to Improve Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- Novel PET Technique Visualizes Spinal Cord Injuries to Predict Recovery
- Next-Gen Tau Radiotracers Outperform FDA-Approved Imaging Agents in Detecting Alzheimer’s
- Breakthrough Method Detects Inflammation in Body Using PET Imaging
- Advanced Imaging Reveals Hidden Metastases in High-Risk Prostate Cancer Patients
Channels
Radiography
view channel
X-Ray Breakthrough Captures Three Image-Contrast Types in Single Shot
Detecting early-stage cancer or subtle changes deep inside tissues has long challenged conventional X-ray systems, which rely only on how structures absorb radiation. This limitation keeps many microstructural... Read more
AI Generates Future Knee X-Rays to Predict Osteoarthritis Progression Risk
Osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease affecting over 500 million people worldwide, is the leading cause of disability among older adults. Current diagnostic tools allow doctors to assess damage... Read moreMRI
view channel
Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
Vascular dysfunction in the spinal cord contributes to multiple neurological conditions, including traumatic injuries and degenerative cervical myelopathy, where reduced blood flow can lead to progressive... Read more
AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
A cardiac MRI can reveal critical information about the heart’s function and any abnormalities, but traditional scans take 30 to 90 minutes and often suffer from poor image quality due to patient movement.... Read more
AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is one of the most common inherited heart conditions and a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young individuals and athletes. While many patients live normal lives, some... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Wearable Ultrasound Imaging System to Enable Real-Time Disease Monitoring
Chronic conditions such as hypertension and heart failure require close monitoring, yet today’s ultrasound imaging is largely confined to hospitals and short, episodic scans. This reactive model limits... Read more
Ultrasound Technique Visualizes Deep Blood Vessels in 3D Without Contrast Agents
Producing clear 3D images of deep blood vessels has long been difficult without relying on contrast agents, CT scans, or MRI. Standard ultrasound typically provides only 2D cross-sections, limiting clinicians’... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
3D Scanning Approach Enables Ultra-Precise Brain Surgery
Precise navigation is critical in neurosurgery, yet even small alignment errors can affect outcomes when operating deep within the brain. A new 3D surface-scanning approach now provides a radiation-free... Read more
AI Tool Improves Medical Imaging Process by 90%
Accurately labeling different regions within medical scans, a process known as medical image segmentation, is critical for diagnosis, surgery planning, and research. Traditionally, this has been a manual... Read more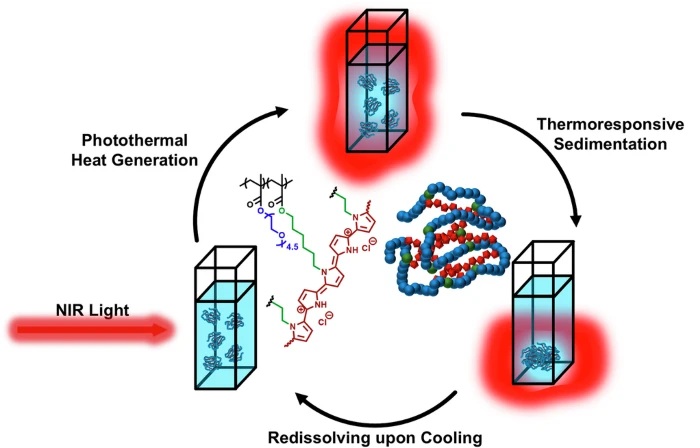
New Ultrasmall, Light-Sensitive Nanoparticles Could Serve as Contrast Agents
Medical imaging technologies face ongoing challenges in capturing accurate, detailed views of internal processes, especially in conditions like cancer, where tracking disease development and treatment... Read more
AI Algorithm Accurately Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis Using Routine CT Images
In pancreatic cancer, detecting whether the disease has spread to other organs is critical for determining whether surgery is appropriate. If metastasis is present, surgery is not recommended, yet current... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more




 Guided Devices.jpg)