New Study Reveals Link Between Biomarkers and Heart Disease in Male HIV Patients
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 10 Aug 2016 |
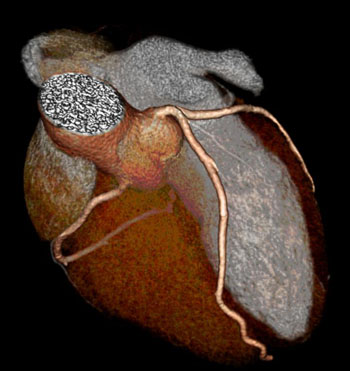
Image: Cardiac CT scans have revealed a link between higher inflammatory biomarkers and heart disease in male HIV Patients (Photo courtesy of the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study).
Results of a new Computed Tomography (CT) imaging study of male Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) patients show a link between an increased prevalence of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD), and higher inflammatory biomarkers.
The results of the study were published in the June 27, 2016, issue of the Journal of the American Heart Association (JAHA). The study included 925 men, including 575 men with HIV. The researchers used CT angiography imaging to look for signs of sub-clinical CAD, and for the presence of seven inflammatory biomarkers. CAD includes narrowed arteries, and various changes in the characteristics of plaque deposits.
The study was carried out by researchers at the Keck School of Medicine, University of California (UC; Los Angeles, CA, USA), Johns Hopkins University (Baltimore, MD, USA) and five additional institutions. CT imaging enabled researchers to detect subclinical CAD, before clinical symptoms became apparent and provided more inflammatory markers than in previous studies. The researchers are also using cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) to investigate coronary artery function, and changes in the heart muscle of HIV patients.
Research team leader Hossein Bahrami, MD, PhD, said, "We found that men infected with HIV had higher levels of inflammatory biomarkers than men who were not infected. There was a strong, independent association between the presence of these inflammatory biomarkers and subclinical CAD detected by CT scan. Although this study does not definitely prove the causal relationship between these markers and heart disease, it is suggestive of a possible role that persistent inflammation (even in HIV infected patients that are under appropriate treatments) may play in increasing the risk of heart disease in these patients. Inflammation has only recently been studied as a possible reason for chronic heart disease. Confirming the relationship between HIV-related inflammation and the marked increase of CAD among men infected with HIV allows us to move forward in our attempts to better manage the health of these patients according to their specific medical needs."
Related Links:
Keck School of Medicine, University of California
Johns Hopkins University
The results of the study were published in the June 27, 2016, issue of the Journal of the American Heart Association (JAHA). The study included 925 men, including 575 men with HIV. The researchers used CT angiography imaging to look for signs of sub-clinical CAD, and for the presence of seven inflammatory biomarkers. CAD includes narrowed arteries, and various changes in the characteristics of plaque deposits.
The study was carried out by researchers at the Keck School of Medicine, University of California (UC; Los Angeles, CA, USA), Johns Hopkins University (Baltimore, MD, USA) and five additional institutions. CT imaging enabled researchers to detect subclinical CAD, before clinical symptoms became apparent and provided more inflammatory markers than in previous studies. The researchers are also using cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) to investigate coronary artery function, and changes in the heart muscle of HIV patients.
Research team leader Hossein Bahrami, MD, PhD, said, "We found that men infected with HIV had higher levels of inflammatory biomarkers than men who were not infected. There was a strong, independent association between the presence of these inflammatory biomarkers and subclinical CAD detected by CT scan. Although this study does not definitely prove the causal relationship between these markers and heart disease, it is suggestive of a possible role that persistent inflammation (even in HIV infected patients that are under appropriate treatments) may play in increasing the risk of heart disease in these patients. Inflammation has only recently been studied as a possible reason for chronic heart disease. Confirming the relationship between HIV-related inflammation and the marked increase of CAD among men infected with HIV allows us to move forward in our attempts to better manage the health of these patients according to their specific medical needs."
Related Links:
Keck School of Medicine, University of California
Johns Hopkins University
Latest Imaging IT News
- New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI-Based Technology for Ultrasound Image Analysis Receives FDA Approval
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Digital Pathology Software Improves Workflow Efficiency
- Patient-Centric Portal Facilitates Direct Imaging Access
- New Workstation Supports Customer-Driven Imaging Workflow
Channels
Radiography
view channel
World's Largest Class Single Crystal Diamond Radiation Detector Opens New Possibilities for Diagnostic Imaging
Diamonds possess ideal physical properties for radiation detection, such as exceptional thermal and chemical stability along with a quick response time. Made of carbon with an atomic number of six, diamonds... Read more
AI-Powered Imaging Technique Shows Promise in Evaluating Patients for PCI
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), also known as coronary angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure where small metal tubes called stents are inserted into partially blocked coronary arteries... Read moreMRI
view channel
AI Tool Predicts Relapse of Pediatric Brain Cancer from Brain MRI Scans
Many pediatric gliomas are treatable with surgery alone, but relapses can be catastrophic. Predicting which patients are at risk for recurrence remains challenging, leading to frequent follow-ups with... Read more
AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a condition in which the immune system attacks the brain and spinal cord, leading to impairments in movement, sensation, and cognition. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) markers... Read more
Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
Approximately 360,000 individuals in the UK suffer from focal epilepsy, a condition in which seizures spread from one part of the brain. Around a third of these patients experience persistent seizures... Read moreUltrasound
view channel.jpeg)
AI-Powered Lung Ultrasound Outperforms Human Experts in Tuberculosis Diagnosis
Despite global declines in tuberculosis (TB) rates in previous years, the incidence of TB rose by 4.6% from 2020 to 2023. Early screening and rapid diagnosis are essential elements of the World Health... Read more
AI Identifies Heart Valve Disease from Common Imaging Test
Tricuspid regurgitation is a condition where the heart's tricuspid valve does not close completely during contraction, leading to backward blood flow, which can result in heart failure. A new artificial... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
Interleukin-13 receptor α-2 (IL13Rα2) is a cell surface receptor commonly found in solid tumors such as glioblastoma, melanoma, and breast cancer. It is minimally expressed in normal tissues, making it... Read more
Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
COX-2, an enzyme that plays a key role in brain inflammation, can be significantly upregulated by inflammatory stimuli and neuroexcitation. Researchers suggest that COX-2 density in the brain could serve... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
Given the need to detect lung cancer at earlier stages, there is an increasing need for a definitive diagnostic pathway for patients with suspicious pulmonary nodules. However, obtaining tissue samples... Read more
AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
Lung cancer remains one of the most challenging diseases, making early diagnosis vital for effective treatment. Fortunately, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing lung cancer... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more




















