Quantitative Ultrasound Helps Stage Fatty Liver
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 17 Feb 2016 |
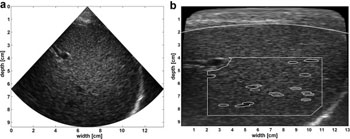
Image: Original B-Mode image next to back scan-converted B-mode image with interactively drawn fat layer contour (white dotted line); initial fixed region of interest (white rectangle); automatic segmentation within region of interest (white ellipses) (Photo courtesy of Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology).
A new study suggests that computer-aided ultrasound could be used to stage hepatic steatosis, with a high correlation to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) spectroscopy.
Researchers at Radboud University Medical Center (Nijmegen, the Netherlands) conducted a pilot study in 14 patients on long-term home parenteral nutrition using a phased array ultrasound transducer connected to a calibrated ultrasound machine, with the radio frequency (RF) data converted into conventional B-mode images with the aid of computer software. All patients were also subjected to proton MRI spectroscopy measurement of liver fat content for reference.
The results showed that computer-aided ultrasound parameters, similar to those in a previous validation study in cows, demonstrated significant correlation with fat content as measured by MRI spectroscopy, with the most significant parameters being residual attenuation coefficient and lateral speckle size. According to the researchers, the method shows promise as a noninvasive, easy, and inexpensive alternative to invasive biopsies or expensive MRI spectroscopy techniques. The study was published in the March 2016 issue of Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology.
“Patients on home parenteral nutrition are at risk for developing liver dysfunction, which is due partly to the accumulation of lipids in the liver and may progress to end-stage liver disease with overt liver failure,” said lead author Gert Weijers, PhD, of the Radboud Medical Ultrasound Imaging Centre (MUSIC). “Therefore, a timely diagnosis with easy access to repeated assessment of the degree of liver steatosis is of great importance.”
Steatosis in the liver, when it is not due to excessive alcohol use, is most often related to insulin resistance and to metabolic syndrome, and as a result may respond to treatments originally developed for other insulin-resistant states, such as diabetes mellitus type 2. Steatosis is also the most common liver disease of high-yielding dairy cattle during early lactation, making it a suitable animal model for studying liver fat accumulation.
Related Links:
Radboud University Medical Center
Researchers at Radboud University Medical Center (Nijmegen, the Netherlands) conducted a pilot study in 14 patients on long-term home parenteral nutrition using a phased array ultrasound transducer connected to a calibrated ultrasound machine, with the radio frequency (RF) data converted into conventional B-mode images with the aid of computer software. All patients were also subjected to proton MRI spectroscopy measurement of liver fat content for reference.
The results showed that computer-aided ultrasound parameters, similar to those in a previous validation study in cows, demonstrated significant correlation with fat content as measured by MRI spectroscopy, with the most significant parameters being residual attenuation coefficient and lateral speckle size. According to the researchers, the method shows promise as a noninvasive, easy, and inexpensive alternative to invasive biopsies or expensive MRI spectroscopy techniques. The study was published in the March 2016 issue of Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology.
“Patients on home parenteral nutrition are at risk for developing liver dysfunction, which is due partly to the accumulation of lipids in the liver and may progress to end-stage liver disease with overt liver failure,” said lead author Gert Weijers, PhD, of the Radboud Medical Ultrasound Imaging Centre (MUSIC). “Therefore, a timely diagnosis with easy access to repeated assessment of the degree of liver steatosis is of great importance.”
Steatosis in the liver, when it is not due to excessive alcohol use, is most often related to insulin resistance and to metabolic syndrome, and as a result may respond to treatments originally developed for other insulin-resistant states, such as diabetes mellitus type 2. Steatosis is also the most common liver disease of high-yielding dairy cattle during early lactation, making it a suitable animal model for studying liver fat accumulation.
Related Links:
Radboud University Medical Center
Latest Ultrasound News
- Reusable Gel Pad Made from Tamarind Seed Could Transform Ultrasound Examinations
- AI Model Accurately Detects Placenta Accreta in Pregnancy Before Delivery
- Portable Ultrasound Sensor to Enable Earlier Breast Cancer Detection
- Portable Imaging Scanner to Diagnose Lymphatic Disease in Real Time
- Imaging Technique Generates Simultaneous 3D Color Images of Soft-Tissue Structure and Vasculature
- Wearable Ultrasound Imaging System to Enable Real-Time Disease Monitoring
- Ultrasound Technique Visualizes Deep Blood Vessels in 3D Without Contrast Agents
- Ultrasound Probe Images Entire Organ in 4D

- Disposable Ultrasound Patch Performs Better Than Existing Devices
- Non-Invasive Ultrasound-Based Tool Accurately Detects Infant Meningitis
- Breakthrough Deep Learning Model Enhances Handheld 3D Medical Imaging
- Pain-Free Breast Imaging System Performs One Minute Cancer Scan
- Wireless Chronic Pain Management Device to Reduce Need for Painkillers and Surgery
- New Medical Ultrasound Imaging Technique Enables ICU Bedside Monitoring
- New Incision-Free Technique Halts Growth of Debilitating Brain Lesions
- AI-Powered Lung Ultrasound Outperforms Human Experts in Tuberculosis Diagnosis
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read more
AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
Chronological age does not always reflect how fast the body is truly aging, and current biological age tests often rely on DNA-based markers that may miss early organ-level decline. Detecting subtle, age-related... Read moreMRI
view channel
New Material Boosts MRI Image Quality
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a cornerstone of modern diagnostics, yet certain deep or anatomically complex tissues, including delicate structures of the eye and orbit, remain difficult to visualize clearly.... Read more
AI Model Reads and Diagnoses Brain MRI in Seconds
Brain MRI scans are critical for diagnosing strokes, hemorrhages, and other neurological disorders, but interpreting them can take hours or even days due to growing demand and limited specialist availability.... Read moreMRI Scan Breakthrough to Help Avoid Risky Invasive Tests for Heart Patients
Heart failure patients often require right heart catheterization to assess how severely their heart is struggling to pump blood, a procedure that involves inserting a tube into the heart to measure blood... Read more
MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
Recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies widely, with some patients regaining full function while others are left with lasting disabilities. Prognosis is especially difficult to assess in patients... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
Targeted cancer therapies only work when tumor cells express the specific molecular structures they are designed to attack. In urothelial carcinoma, a common form of bladder cancer, the cell surface protein... Read more
Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
Targeted cancer therapies can be highly effective, but only when a patient’s tumor expresses the specific protein the treatment is designed to attack. Determining this usually requires biopsies or advanced... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Tool Predicts Side Effects from Lung Cancer Treatment
Radiation therapy is a central treatment for lung cancer, but even carefully targeted radiation can affect surrounding healthy tissue. Patients may develop side effects such as lung inflammation, coughing,... Read more
AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer is a form of head and neck cancer that can spread through lymph nodes, significantly affecting survival and treatment decisions. Current therapies often involve combinations of surgery,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Nuclear Medicine Set for Continued Growth Driven by Demand for Precision Diagnostics
Clinical imaging services face rising demand for precise molecular diagnostics and targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy as cancer and chronic disease rates climb. A new market analysis projects rapid expansion... Read more





















