3D Printing and CT Imaging Used to Guide Human Face Transplants
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 17 Dec 2014 |
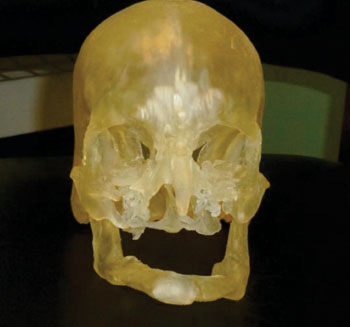
Image: This shows a 3D print model used in surgical planning (Photo courtyes of RSNA).
Surgeons are using computed tomography (CT) imaging and three-dimensional (3-D) printing technology to reconstruct life-size models of patients’ heads to help better control the outcome in face transplantation surgery.
The study’s findings were presented at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), held in Chicago, IL, USA; November 30 to December 5, 2014. Physicians from Brigham and Women’s Hospital (Boston, MA, USA) performed the first US full-face transplantation in 2011 and have subsequently completed four additional face transplants. The procedure is performed on patients who have lost some or all of their face as a result of disease or injury.
In the study, researchers led by Frank J. Rybicki, MD, radiologist and director of the hospital’s Applied Imaging Science Laboratory, Bohdan Pomahac, MD, lead face transplantation surgeon, and Amir Imanzadeh, MD, research fellow, assessed the clinical impact of using 3-D printed models of the recipient’s head in the planning of face transplantation surgery. “This is a complex surgery and its success is dependent on surgical planning,” Dr. Rybicki said. “Our study demonstrated that if you use this model and hold the skull in your hand, there is no better way to plan the procedure.”
Each of the transplant patients underwent preoperative CT scanning with 3-D visualization. To build each life-size skull model, the CT images of the transplant recipient’s head were segmented and processed using specialized software, creating customized data files that were input into a 3-D printer. “In some patients, we need to modify the recipient’s facial bones prior to transplantation,” Dr. Imanzadeh said. “The 3-D printed model helps us to prepare the facial structures so when the actual transplantation occurs, the surgery goes more smoothly.”
Although the entire transplant procedure lasts as long as 25 hours, the actual vascular connections from the donor face to the recipient typically takes approximately one hour, during which time the patient’s blood flow must be stopped. “If there are absent or missing bony structures needed for reconstruction, we can make modifications based on the 3-D printed model prior to the actual transplantation, instead of taking the time to do alterations during ischemia time,” Dr. Rybicki said. “The 3-D model is important for making the transplant cosmetically appealing.”
Moreover, the researchers reported they employed the models in the operating room to optimize the surgeons’ understanding of the anatomy of the recipient’s face during the procedure. “You can spin, rotate and scroll through as many CT images as you want but there’s no substitute for having the real thing in your hand,” Dr. Rybicki said. “The ability to work with the model gives you an unprecedented level of reassurance and confidence in the procedure.”
Senior surgeons and radiologists involved in the five face transplantations agreed that the 3-D printed models provided superior preoperative data and allowed complex anatomy and bony defects to be better appreciated, reducing total procedure time. “Less time spent in the operating room is better for overall patient outcomes,” Dr. Pomahac added.
Based on the results of this study, 3-D printing is now regularly used for surgical planning for face transplantation procedures at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and 3-D printed models may be implemented in other complicated surgeries.
Related Links:
Brigham and Women’s Hospital
The study’s findings were presented at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA), held in Chicago, IL, USA; November 30 to December 5, 2014. Physicians from Brigham and Women’s Hospital (Boston, MA, USA) performed the first US full-face transplantation in 2011 and have subsequently completed four additional face transplants. The procedure is performed on patients who have lost some or all of their face as a result of disease or injury.
In the study, researchers led by Frank J. Rybicki, MD, radiologist and director of the hospital’s Applied Imaging Science Laboratory, Bohdan Pomahac, MD, lead face transplantation surgeon, and Amir Imanzadeh, MD, research fellow, assessed the clinical impact of using 3-D printed models of the recipient’s head in the planning of face transplantation surgery. “This is a complex surgery and its success is dependent on surgical planning,” Dr. Rybicki said. “Our study demonstrated that if you use this model and hold the skull in your hand, there is no better way to plan the procedure.”
Each of the transplant patients underwent preoperative CT scanning with 3-D visualization. To build each life-size skull model, the CT images of the transplant recipient’s head were segmented and processed using specialized software, creating customized data files that were input into a 3-D printer. “In some patients, we need to modify the recipient’s facial bones prior to transplantation,” Dr. Imanzadeh said. “The 3-D printed model helps us to prepare the facial structures so when the actual transplantation occurs, the surgery goes more smoothly.”
Although the entire transplant procedure lasts as long as 25 hours, the actual vascular connections from the donor face to the recipient typically takes approximately one hour, during which time the patient’s blood flow must be stopped. “If there are absent or missing bony structures needed for reconstruction, we can make modifications based on the 3-D printed model prior to the actual transplantation, instead of taking the time to do alterations during ischemia time,” Dr. Rybicki said. “The 3-D model is important for making the transplant cosmetically appealing.”
Moreover, the researchers reported they employed the models in the operating room to optimize the surgeons’ understanding of the anatomy of the recipient’s face during the procedure. “You can spin, rotate and scroll through as many CT images as you want but there’s no substitute for having the real thing in your hand,” Dr. Rybicki said. “The ability to work with the model gives you an unprecedented level of reassurance and confidence in the procedure.”
Senior surgeons and radiologists involved in the five face transplantations agreed that the 3-D printed models provided superior preoperative data and allowed complex anatomy and bony defects to be better appreciated, reducing total procedure time. “Less time spent in the operating room is better for overall patient outcomes,” Dr. Pomahac added.
Based on the results of this study, 3-D printing is now regularly used for surgical planning for face transplantation procedures at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, and 3-D printed models may be implemented in other complicated surgeries.
Related Links:
Brigham and Women’s Hospital
Latest Radiography News
- Machine Learning Algorithm Identifies Cardiovascular Risk from Routine Bone Density Scans
- AI Improves Early Detection of Interval Breast Cancers
- World's Largest Class Single Crystal Diamond Radiation Detector Opens New Possibilities for Diagnostic Imaging
- AI-Powered Imaging Technique Shows Promise in Evaluating Patients for PCI
- Higher Chest X-Ray Usage Catches Lung Cancer Earlier and Improves Survival
- AI-Powered Mammograms Predict Cardiovascular Risk
- Generative AI Model Significantly Reduces Chest X-Ray Reading Time
- AI-Powered Mammography Screening Boosts Cancer Detection in Single-Reader Settings
- Photon Counting Detectors Promise Fast Color X-Ray Images
- AI Can Flag Mammograms for Supplemental MRI
- 3D CT Imaging from Single X-Ray Projection Reduces Radiation Exposure
- AI Method Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Risk by Analyzing Multiple Mammograms
- Printable Organic X-Ray Sensors Could Transform Treatment for Cancer Patients
- Highly Sensitive, Foldable Detector to Make X-Rays Safer
- Novel Breast Cancer Screening Technology Could Offer Superior Alternative to Mammogram
- Artificial Intelligence Accurately Predicts Breast Cancer Years Before Diagnosis
Channels
MRI
view channel
New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
Traditional exercise stress tests conducted within an MRI machine require patients to lie flat, a position that artificially improves heart function by increasing stroke volume due to gravity-driven blood... Read more
Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
Women with extremely dense breasts face a higher risk of missed breast cancer diagnoses, as dense glandular and fibrous tissue can obscure tumors on mammograms. While breast MRI is recommended for supplemental... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
New Incision-Free Technique Halts Growth of Debilitating Brain Lesions
Cerebral cavernous malformations (CCMs), also known as cavernomas, are abnormal clusters of blood vessels that can grow in the brain, spinal cord, or other parts of the body. While most cases remain asymptomatic,... Read more.jpeg)
AI-Powered Lung Ultrasound Outperforms Human Experts in Tuberculosis Diagnosis
Despite global declines in tuberculosis (TB) rates in previous years, the incidence of TB rose by 4.6% from 2020 to 2023. Early screening and rapid diagnosis are essential elements of the World Health... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related death among men in the United States. However, the majority of older men diagnosed with prostate cancer have slow-growing, low-risk forms of... Read more
Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
Interleukin-13 receptor α-2 (IL13Rα2) is a cell surface receptor commonly found in solid tumors such as glioblastoma, melanoma, and breast cancer. It is minimally expressed in normal tissues, making it... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
Currently, patients with conditions such as heart failure, pneumonia, or respiratory distress often require multiple imaging procedures that are intermittent, disruptive, and involve high levels of radiation.... Read more
AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
Radioligand therapy, a form of targeted nuclear medicine, has recently gained attention for its potential in treating specific types of tumors. However, one of the potential side effects of this therapy... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more