CT Workstation Software Decreases Image Reading Time
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 22 May 2012 |
Recent research has demonstrated that new imaging software can help save time without loss of accuracy.
Siemens Healthcare (Erlangen, Germany) conducted a study with six customers in Germany, Austria, and Spain to measure quantitatively and qualitatively the efficiency of the software syngo.via compared to a traditional advanced visualization workstation. The study’s findings revealed that syngo.via could substantially help to save time when reading medical images, without compromising accuracy.
Siemens Healthcare announced in its global initiative Agenda 2013 to drive the development of efficiency increasing healthcare information technology (IT) solutions.
For a clinical institution to be successful, it is critical to obtain the highest possible diagnostic accuracy while maintaining a fast and efficient workflow. The three-dimensional (3D) reading and sophisticated visualization software syngo.via enables clinicians to meet the respective requirements by automatically loading for example computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance (MR) images into the appropriate application and sorting them into the disease-specific corresponding layout. Manual work steps are eliminated and the clinician can begin diagnosing immediately.
Six medical sites participated in the efficiency study, which took account of a total number of seven different clinical workflows. To replicate their clinical routine, each participating site determined the case mix and measured 10 to 20 cases per workflow. For example, the observed average timesavings from syngo.via for CT Cardiac amounted to 77% and for an oncology diagnosis with positron emission tomography (PET)/CT to 45%. Utilizing syngo.via when diagnosing oncology and neurology MR examinations resulted in 32% and 23% average timesavings, respectively. Analysis of images for CT vascular applications was 27% and image assessment for PET/CT and CT oncology follow-up 30% and 16% faster compared to a conventional advanced visualization or picture archiving and communication system (PACS) workstation.
Furthermore, Siemens conducted a usability survey among the study participants. They stated that syngo.via is performing better regarding the aspects data preparation, usability of viewing and measurement tools and documentation and reporting than the former software. “syngo.via is an excellent tool to increase the productivity of radiologists working on cardiac images,” said Prof. Gudrun Feuchtner, from Innsbruck University Hospital (Austria).
Related Links:
Siemens Healthcare
Siemens Healthcare (Erlangen, Germany) conducted a study with six customers in Germany, Austria, and Spain to measure quantitatively and qualitatively the efficiency of the software syngo.via compared to a traditional advanced visualization workstation. The study’s findings revealed that syngo.via could substantially help to save time when reading medical images, without compromising accuracy.
Siemens Healthcare announced in its global initiative Agenda 2013 to drive the development of efficiency increasing healthcare information technology (IT) solutions.
For a clinical institution to be successful, it is critical to obtain the highest possible diagnostic accuracy while maintaining a fast and efficient workflow. The three-dimensional (3D) reading and sophisticated visualization software syngo.via enables clinicians to meet the respective requirements by automatically loading for example computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance (MR) images into the appropriate application and sorting them into the disease-specific corresponding layout. Manual work steps are eliminated and the clinician can begin diagnosing immediately.
Six medical sites participated in the efficiency study, which took account of a total number of seven different clinical workflows. To replicate their clinical routine, each participating site determined the case mix and measured 10 to 20 cases per workflow. For example, the observed average timesavings from syngo.via for CT Cardiac amounted to 77% and for an oncology diagnosis with positron emission tomography (PET)/CT to 45%. Utilizing syngo.via when diagnosing oncology and neurology MR examinations resulted in 32% and 23% average timesavings, respectively. Analysis of images for CT vascular applications was 27% and image assessment for PET/CT and CT oncology follow-up 30% and 16% faster compared to a conventional advanced visualization or picture archiving and communication system (PACS) workstation.
Furthermore, Siemens conducted a usability survey among the study participants. They stated that syngo.via is performing better regarding the aspects data preparation, usability of viewing and measurement tools and documentation and reporting than the former software. “syngo.via is an excellent tool to increase the productivity of radiologists working on cardiac images,” said Prof. Gudrun Feuchtner, from Innsbruck University Hospital (Austria).
Related Links:
Siemens Healthcare
Latest Imaging IT News
- New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI-Based Technology for Ultrasound Image Analysis Receives FDA Approval
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Digital Pathology Software Improves Workflow Efficiency
- Patient-Centric Portal Facilitates Direct Imaging Access
- New Workstation Supports Customer-Driven Imaging Workflow
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI Radiology Tool Identifies Life-Threatening Conditions in Milliseconds
Radiology is emerging as one of healthcare’s most pressing bottlenecks. By 2033, the U.S. could face a shortage of up to 42,000 radiologists, even as imaging volumes grow by 5% annually.... Read more
Machine Learning Algorithm Identifies Cardiovascular Risk from Routine Bone Density Scans
A new study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research reveals that an automated machine learning program can predict the risk of cardiovascular events and falls or fractures by analyzing bone... Read more
AI Improves Early Detection of Interval Breast Cancers
Interval breast cancers, which occur between routine screenings, are easier to treat when detected earlier. Early detection can reduce the need for aggressive treatments and improve the chances of better outcomes.... Read more
World's Largest Class Single Crystal Diamond Radiation Detector Opens New Possibilities for Diagnostic Imaging
Diamonds possess ideal physical properties for radiation detection, such as exceptional thermal and chemical stability along with a quick response time. Made of carbon with an atomic number of six, diamonds... Read moreMRI
view channel
New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
Traditional exercise stress tests conducted within an MRI machine require patients to lie flat, a position that artificially improves heart function by increasing stroke volume due to gravity-driven blood... Read more
Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
Women with extremely dense breasts face a higher risk of missed breast cancer diagnoses, as dense glandular and fibrous tissue can obscure tumors on mammograms. While breast MRI is recommended for supplemental... Read moreUltrasound
view channel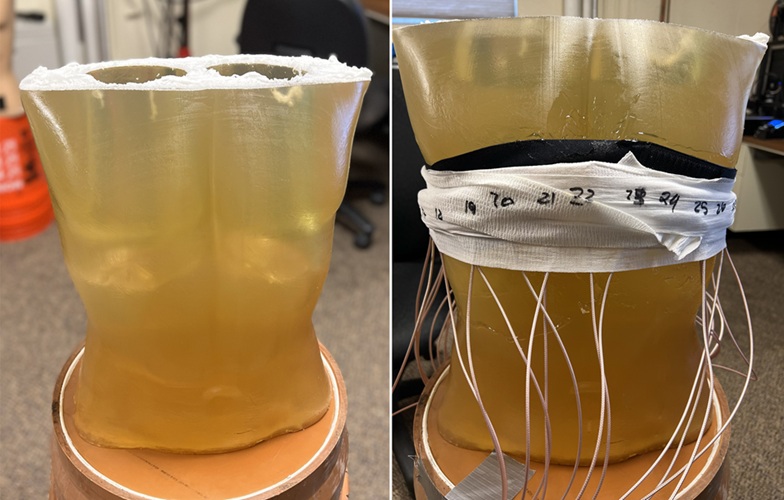
New Medical Ultrasound Imaging Technique Enables ICU Bedside Monitoring
Ultrasound computed tomography (USCT) presents a safer alternative to imaging techniques like X-ray computed tomography (commonly known as CT or “CAT” scans) because it does not produce ionizing radiation.... Read more
New Incision-Free Technique Halts Growth of Debilitating Brain Lesions
Cerebral cavernous malformations (CCMs), also known as cavernomas, are abnormal clusters of blood vessels that can grow in the brain, spinal cord, or other parts of the body. While most cases remain asymptomatic,... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related death among men in the United States. However, the majority of older men diagnosed with prostate cancer have slow-growing, low-risk forms of... Read more
Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
Interleukin-13 receptor α-2 (IL13Rα2) is a cell surface receptor commonly found in solid tumors such as glioblastoma, melanoma, and breast cancer. It is minimally expressed in normal tissues, making it... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel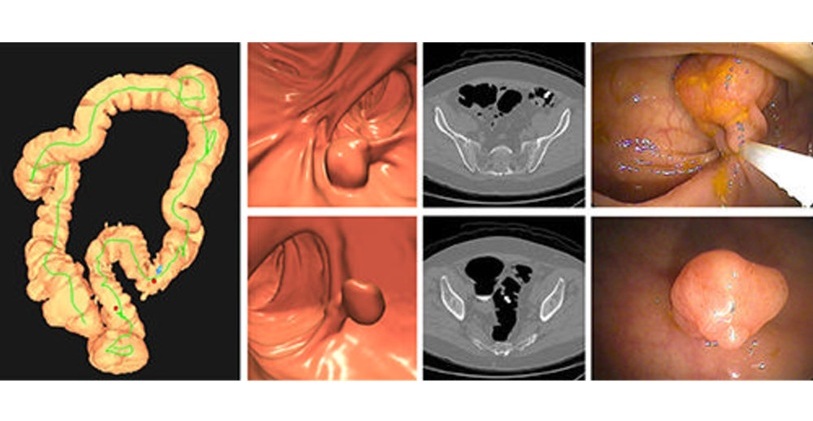
CT Colonography Beats Stool DNA Testing for Colon Cancer Screening
As colorectal cancer remains the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, early detection through screening is vital to reduce advanced-stage treatments and associated costs.... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
Currently, patients with conditions such as heart failure, pneumonia, or respiratory distress often require multiple imaging procedures that are intermittent, disruptive, and involve high levels of radiation.... Read more
AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
Radioligand therapy, a form of targeted nuclear medicine, has recently gained attention for its potential in treating specific types of tumors. However, one of the potential side effects of this therapy... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more












.jpeg)



