New Focused Ultrasound Treatment Proves Effective for Parkinson’s Disease Patients
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 17 Mar 2023 |

Parkinson's disease is a neurological condition characterized by the loss of dopamine neurons within the brain. While medications such as levodopa can be effective in managing this condition, some patients may experience dyskinesia and motor impairment. Dyskinesia, an involuntary movement of the body's various parts, may occur with long-term use of levodopa. Meanwhile, motor impairment entails the return of debilitating Parkinsonian symptoms once the medication loses its effectiveness. In a latest study, researchers have demonstrated that a novel focused ultrasound treatment can be beneficial in reducing dyskinesia and improving motor impairment in patients with Parkinson's disease. Patients undergoing focused ultrasound therapy can return home the same day post-surgery.
In 2016, the FDA had approved the use of focused ultrasound therapy to treat essential tremors. The research team at the UNC School of Medicine (Chapel Hill, NC, USA) conducted a pivotal trial that resulted in the FDA approving the use of focused ultrasound ablation to manage dyskinesia and motor impairment in Parkinson's disease. The trial involved 94 Parkinson's patients with either dyskinesias or motor impairment who were randomly selected to receive focused ultrasound ablation or a "sham" procedure. The main objective was to evaluate therapy response after three months, defined as a three-point decrease in the score from baseline either on the Movement Disorders Society-Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale, part III (off medication state), or in the score on the Unified Dyskinesia Rating Scale (on medication state). Secondary outcomes included changes from baseline to month three in the scores on various parts of the Movement Disorders Society–Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale.
In the trial, the researchers administered ultrasound ablation to 69 patients and the sham (control) procedure to 25 patients. In the focused ultrasound group, 65 patients completed the primary-outcome assessment, while 22 in the control group completed the study. In the focused ultrasound group, 45 patients (69%) had a response, as compared with seven (32%) in the control group. The adverse effects related to ablation of the globus pallidus were infrequent and included speech difficulty, visual disturbance, and gait difficulty – in one patient each. There was one serious adverse event documented one week after the treatment in one patient.
“Focused ultrasound is an exciting new treatment for patients with certain neurological disorders,” said Dr. Vibhor Krishna, associate professor of neurosurgery at the UNC School of Medicine, who is the study co-author. “The procedure is incisionless, eliminating the risks associated with surgery. Using focused ultrasound, we can target a specific area of the brain and safely ablate the diseased tissue.”
Related Links:
UNC School of Medicine
Latest Ultrasound News
- Groundbreaking Technology Enables Precise, Automatic Measurement of Peripheral Blood Vessels
- Deep Learning Advances Super-Resolution Ultrasound Imaging
- Novel Ultrasound-Launched Targeted Nanoparticle Eliminates Biofilm and Bacterial Infection
- AI-Guided Ultrasound System Enables Rapid Assessments of DVT
- Focused Ultrasound Technique Gets Quality Assurance Protocol
- AI-Guided Handheld Ultrasound System Helps Capture Diagnostic-Quality Cardiac Images
- Non-Invasive Ultrasound Imaging Device Diagnoses Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease
- Wearable Ultrasound Platform Paves Way for 24/7 Blood Pressure Monitoring On the Wrist
- Diagnostic Ultrasound Enhancing Agent to Improve Image Quality in Pediatric Heart Patients
- AI Detects COVID-19 in Lung Ultrasound Images
- New Ultrasound Technology to Revolutionize Respiratory Disease Diagnoses
- Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Highly Useful For Interventions
- Ultrasensitive Broadband Transparent Ultrasound Transducer Enhances Medical Diagnosis
- Artificial Intelligence Detects Heart Defects in Newborns from Ultrasound Images
- Ultrasound Imaging Technology Allows Doctors to Watch Spinal Cord Activity during Surgery

- Shape-Shifting Ultrasound Stickers Detect Post-Surgical Complications
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Novel Breast Imaging System Proves As Effective As Mammography
Breast cancer remains the most frequently diagnosed cancer among women. It is projected that one in eight women will be diagnosed with breast cancer during her lifetime, and one in 42 women who turn 50... Read more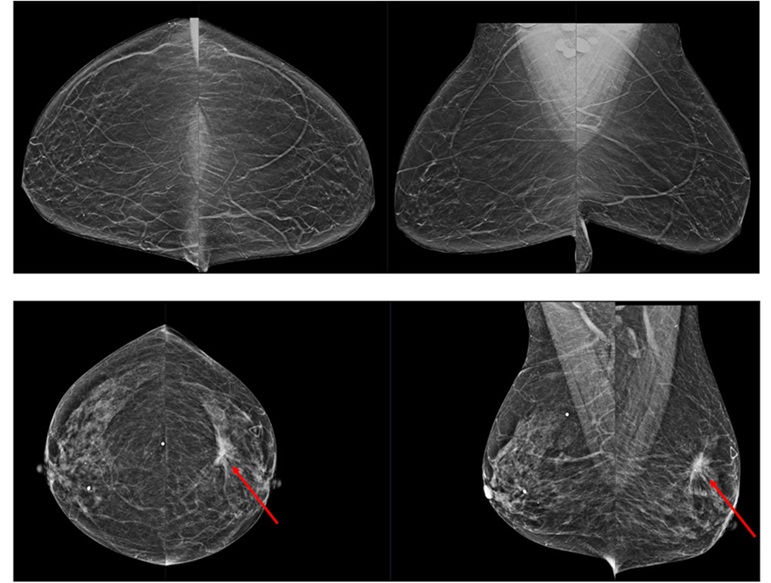
AI Assistance Improves Breast-Cancer Screening by Reducing False Positives
Radiologists typically detect one case of cancer for every 200 mammograms reviewed. However, these evaluations often result in false positives, leading to unnecessary patient recalls for additional testing,... Read moreMRI
view channel
Diamond Dust Could Offer New Contrast Agent Option for Future MRI Scans
Gadolinium, a heavy metal used for over three decades as a contrast agent in medical imaging, enhances the clarity of MRI scans by highlighting affected areas. Despite its utility, gadolinium not only... Read more.jpg)
Combining MRI with PSA Testing Improves Clinical Outcomes for Prostate Cancer Patients
Prostate cancer is a leading health concern globally, consistently being one of the most common types of cancer among men and a major cause of cancer-related deaths. In the United States, it is the most... Read more
PET/MRI Improves Diagnostic Accuracy for Prostate Cancer Patients
The Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) is a five-point scale to assess potential prostate cancer in MR images. PI-RADS category 3 which offers an unclear suggestion of clinically significant... Read more
Next Generation MR-Guided Focused Ultrasound Ushers In Future of Incisionless Neurosurgery
Essential tremor, often called familial, idiopathic, or benign tremor, leads to uncontrollable shaking that significantly affects a person’s life. When traditional medications do not alleviate symptoms,... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel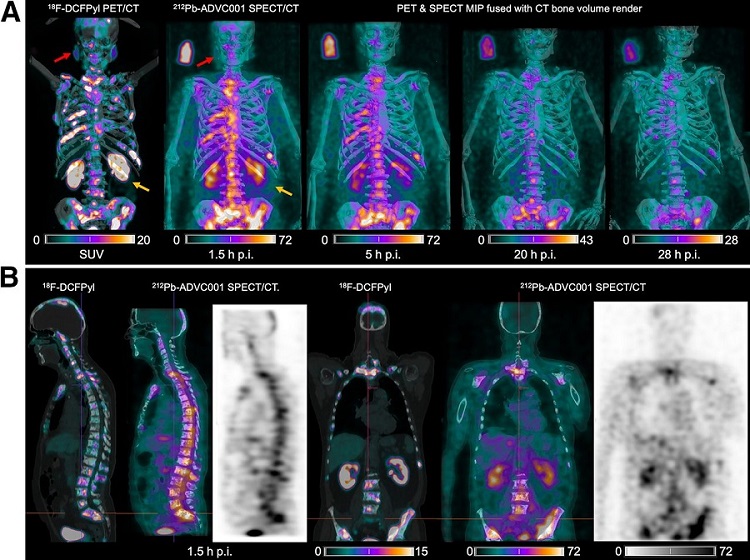
New SPECT/CT Technique Could Change Imaging Practices and Increase Patient Access
The development of lead-212 (212Pb)-PSMA–based targeted alpha therapy (TAT) is garnering significant interest in treating patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. The imaging of 212Pb,... Read moreNew Radiotheranostic System Detects and Treats Ovarian Cancer Noninvasively
Ovarian cancer is the most lethal gynecological cancer, with less than a 30% five-year survival rate for those diagnosed in late stages. Despite surgery and platinum-based chemotherapy being the standard... Read more
AI System Automatically and Reliably Detects Cardiac Amyloidosis Using Scintigraphy Imaging
Cardiac amyloidosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of abnormal protein deposits (amyloids) in the heart muscle, severely affects heart function and can lead to heart failure or death without... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
PET Scans Reveal Hidden Inflammation in Multiple Sclerosis Patients
A key challenge for clinicians treating patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) is that after a certain amount of time, they continue to worsen even though their MRIs show no change. A new study has now... Read more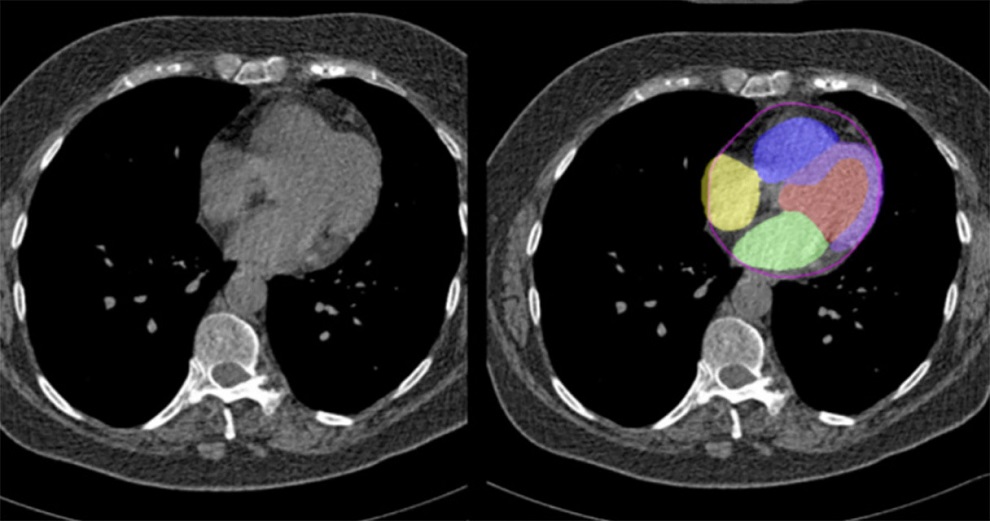
Artificial Intelligence Evaluates Cardiovascular Risk from CT Scans
Chest computed tomography (CT) is a common diagnostic tool, with approximately 15 million scans conducted each year in the United States, though many are underutilized or not fully explored.... Read more
New AI Method Captures Uncertainty in Medical Images
In the field of biomedicine, segmentation is the process of annotating pixels from an important structure in medical images, such as organs or cells. Artificial Intelligence (AI) models are utilized to... Read more.jpg)
CT Coronary Angiography Reduces Need for Invasive Tests to Diagnose Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), one of the leading causes of death worldwide, involves the narrowing of coronary arteries due to atherosclerosis, resulting in insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle.... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Bayer and Google Partner on New AI Product for Radiologists
Medical imaging data comprises around 90% of all healthcare data, and it is a highly complex and rich clinical data modality and serves as a vital tool for diagnosing patients. Each year, billions of medical... Read more