Ultrasound Imaging Technology Allows Doctors to Watch Spinal Cord Activity during Surgery
Posted on 11 Mar 2024
Back pain treatments during surgery have historically been difficult to evaluate effectively, largely because patients under anesthesia cannot communicate their pain levels. Furthermore, imaging the spinal cord – a crucial part of back pain treatment assessment – presents its own challenges. The spinal cord, referred to as an "unfriendly area" for traditional imaging, is subject to significant motion artifacts caused by heart pulsation and breathing, which introduce unwanted noise into the signal. These factors make the spinal cord a challenging target for standard neuroimaging techniques. Now, for the first time, an ultrasound imaging technology enables the generation of high-resolution images of the human spinal cord during surgery, marking a significant advancement that could provide relief for millions suffering from chronic back pain.
The technology, known as fUSI or functional ultrasound imaging, has been developed by scientists at UC Riverside (Riverside, CA, USA) and enables clinicians to observe the spinal cord and map its response to various treatments in real-time. Notably, the fUSI scanner is mobile and does not require the extensive infrastructure typically associated with classical neuroimaging methods like functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). Additionally, fUSI has a reduced sensitivity to motion artifacts compared to other imaging techniques. It works by emitting sound waves into the targeted area, and the red blood cells in that region echo the sound back, producing a detailed image.
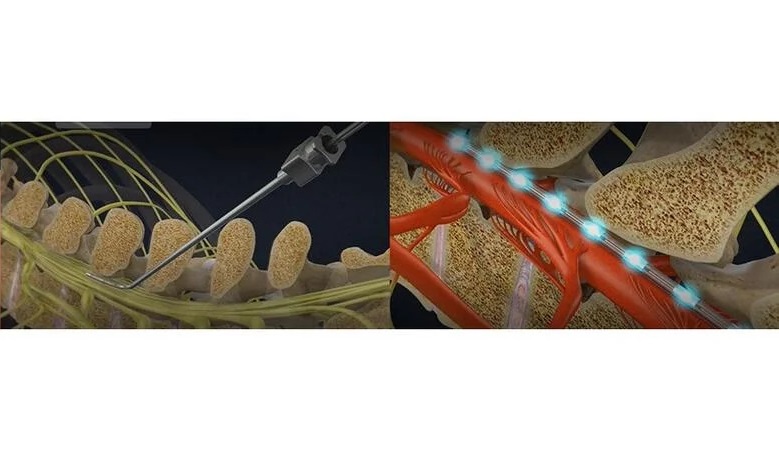
The application of fUSI was tested on six patients suffering from chronic low back pain, all of whom were scheduled for last-resort pain surgery, as no other treatments, including medication, had provided relief. In these procedures, clinicians stimulated the spinal cord with electrodes, hoping that the electrical stimulation would lessen the patients’ pain and enhance their quality of life. The results revealed that fUSI could detect changes in blood flow at unprecedentedly low speeds, less than one millimeter per second, marking a significant improvement over the two-centimeter-per-second detection capability of fMRI. This level of sensitivity suggests that the success rate of such surgeries, currently around 50%, could be significantly improved with the use of fUSI. Going forward, the researchers also plan to demonstrate fUSI's potential in optimizing treatments for individuals who have lost bladder control due to spinal cord injuries or aging.
“With less risk of damage than older methods, fUSI will enable more effective pain treatments that are optimized for individual patients,” said Vasileios Christopoulos, assistant professor of bioengineering at UC Riverside, who is pioneering the use of fUSI for spinal cord imaging. “It is a very exciting development.”
Related Links:
UC Riverside










 Guided Devices.jpg)



