Novel Cannula Delivery System Enables Targeted Delivery of Imaging Agents and Drugs
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 17 Apr 2025 |
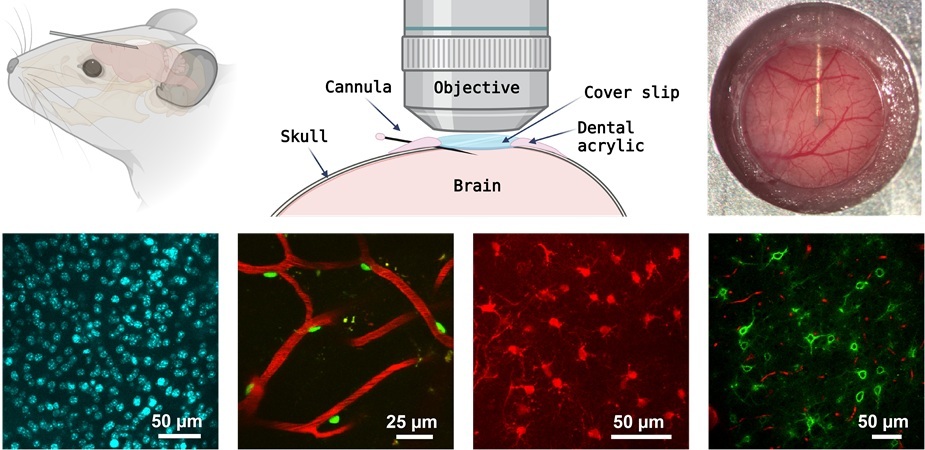
Multiphoton microscopy has become an invaluable tool in neuroscience, allowing researchers to observe brain activity in real time with high-resolution imaging. A crucial aspect of many multiphoton microscopy studies is the effective delivery of chemical compounds, including imaging agents and drugs, to the brain. However, many of these compounds face a significant obstacle—the blood-brain barrier—which prevents them from being delivered through systemic administration. To overcome this challenge, a research team has developed an innovative cannula delivery system that enables the precise administration of compounds during extended live (in vivo) imaging via multiphoton microscopy. The system features a low-profile micropipette, or "cannula," implanted at a shallow angle of just 8 degrees, almost parallel to the brain's surface. This setup ensures that imaging agents can be delivered directly to the brain without interfering with the optical path needed for high-resolution imaging.
A significant challenge in optical imaging studies is that many fluorescent sensors and reporters used to study biological processes are not genetically encoded. These imaging agents often require direct infusion into the brain, which typically limits the ability to conduct longitudinal imaging studies. Researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (Boston, MA, USA) have now introduced a shallow-angle, chronically implanted cannula for the delivery of imaging agents to the brain during long-term in vivo imaging sessions. To validate the efficacy of their cannula delivery system, the research team conducted a series of experiments. They successfully administered fluorescent cell markers into the brain while simultaneously imaging them using multiphoton microscopy.
Additionally, in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease, the team used a special dye, Fluoro-Jade C, to track degenerating neurons, and they also performed long-term imaging of brain tissue oxygen levels using a phosphorescent oxygen sensor. This technique marks a significant advancement for mouse cranial imaging windows, enhancing both dye delivery and the quality of imaging data. While this method is not entirely noninvasive, it presents a promising development for conducting longitudinal studies on brain function, disease progression, and potential treatments. The method offers researchers more accurate and reliable tools for a wide range of brain imaging applications. To facilitate broader adoption of this technology, the team has provided comprehensive guidance on the construction and implantation of the cannula in their study published in Neurophotonics.
Latest Nuclear Medicine News
- Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
- Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
- Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
- New Molecular Imaging Test to Improve Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- Novel PET Technique Visualizes Spinal Cord Injuries to Predict Recovery
- Next-Gen Tau Radiotracers Outperform FDA-Approved Imaging Agents in Detecting Alzheimer’s
- Breakthrough Method Detects Inflammation in Body Using PET Imaging
- Advanced Imaging Reveals Hidden Metastases in High-Risk Prostate Cancer Patients
- Combining Advanced Imaging Technologies Offers Breakthrough in Glioblastoma Treatment
- New Molecular Imaging Agent Accurately Identifies Crucial Cancer Biomarker
- New Scans Light Up Aggressive Tumors for Better Treatment
- AI Stroke Brain Scan Readings Twice as Accurate as Current Method
- AI Analysis of PET/CT Images Predicts Side Effects of Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer
- New Imaging Agent to Drive Step-Change for Brain Cancer Imaging
- Portable PET Scanner to Detect Earliest Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Machine Learning Algorithm Identifies Cardiovascular Risk from Routine Bone Density Scans
A new study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research reveals that an automated machine learning program can predict the risk of cardiovascular events and falls or fractures by analyzing bone... Read more
AI Improves Early Detection of Interval Breast Cancers
Interval breast cancers, which occur between routine screenings, are easier to treat when detected earlier. Early detection can reduce the need for aggressive treatments and improve the chances of better outcomes.... Read more
World's Largest Class Single Crystal Diamond Radiation Detector Opens New Possibilities for Diagnostic Imaging
Diamonds possess ideal physical properties for radiation detection, such as exceptional thermal and chemical stability along with a quick response time. Made of carbon with an atomic number of six, diamonds... Read moreMRI
view channel
Simple Brain Scan Diagnoses Parkinson's Disease Years Before It Becomes Untreatable
Parkinson's disease (PD) remains a challenging condition to treat, with no known cure. Though therapies have improved over time, and ongoing research focuses on methods to slow or alter the disease’s progression,... Read more
Cutting-Edge MRI Technology to Revolutionize Diagnosis of Common Heart Problem
Aortic stenosis is a common and potentially life-threatening heart condition. It occurs when the aortic valve, which regulates blood flow from the heart to the rest of the body, becomes stiff and narrow.... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
New Incision-Free Technique Halts Growth of Debilitating Brain Lesions
Cerebral cavernous malformations (CCMs), also known as cavernomas, are abnormal clusters of blood vessels that can grow in the brain, spinal cord, or other parts of the body. While most cases remain asymptomatic,... Read more.jpeg)
AI-Powered Lung Ultrasound Outperforms Human Experts in Tuberculosis Diagnosis
Despite global declines in tuberculosis (TB) rates in previous years, the incidence of TB rose by 4.6% from 2020 to 2023. Early screening and rapid diagnosis are essential elements of the World Health... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
Interleukin-13 receptor α-2 (IL13Rα2) is a cell surface receptor commonly found in solid tumors such as glioblastoma, melanoma, and breast cancer. It is minimally expressed in normal tissues, making it... Read more
Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
COX-2, an enzyme that plays a key role in brain inflammation, can be significantly upregulated by inflammatory stimuli and neuroexcitation. Researchers suggest that COX-2 density in the brain could serve... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
Currently, patients with conditions such as heart failure, pneumonia, or respiratory distress often require multiple imaging procedures that are intermittent, disruptive, and involve high levels of radiation.... Read more
AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
Radioligand therapy, a form of targeted nuclear medicine, has recently gained attention for its potential in treating specific types of tumors. However, one of the potential side effects of this therapy... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more