Combining Advanced Imaging Technologies Offers Breakthrough in Glioblastoma Treatment
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 27 Dec 2024 |
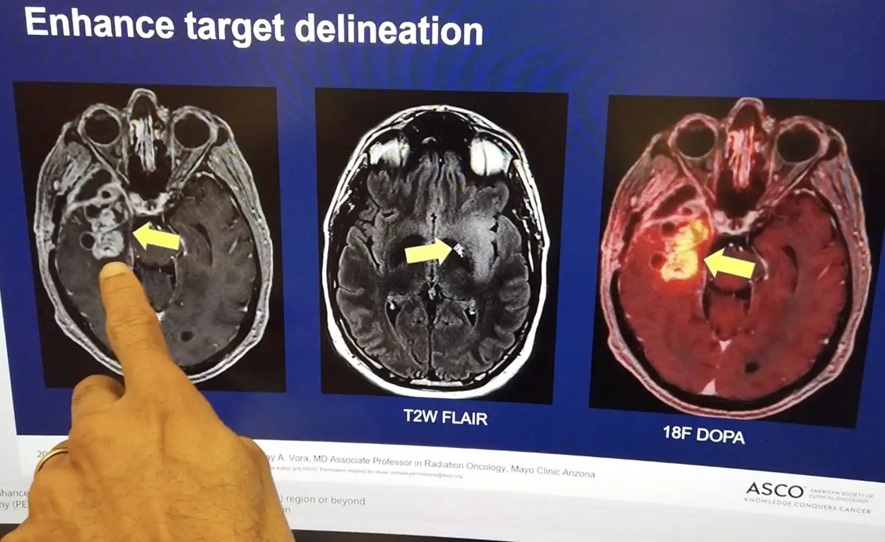
Glioblastoma is the deadliest form of primary brain cancer, largely due to its aggressive growth and resistance to treatment. The tumor infiltrates healthy brain tissue with hair-like extensions, complicating surgical removal. Surgeons face the delicate task of excising as much of the tumor as possible while safeguarding vital brain regions that control essential functions like movement and speech. Moreover, the tumor's complex cellular structure and its ability to evade conventional therapies add to the difficulty of treating the condition. While standard radiation therapy is commonly employed and can be effective, it also carries the risk of damaging healthy brain tissue, leading to unintended side effects. Now, a new treatment strategy combining advanced imaging may offer improved survival rates for older patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma, all while preserving their quality of life.
Mayo Clinic (Rochester, MN, USA) has shared the findings from its phase 2, single-arm study using one of the most innovative radiation treatments available today—proton beam therapy. This advanced, nonsurgical radiation therapy targets cancer cells with remarkable precision while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue. The study focused on patients over the age of 65 who had been newly diagnosed with WHO grade 4, malignant glioblastoma. In the SAGA clinical trial (Stereotactic Ablative Radiation Treatment for Glioblastoma), the research team utilized short-course hypofractionated proton beam therapy, enhanced by advanced imaging techniques. These included 18F-DOPA PET and contrast-enhanced MRI, which helped map the target area in the patient's brain and identify the most metabolically active regions of the tumor. By combining these imaging technologies, the team was able to deliver treatment in just one to two weeks, compared to the usual three to six weeks.
The results of the study published in The Lancet Oncology showed that 56% of participants survived for 12 months, with a median overall survival of 13.1 months. The combination of advanced imaging and proton beam therapy allowed for more precise radiation delivery, sparing healthy brain tissue from unnecessary exposure. The patients tolerated the treatment well, with survival outcomes exceeding expectations. This study was the first clinical trial to investigate short-course hypofractionated proton beam therapy, incorporating advanced imaging techniques, for older patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Following these promising results, Mayo Clinic has initiated a larger, randomized clinical trial.
“As compared to prior phase 3 studies in an older population having a median survival of only six to nine months, these results are promising," said Sujay Vora, M.D., radiation oncologist at Mayo Clinic, who led the research team. "In some cases, patients with tumors that have favorable genetics lived even longer, with a median survival of 22 months. We are very excited about these results."
"Our goal is to transform the way we treat glioblastoma using shorter courses of radiation to minimize the burden on patients and their families and help them complete safe and effective treatment in a shorter amount of time," added William Breen, M.D., radiation oncologist and principal investigator of the current study.
Related Links:
Mayo Clinic
Latest Nuclear Medicine News
- Novel Bacteria-Specific PET Imaging Approach Detects Hard-To-Diagnose Lung Infections
- New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
- Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
- Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
- Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
- New Molecular Imaging Test to Improve Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- Novel PET Technique Visualizes Spinal Cord Injuries to Predict Recovery
- Next-Gen Tau Radiotracers Outperform FDA-Approved Imaging Agents in Detecting Alzheimer’s
- Breakthrough Method Detects Inflammation in Body Using PET Imaging
- Advanced Imaging Reveals Hidden Metastases in High-Risk Prostate Cancer Patients
- New Molecular Imaging Agent Accurately Identifies Crucial Cancer Biomarker
- New Scans Light Up Aggressive Tumors for Better Treatment
- AI Stroke Brain Scan Readings Twice as Accurate as Current Method
- AI Analysis of PET/CT Images Predicts Side Effects of Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer
- New Imaging Agent to Drive Step-Change for Brain Cancer Imaging
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI Detects Fatty Liver Disease from Chest X-Rays
Fatty liver disease, which results from excess fat accumulation in the liver, is believed to impact approximately one in four individuals globally. If not addressed in time, it can progress to severe conditions... Read more
AI Detects Hidden Heart Disease in Existing CT Chest Scans
Coronary artery calcium (CAC) is a major indicator of cardiovascular risk, but its assessment typically requires a specialized “gated” CT scan that synchronizes with the heartbeat. In contrast, most chest... Read moreMRI
view channel
New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
Traditional exercise stress tests conducted within an MRI machine require patients to lie flat, a position that artificially improves heart function by increasing stroke volume due to gravity-driven blood... Read more
Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
Women with extremely dense breasts face a higher risk of missed breast cancer diagnoses, as dense glandular and fibrous tissue can obscure tumors on mammograms. While breast MRI is recommended for supplemental... Read moreUltrasound
view channel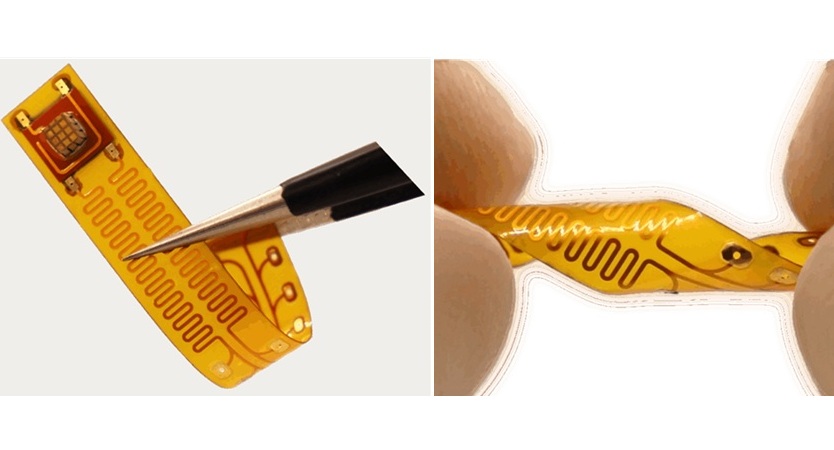
Wireless Chronic Pain Management Device to Reduce Need for Painkillers and Surgery
Chronic pain affects millions of people globally, often leading to long-term disability and dependence on opioid medications, which carry significant risks of side effects and addiction.... Read more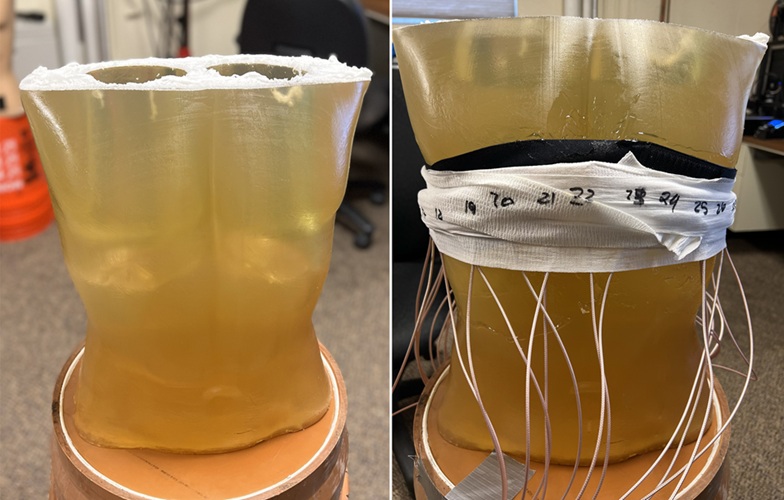
New Medical Ultrasound Imaging Technique Enables ICU Bedside Monitoring
Ultrasound computed tomography (USCT) presents a safer alternative to imaging techniques like X-ray computed tomography (commonly known as CT or “CAT” scans) because it does not produce ionizing radiation.... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
CT Colonography Beats Stool DNA Testing for Colon Cancer Screening
As colorectal cancer remains the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, early detection through screening is vital to reduce advanced-stage treatments and associated costs.... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
Currently, patients with conditions such as heart failure, pneumonia, or respiratory distress often require multiple imaging procedures that are intermittent, disruptive, and involve high levels of radiation.... Read more
AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
Radioligand therapy, a form of targeted nuclear medicine, has recently gained attention for its potential in treating specific types of tumors. However, one of the potential side effects of this therapy... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more













.jpeg)


