New PET Radiotracer Enables Same-Day Imaging of Key Gastrointestinal Cancer Biomarker
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 10 Jun 2024 |
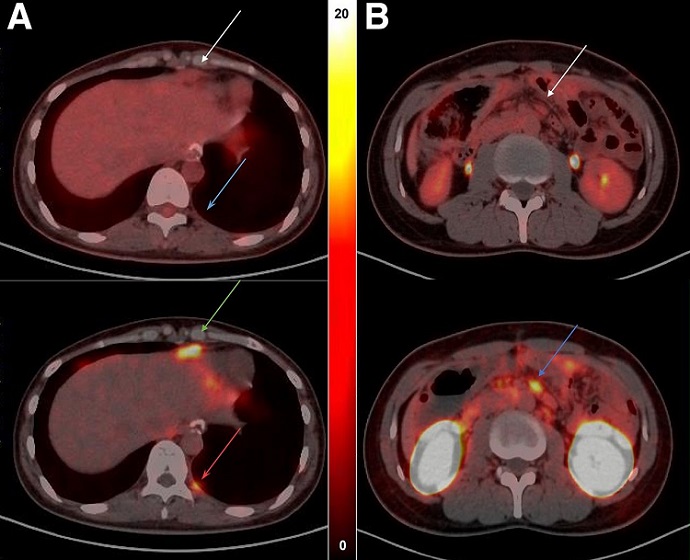
Gastrointestinal cancers rank among the most prevalent cancers worldwide, contributing to over a quarter of all cancer cases and over one-third of cancer-related deaths annually. The initial symptoms of these cancers can be misleading, and they are often identified at a late stage, typically resulting in a grim prognosis and increased mortality rates. Claudin18.2 (CLDN18.2), a protein prominently expressed in gastrointestinal cancers, serves as a crucial biomarker, and numerous therapies targeting CLDN18.2 are currently being tested in clinical trials. However, there is no standardized test for detecting CLDN18.2; most existing methods use immunohistochemistry, a technique that only examines a limited tissue sample and fails to capture the variability in CLDN18.2 expression across different tumor areas. Now, a new PET radiotracer, 68Ga-NC-BCH, has been shown to enable same-day imaging of CLDN18.2 with its uptake demonstrating a significant correlation with CLDN18.2 levels, which could help oncologists in tailoring and monitoring treatments for their patients.
Researchers at Peking University Cancer Hospital (Beijing, China) initially synthesized the 68Ga-NC-BCH radiotracer and conducted preliminary tests on human gastrointestinal cancer cell lines and mouse models. Subsequently, 11 patients underwent whole-body scans using 68Ga-NC-BCH PET alongside 18F-FDG PET to assess the distribution of the radiopharmaceutical, radiation dosimetry, and the connection between tracer uptake and CLDN18.2 levels. The production of 68Ga-NC-BCH was consistently reliable, showing excellent radiochemical qualities. It displayed rapid clearance from the bloodstream, high specificity for CLDN18.2, and significant selective accumulation in CLDN18.2-positive cells and tumor-bearing mice. In patients, 68Ga-NC-BCH showed notable absorption in the stomach and kidneys and lower uptake in the pancreas. When compared to 18F-FDG, 68Ga-NC-BCH detected additional lesions in the lymph nodes and peritoneum, which are frequently the primary sites of metastasis in advanced gastric cancer.
“The detection of CLDN18.2 expression levels is essential for identifying patients who can benefit from targeted therapies,” said Hua Zhu, PhD, professor at Peking University Cancer Hospital. “In this study, we developed a CLDN18.2-targeting radiotracer and conducted whole-body PET imaging to determine its ability to detect the biomarker.”
“68Ga-NC-BCH PET is a safe, noninvasive imaging method for detecting CLDN18.2 expression in patients,” added Zhu. “The rapid uptake of the radiotracer allows patients to complete the whole imaging workflow within one day, greatly increasing compliance and reducing radiation exposure. This can greatly help oncologists in making treatment decisions.”
Related Links:
Peking University Cancer Hospital
Latest Nuclear Medicine News
- New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
- Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
- Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
- Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
- New Molecular Imaging Test to Improve Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- Novel PET Technique Visualizes Spinal Cord Injuries to Predict Recovery
- Next-Gen Tau Radiotracers Outperform FDA-Approved Imaging Agents in Detecting Alzheimer’s
- Breakthrough Method Detects Inflammation in Body Using PET Imaging
- Advanced Imaging Reveals Hidden Metastases in High-Risk Prostate Cancer Patients
- Combining Advanced Imaging Technologies Offers Breakthrough in Glioblastoma Treatment
- New Molecular Imaging Agent Accurately Identifies Crucial Cancer Biomarker
- New Scans Light Up Aggressive Tumors for Better Treatment
- AI Stroke Brain Scan Readings Twice as Accurate as Current Method
- AI Analysis of PET/CT Images Predicts Side Effects of Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer
- New Imaging Agent to Drive Step-Change for Brain Cancer Imaging
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Machine Learning Algorithm Identifies Cardiovascular Risk from Routine Bone Density Scans
A new study published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research reveals that an automated machine learning program can predict the risk of cardiovascular events and falls or fractures by analyzing bone... Read more
AI Improves Early Detection of Interval Breast Cancers
Interval breast cancers, which occur between routine screenings, are easier to treat when detected earlier. Early detection can reduce the need for aggressive treatments and improve the chances of better outcomes.... Read more
World's Largest Class Single Crystal Diamond Radiation Detector Opens New Possibilities for Diagnostic Imaging
Diamonds possess ideal physical properties for radiation detection, such as exceptional thermal and chemical stability along with a quick response time. Made of carbon with an atomic number of six, diamonds... Read moreMRI
view channel
MRI to Replace Painful Spinal Tap for Faster MS Diagnosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a challenging neurological condition to diagnose due to its wide array of symptoms, with not all patients experiencing the same symptoms or at the same intensity, and the disease... Read more
MRI Scans Can Identify Cardiovascular Disease Ten Years in Advance
Cardiovascular disease encompasses various conditions that narrow or block blood vessels, such as heart attacks, strokes, and heart failure. While some individuals are genetically predisposed, lifestyle... Read more
Simple Brain Scan Diagnoses Parkinson's Disease Years Before It Becomes Untreatable
Parkinson's disease (PD) remains a challenging condition to treat, with no known cure. Though therapies have improved over time, and ongoing research focuses on methods to slow or alter the disease’s progression,... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
New Incision-Free Technique Halts Growth of Debilitating Brain Lesions
Cerebral cavernous malformations (CCMs), also known as cavernomas, are abnormal clusters of blood vessels that can grow in the brain, spinal cord, or other parts of the body. While most cases remain asymptomatic,... Read more.jpeg)
AI-Powered Lung Ultrasound Outperforms Human Experts in Tuberculosis Diagnosis
Despite global declines in tuberculosis (TB) rates in previous years, the incidence of TB rose by 4.6% from 2020 to 2023. Early screening and rapid diagnosis are essential elements of the World Health... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
Currently, patients with conditions such as heart failure, pneumonia, or respiratory distress often require multiple imaging procedures that are intermittent, disruptive, and involve high levels of radiation.... Read more
AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
Radioligand therapy, a form of targeted nuclear medicine, has recently gained attention for its potential in treating specific types of tumors. However, one of the potential side effects of this therapy... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more