Deep Learning Improves Lung Ultrasound Interpretation
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 31 Jan 2024 |
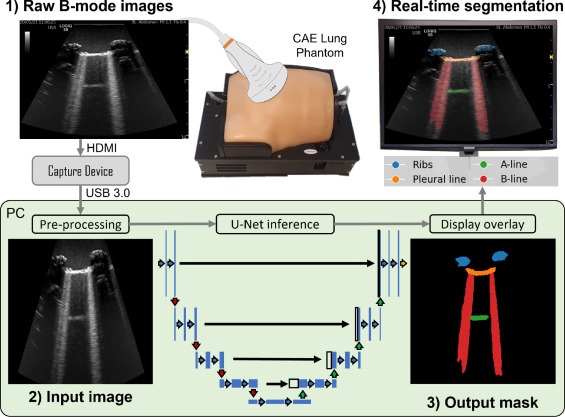
Lung ultrasound (LUS) has become a valuable tool for lung health assessment due to its safety and cost-effectiveness. Yet, the challenge in interpreting LUS images, largely due to its dependence on artefacts, leads to variability among operators and hampers its wider application. Now, a new study has found that deep learning can enhance the real-time interpretation of lung ultrasound. This study found that a deep learning model trained on lung ultrasound images was capable of segmenting and identifying artefacts in these images, as demonstrated in tests on a phantom model.
In the study, researchers at the University of Leeds (West Yorkshire, UK) employed a deep learning technique for multi-class segmentation in ultrasound images of a lung training phantom. This technique was used to distinguish various objects and artefacts, such as ribs, pleural lines, A-lines, B-lines, and B-line confluences. The team developed a modified version of the U-Net architecture for image segmentation, aiming to strike a balance between the model’s speed and accuracy. During the training phase, they implemented an ultrasound-specific augmentation pipeline to enhance the model’s ability to generalize new, unseen data such as geometric transformations and ultrasound-specific augmentations. The trained network was then applied to segment live image feeds from a cart-based point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) system, using a convex curved-array transducer to image the training phantom and stream frames. The model, trained on a single graphics processing unit, required about 12 minutes for training with 450 ultrasound images.
The model demonstrated a high accuracy rate of 95.7%, with moderate-to-high Dice similarity coefficient scores. Real-time application of the model at up to 33.4 frames per second significantly enhanced the visualization of lung ultrasound images. Furthermore, the team evaluated the pixel-wise correlation between manually labeled and model-predicted segmentation masks. Through a normalized confusion matrix, they noted that the model accurately predicted 86.8% of pixels labeled as ribs, 85.4% for the pleural line, and 72.2% for B-line confluence. However, it correctly predicted only 57.7% of A-line and 57.9% of B-line pixels.
Additionally, the researchers employed transfer learning with their model, using knowledge from one dataset to improve training on a related dataset. This approach yielded Dice similarity coefficients of 0.48 for simple pleural effusion, 0.32 for lung consolidation, and 0.25 for the pleural line. The findings suggest that this model could aid in lung ultrasound training and help bridge skill gaps. The researchers have also proposed a semi-quantitative measure, the B-line Artifact Score, which estimates the percentage of an intercostal space occupied by B-lines. This measure could potentially be linked to the severity of lung conditions.
“Future work should consider the translation of these methods to clinical data, considering transfer learning as a viable method to build models which can assist in the interpretation of lung ultrasound and reduce inter-operator variability associated with this subjective imaging technique,” the researchers stated.
Related Links:
University of Leeds
Latest Ultrasound News
- Smart Ultrasound-Activated Immune Cells Destroy Cancer Cells for Extended Periods
- Tiny Magnetic Robot Takes 3D Scans from Deep Within Body
- High Resolution Ultrasound Speeds Up Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
- World's First Wireless, Handheld, Whole-Body Ultrasound with Single PZT Transducer Makes Imaging More Accessible
- Artificial Intelligence Detects Undiagnosed Liver Disease from Echocardiograms
- Ultrasound Imaging Non-Invasively Tracks Tumor Response to Radiation and Immunotherapy
- AI Improves Detection of Congenital Heart Defects on Routine Prenatal Ultrasounds
- AI Diagnoses Lung Diseases from Ultrasound Videos with 96.57% Accuracy
- New Contrast Agent for Ultrasound Imaging Ensures Affordable and Safer Medical Diagnostics
- Ultrasound-Directed Microbubbles Boost Immune Response Against Tumors
- POC Ultrasound Enhances Early Pregnancy Care and Cuts Emergency Visits
- AI-Based Models Outperform Human Experts at Identifying Ovarian Cancer in Ultrasound Images
- Automated Breast Ultrasound Provides Alternative to Mammography in Low-Resource Settings
- Transparent Ultrasound Transducer for Photoacoustic and Ultrasound Endoscopy to Improve Diagnostic Accuracy
- Wearable Ultrasound Patch Enables Continuous Blood Pressure Monitoring
- AI Image-Recognition Program Reads Echocardiograms Faster, Cuts Results Wait Time
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI-Powered Imaging Technique Shows Promise in Evaluating Patients for PCI
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), also known as coronary angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure where small metal tubes called stents are inserted into partially blocked coronary arteries... Read more
Higher Chest X-Ray Usage Catches Lung Cancer Earlier and Improves Survival
Lung cancer continues to be the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. While advanced technologies like CT scanners play a crucial role in detecting lung cancer, more accessible and affordable... Read moreMRI
view channel
Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
Approximately 360,000 individuals in the UK suffer from focal epilepsy, a condition in which seizures spread from one part of the brain. Around a third of these patients experience persistent seizures... Read more
AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
Current research shows that the accuracy of diagnosing Parkinson’s disease typically ranges from 55% to 78% within the first five years of assessment. This is partly due to the similarities shared by Parkinson’s... Read more
Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are transforming the way medical images are analyzed, offering unprecedented capabilities in quantitatively extracting features that go beyond traditional visual... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
Each year, approximately 800,000 people in the U.S. experience strokes, with marginalized and minoritized groups being disproportionately affected. Strokes vary in terms of size and location within the... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
COX-2, an enzyme that plays a key role in brain inflammation, can be significantly upregulated by inflammatory stimuli and neuroexcitation. Researchers suggest that COX-2 density in the brain could serve... Read more
Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which represents 15-20% of all breast cancer cases, is one of the most aggressive subtypes, with a five-year survival rate of about 40%. Due to its significant heterogeneity... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
Given the need to detect lung cancer at earlier stages, there is an increasing need for a definitive diagnostic pathway for patients with suspicious pulmonary nodules. However, obtaining tissue samples... Read more
AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
Lung cancer remains one of the most challenging diseases, making early diagnosis vital for effective treatment. Fortunately, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing lung cancer... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more