AI-Based Breast Cancer Risk Calculator Could Reduce Unnecessary Biopsies
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 17 Aug 2023 |

Breast cancer is a significant health concern, affecting one in eight women during their lifetime and even some men. Mammograms have become a standard screening procedure, recommended annually for women starting at age 40 to detect breast cancer at its earliest stages. Although this leads to more biopsies, a surprisingly small proportion (less than two out of 10,000 women biopsied) comes out positive. The consequences are not only wasted time, resources, and money but also unnecessary anxiety for the patient. Now, scientists have devised a more intelligent model to assess breast cancer risk, aiming to reduce unnecessary biopsies.
Scientists at Houston Methodist Hospital (Houston, TX, USA) have developed an advanced clinical decision support tool, known as iBRISK (intelligent-augmented breast cancer risk calculator), which leverages deep learning to provide a more accurate assessment of a woman's risk of developing breast cancer. This tool was created by applying deep learning to clinical risk factors and mammographic descriptors from nearly 10,000 individuals, and its effectiveness was subsequently validated on more than 1,000 additional patients.
Currently, hospitals in the U.S. rely on the Breast Imaging Reporting and Database System (BI-RADS), devised by the American College of Radiology, to gauge breast cancer risk and determine whether a biopsy is needed. However, the scientists at Houston Methodist Hospital have gone beyond the standard BI-RADS data by utilizing AI technology and multiple patient data points to refine the assessment. The iBRISK system integrates natural language processing, medical image analysis, and deep learning with multi-modal BI-RADS patient data to generate one of three recommendations: a biopsy is not recommended, consideration for biopsy, or a biopsy is recommended. The researchers identified approximately 100 parameters for analysis, such as age, sex, socio-economic data, medical history, and insurance plans. Through the application of deep learning, the AI tool reduced these data points down to the 20 most essential risk indicators.
In a new study, the iBRISK model was applied to an independent set of breast images from over 4,200 patients, screened at three different institutions between 2006 and 2016. The model was developed particularly to evaluate the probability of malignancy of BI-RADS category 4 lesions. The model's accuracy rate was found to be approximately 89.5%, with an impressive specificity of 81%. Only two of the 1,228 individuals in the low Probability of Malignancy (POM) group had malignant lesions, while the high POM malignancy rate was 85.9%. The scientists also calculated the iBRISK score's effectiveness at predicting malignancy, resulting in an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.97. The potential impact of iBRISK is substantial. Not only could it lead to more accurate breast cancer risk assessments, but it may also save hundreds of millions of dollars each year at a single institution by eliminating unnecessary biopsies. By employing intelligent AI methodologies, the iBRISK tool represents a significant advancement in breast cancer screening and demonstrates the potential to improve medical decision-making, efficiency, and patient care.
“Our study demonstrates that iBRISK can effectively aid in risk stratification of BI-RADS 4 lesions and reduce overbiopsy of these lesions,” the authors concluded. “Ultimately, the iBRISK calculator will be published as an online interface and made open access, noncommercial, and accessible by health systems and centers worldwide. Future studies aim to improve the model further, particularly by including more granular data and other BI-RADS categories.”
Related Links:
Houston Methodist Hospital
Latest General/Advanced Imaging News
- AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
- Ultra-Low Dose CT Aids Pneumonia Diagnosis in Immunocompromised Patients
- AI Reduces CT Lung Cancer Screening Workload by Almost 80%
- Cutting-Edge Technology Combines Light and Sound for Real-Time Stroke Monitoring
- AI System Detects Subtle Changes in Series of Medical Images Over Time
- New CT Scan Technique to Improve Prognosis and Treatments for Head and Neck Cancers
- World’s First Mobile Whole-Body CT Scanner to Provide Diagnostics at POC
- Comprehensive CT Scans Could Identify Atherosclerosis Among Lung Cancer Patients
- AI Improves Detection of Colorectal Cancer on Routine Abdominopelvic CT Scans
- Super-Resolution Technology Enhances Clinical Bone Imaging to Predict Osteoporotic Fracture Risk
- AI-Powered Abdomen Map Enables Early Cancer Detection
- Deep Learning Model Detects Lung Tumors on CT
- AI Predicts Cardiovascular Risk from CT Scans
- Deep Learning Based Algorithms Improve Tumor Detection in PET/CT Scans
- New Technology Provides Coronary Artery Calcification Scoring on Ungated Chest CT Scans
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI-Powered Imaging Technique Shows Promise in Evaluating Patients for PCI
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), also known as coronary angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure where small metal tubes called stents are inserted into partially blocked coronary arteries... Read more
Higher Chest X-Ray Usage Catches Lung Cancer Earlier and Improves Survival
Lung cancer continues to be the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. While advanced technologies like CT scanners play a crucial role in detecting lung cancer, more accessible and affordable... Read moreMRI
view channel
Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
Approximately 360,000 individuals in the UK suffer from focal epilepsy, a condition in which seizures spread from one part of the brain. Around a third of these patients experience persistent seizures... Read more
AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
Current research shows that the accuracy of diagnosing Parkinson’s disease typically ranges from 55% to 78% within the first five years of assessment. This is partly due to the similarities shared by Parkinson’s... Read more
Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are transforming the way medical images are analyzed, offering unprecedented capabilities in quantitatively extracting features that go beyond traditional visual... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
Each year, approximately 800,000 people in the U.S. experience strokes, with marginalized and minoritized groups being disproportionately affected. Strokes vary in terms of size and location within the... Read moreUltrasound
view channel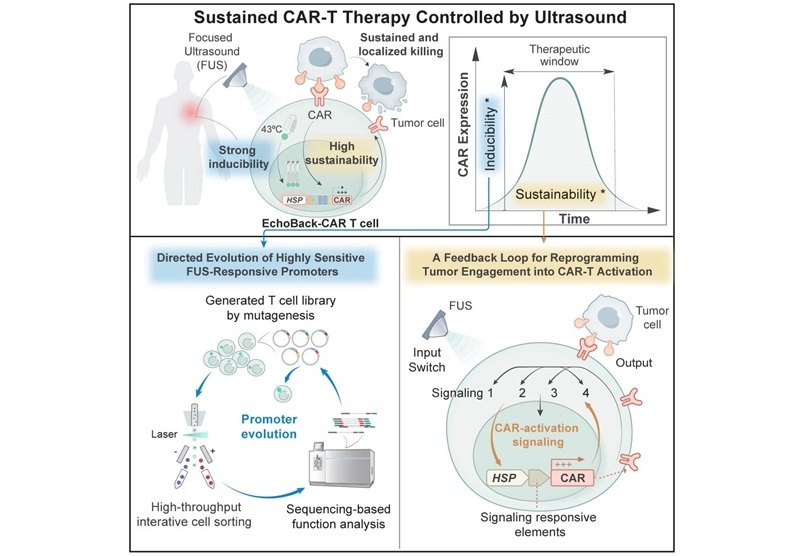
Smart Ultrasound-Activated Immune Cells Destroy Cancer Cells for Extended Periods
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has emerged as a highly promising cancer treatment, especially for bloodborne cancers like leukemia. This highly personalized therapy involves extracting... Read more
Tiny Magnetic Robot Takes 3D Scans from Deep Within Body
Colorectal cancer ranks as one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide. However, when detected early, it is highly treatable. Now, a new minimally invasive technique could significantly... Read more
High Resolution Ultrasound Speeds Up Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
Each year, approximately one million prostate cancer biopsies are conducted across Europe, with similar numbers in the USA and around 100,000 in Canada. Most of these biopsies are performed using MRI images... Read more
World's First Wireless, Handheld, Whole-Body Ultrasound with Single PZT Transducer Makes Imaging More Accessible
Ultrasound devices play a vital role in the medical field, routinely used to examine the body's internal tissues and structures. While advancements have steadily improved ultrasound image quality and processing... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
COX-2, an enzyme that plays a key role in brain inflammation, can be significantly upregulated by inflammatory stimuli and neuroexcitation. Researchers suggest that COX-2 density in the brain could serve... Read more
Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which represents 15-20% of all breast cancer cases, is one of the most aggressive subtypes, with a five-year survival rate of about 40%. Due to its significant heterogeneity... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more