New MRI Imaging Technique Can Diagnose Early Stage Parkinson's
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 18 Jul 2022 |
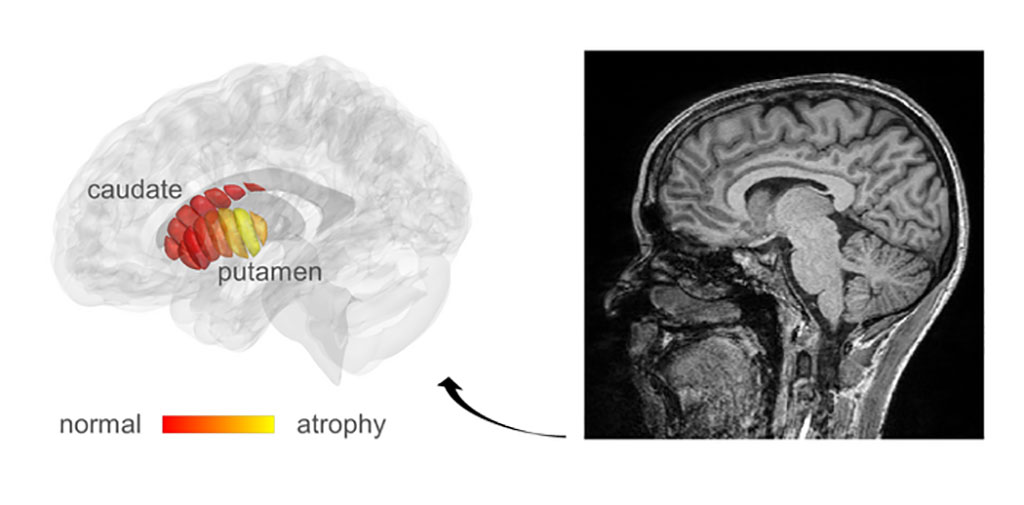
Parkinson's is a progressive and debilitating disease of the brain that eventually compromises patients' ability to walk and even to talk. Its diagnosis is complex, and in the early stages – impossible. The usual method of visualizing brain structure utilizes a technique most of us are familiar with, called MRI. However, it is not sensitive enough to reveal the biological changes that take place in the brain of Parkinson patients, and at present is primarily only used to eliminate other possible diagnoses. Now, researchers have realized that the cellular changes in Parkinson's could possibly be revealed by adapting a related technique, known as quantitative MRI (qMRI).
The method has enabled researchers at The Hebrew University of Jerusalem (Jerusalem, Israel) to look at microstructures within the part of the deep brain known as the striatum – an organ which is known to deteriorate during the progress of Parkinson's disease. Using a novel method of analysis developed by the team, biological changes in the cellar tissue of the striatum were clearly revealed. Moreover, they were able to demonstrate that these changes were associated with the early stages of Parkinson's and patients’ movement dysfunction.
qMRI achieves its sensitivity by taking several MRI images using different excitation energies – rather like taking the same photograph in different colors of lighting. The researchers were able to use their qMRI analysis to reveal changes in the tissue structure within distinct regions of the striatum. The structural sensitivity of these measurements could only have been previously achieved in laboratories examining the brain cells of patients post mortem. This is not an ideal situation for detecting early disease or monitoring the efficacy of a drug.
The new information will facilitate early diagnosis of the disease and provide "markers" for monitoring the efficacy of future drug therapies. The researchers now plan to extend the technique to investigate microstructural changes in other regions of the brain. Furthermore, the team is now developing qMRI into a tool that can be used in a clinical setting and could be ready about 3-5 years down the line. The researchers further suggest that this type of analysis will enable identification of subgroups within the population suffering from Parkinson’s disease – some of whom may respond differently to some drugs than others.
"When you don't have measurements, you don't know what is normal and what is abnormal brain structure, and what is changing during the progress of the disease," explained Professor Aviv Mezer who led the team of researchers. “What we have discovered is the tip of the iceberg.” Ultimately, he sees this analysis “leading to personalized treatment, allowing future discoveries of drug with each person receiving the most appropriate drug.”
Related Links:
The Hebrew University of Jerusalem
Latest MRI News
- New Material Boosts MRI Image Quality
- AI Model Reads and Diagnoses Brain MRI in Seconds
- MRI Scan Breakthrough to Help Avoid Risky Invasive Tests for Heart Patients
- MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
- Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
- AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
- AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
- New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
- Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
- MRI to Replace Painful Spinal Tap for Faster MS Diagnosis
- MRI Scans Can Identify Cardiovascular Disease Ten Years in Advance
- Simple Brain Scan Diagnoses Parkinson's Disease Years Before It Becomes Untreatable
- Cutting-Edge MRI Technology to Revolutionize Diagnosis of Common Heart Problem
- New MRI Technique Reveals True Heart Age to Prevent Attacks and Strokes
- AI Tool Predicts Relapse of Pediatric Brain Cancer from Brain MRI Scans
- AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI Tool Predicts Breast Cancer Risk Years Ahead Using Routine Mammograms
Breast cancer screening saves lives but still relies largely on uniform schedules despite wide differences in individual risk. This one-size-fits-all approach can miss cancers in higher-risk women while... Read more
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Reusable Gel Pad Made from Tamarind Seed Could Transform Ultrasound Examinations
Ultrasound imaging depends on a conductive gel to eliminate air between the probe and the skin so sound waves can pass clearly into the body. While the imaging technology is fast, safe, and noninvasive,... Read more
AI Model Accurately Detects Placenta Accreta in Pregnancy Before Delivery
Placenta accreta spectrum (PAS) is a life-threatening pregnancy complication in which the placenta abnormally attaches to the uterine wall. The condition is a leading cause of maternal mortality and morbidity... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
Targeted cancer therapies only work when tumor cells express the specific molecular structures they are designed to attack. In urothelial carcinoma, a common form of bladder cancer, the cell surface protein... Read more
Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
Targeted cancer therapies can be highly effective, but only when a patient’s tumor expresses the specific protein the treatment is designed to attack. Determining this usually requires biopsies or advanced... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Tool Predicts Side Effects from Lung Cancer Treatment
Radiation therapy is a central treatment for lung cancer, but even carefully targeted radiation can affect surrounding healthy tissue. Patients may develop side effects such as lung inflammation, coughing,... Read more
AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer is a form of head and neck cancer that can spread through lymph nodes, significantly affecting survival and treatment decisions. Current therapies often involve combinations of surgery,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Nuclear Medicine Set for Continued Growth Driven by Demand for Precision Diagnostics
Clinical imaging services face rising demand for precise molecular diagnostics and targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy as cancer and chronic disease rates climb. A new market analysis projects rapid expansion... Read more























