AI Software Can Cut PET Scan Time in Half
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 27 May 2022 |
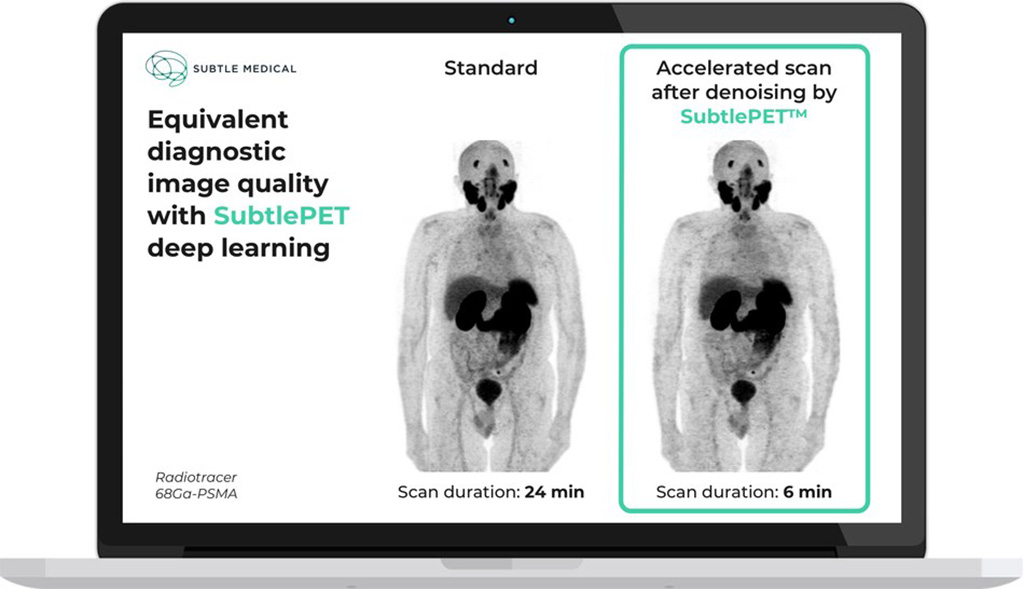
Recent research in PET has focused on decreasing noise and increasing signal-to-noise ratios (SNR). Digital PET with silicon photomultipliers (SiPM) has led to improved timing, energy, spatial resolution, and effective time-of-flight (TOF) sensitivity. This has resulted in faster scanning with less injected activity. However, despite these advances, there is an ever-increasing demand for PET scans, which can contribute to significant delays in scheduling examinations and patient management. Deep learning (DL), a subdivision of artificial intelligence (AI), has many emerging applications in nuclear medicine. DL is able to increase PET resolution, decrease noise, and thus enhance image quality. It may allow for reducing injected activity, acquisition time, or a combination of both. Now, a new study that investigated whether AI-based denoising halves PET acquisition time in digital PET/CT has found that AI allows [18F]FDG PET duration in digital PET/CT to be halved, while restoring degraded ½-duration PET image quality.
The study by investigators at Baclesse Cancer Center (Caen, France) examined Subtle Medical, Inc.’s (Menlo Park, CA, USA) SubtlePET post-reconstruction PET denoising software that has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration and validated by the European Commission for [18F]FDG PET. The algorithm is based on deep convolutional neural networks (DCNN), the most common DL architecture. SubtlePET uses multi-slice 2.5D encoder-decoder U-Net DCNN. It takes the pixel’s neighborhood into account to reduce noise and increase image quality. Using a residual learning approach that is optimized for quantitative (L1 norm) and structural similarity (SSIM), it has learned to separate and suppress noise components while preserving non-noise components.
The software applies denoising to improve the image quality of low count PET (positron emission tomography) scans acquired in up to 25% of the original scan time, enabling centers to expedite patient care and improve patient comfort during PET exams. SubtlePET is FDA-cleared for use with 18F-FDG and 18F-Amyloid tracers and is CE-marked for use with 18F-FDG, 18F-Amyloid, 18F-Fluciclovine, 18F-DOPA, 18F-Choline, 18F-DCFPyL, Ga-68 Dotatate, and Ga-68 PSMA radiotracer PET images, expanding coverage for Prostate (PSMA) and Neuroendocrine tumors. The vendor-neutral software is a virtual upgrade to any brand of PET or PET/CT machine that boosts scanner performance across the entire fleet.
In the latest study, researchers aimed to evaluate the feasibility of halving PET acquisition time in a routine clinical setting by using SubtlePET while preserving visual and semi-quantitative PET performances in digital TOF PET/CT. The prospective study showed good visual and semi-quantitative performances of AI-denoised half-count PET compared to original PET in a digital PET/CT. The researchers simulated a two-fold reduction in the PET acquisition time and then applied SubtlePET. All PET series were successfully denoised within two minutes in an automatic workflow using a common GPU card. This makes it compatible with routine clinical use.
Visually, global image quality scores were similar between PET90 and PET45AI but lower and clinically insufficient in half-count PET45 due to high noise. The researchers obtained a few discordances (2.3%) between original PET90 and denoised PET45AI in the absolute detection of 856 lesions. The study findings support the routine use of Subtle PET combined with a two-fold faster PET acquisition. According to the researchers, the benefit of decreasing PET duration, thus reducing waiting time for appointments and helping patients who experience discomfort, outweighs the minor decrease in performance.
Related Links:
Baclesse Cancer Center
Subtle Medical, Inc.
Latest General/Advanced Imaging News
- AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
- Ultra-Low Dose CT Aids Pneumonia Diagnosis in Immunocompromised Patients
- AI Reduces CT Lung Cancer Screening Workload by Almost 80%
- Cutting-Edge Technology Combines Light and Sound for Real-Time Stroke Monitoring
- AI System Detects Subtle Changes in Series of Medical Images Over Time
- New CT Scan Technique to Improve Prognosis and Treatments for Head and Neck Cancers
- World’s First Mobile Whole-Body CT Scanner to Provide Diagnostics at POC
- Comprehensive CT Scans Could Identify Atherosclerosis Among Lung Cancer Patients
- AI Improves Detection of Colorectal Cancer on Routine Abdominopelvic CT Scans
- Super-Resolution Technology Enhances Clinical Bone Imaging to Predict Osteoporotic Fracture Risk
- AI-Powered Abdomen Map Enables Early Cancer Detection
- Deep Learning Model Detects Lung Tumors on CT
- AI Predicts Cardiovascular Risk from CT Scans
- Deep Learning Based Algorithms Improve Tumor Detection in PET/CT Scans
- New Technology Provides Coronary Artery Calcification Scoring on Ungated Chest CT Scans
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI-Powered Imaging Technique Shows Promise in Evaluating Patients for PCI
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), also known as coronary angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure where small metal tubes called stents are inserted into partially blocked coronary arteries... Read more
Higher Chest X-Ray Usage Catches Lung Cancer Earlier and Improves Survival
Lung cancer continues to be the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. While advanced technologies like CT scanners play a crucial role in detecting lung cancer, more accessible and affordable... Read moreMRI
view channel
Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
Approximately 360,000 individuals in the UK suffer from focal epilepsy, a condition in which seizures spread from one part of the brain. Around a third of these patients experience persistent seizures... Read more
AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
Current research shows that the accuracy of diagnosing Parkinson’s disease typically ranges from 55% to 78% within the first five years of assessment. This is partly due to the similarities shared by Parkinson’s... Read more
Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are transforming the way medical images are analyzed, offering unprecedented capabilities in quantitatively extracting features that go beyond traditional visual... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
Each year, approximately 800,000 people in the U.S. experience strokes, with marginalized and minoritized groups being disproportionately affected. Strokes vary in terms of size and location within the... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Smart Ultrasound-Activated Immune Cells Destroy Cancer Cells for Extended Periods
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has emerged as a highly promising cancer treatment, especially for bloodborne cancers like leukemia. This highly personalized therapy involves extracting... Read more
Tiny Magnetic Robot Takes 3D Scans from Deep Within Body
Colorectal cancer ranks as one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide. However, when detected early, it is highly treatable. Now, a new minimally invasive technique could significantly... Read more
High Resolution Ultrasound Speeds Up Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
Each year, approximately one million prostate cancer biopsies are conducted across Europe, with similar numbers in the USA and around 100,000 in Canada. Most of these biopsies are performed using MRI images... Read more
World's First Wireless, Handheld, Whole-Body Ultrasound with Single PZT Transducer Makes Imaging More Accessible
Ultrasound devices play a vital role in the medical field, routinely used to examine the body's internal tissues and structures. While advancements have steadily improved ultrasound image quality and processing... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
COX-2, an enzyme that plays a key role in brain inflammation, can be significantly upregulated by inflammatory stimuli and neuroexcitation. Researchers suggest that COX-2 density in the brain could serve... Read more
Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which represents 15-20% of all breast cancer cases, is one of the most aggressive subtypes, with a five-year survival rate of about 40%. Due to its significant heterogeneity... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more