Siemens and CEA Design World's Most Powerful MRI Scanner for Human Imaging
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 20 Oct 2021 |
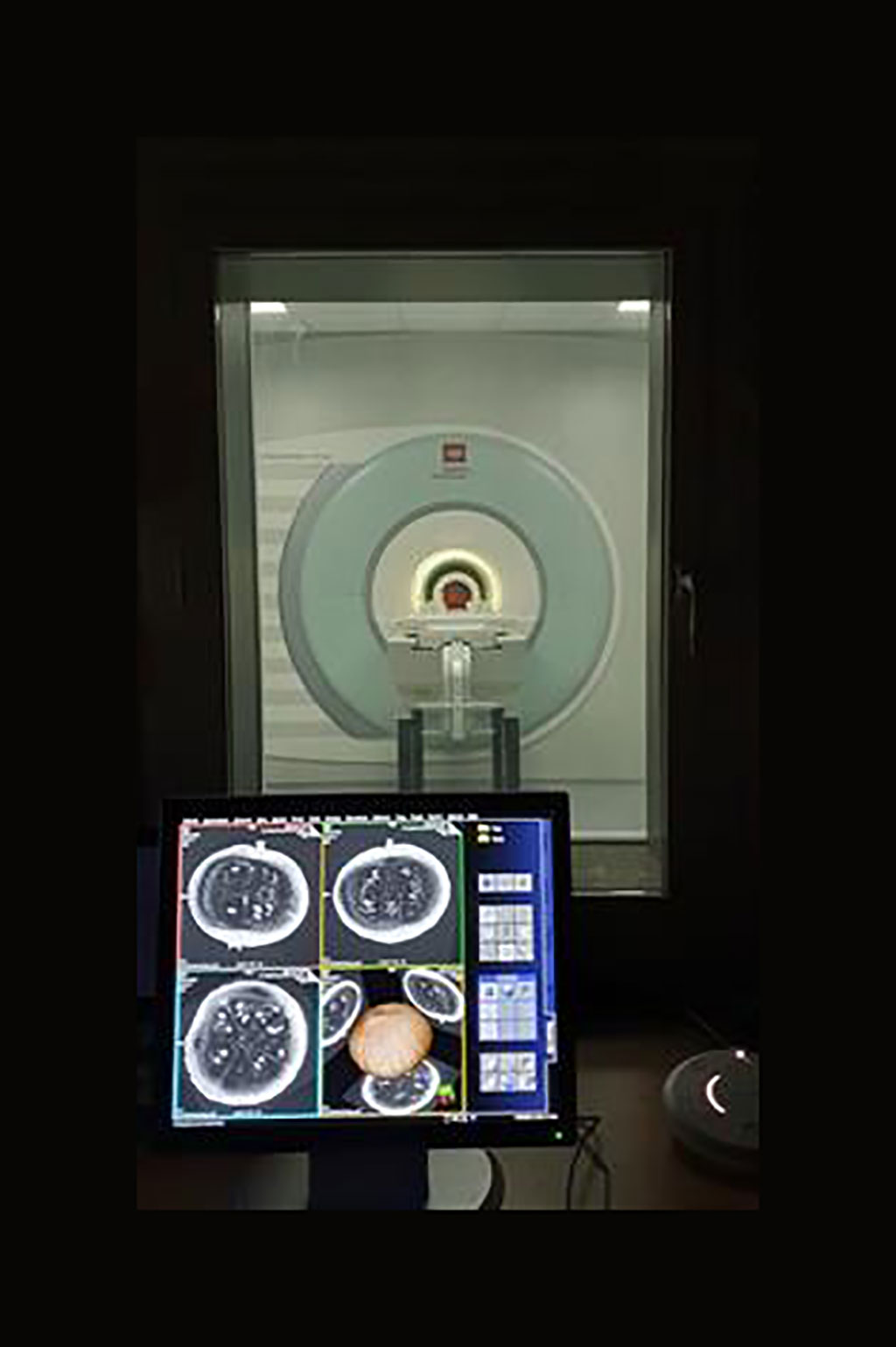
The most powerful MRI scanner in the world designed by engineers and researchers at Siemens Healthineers (Erlangen, Germany) and the French Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission (CEA; Paris, France) has delivered its first images.
A pumpkin was chosen for its multiple textures by CEA engineers and researchers to make the first images with the world's most powerful 11.7 T human whole body MRI of the Iseult project, installed at NeuroSpin at CEA-Paris-Saclay. Siemens has installed the MAGNETOM 11.7 T imaging equipment that has enabled the acquisition of these first images. These first acquisitions validate the entire process that has made it possible, thanks to multiple technological breakthroughs, to transform an "outstanding" magnet into an MRI machine.
132 tons, 5 m in length, 5 m in external diameter and 90 cm in internal diameter (to allow the passage of a whole human body): these are the extraordinary dimensions of the magnet of the Iseult project, which reaches a nominal magnetic field of 11.7 teslas, much more powerful than that of standard hospital MRIs (typically 1.5 or 3 T). To achieve this field, the magnet is powered by a current of 1,500 amps. The conductor coils are permanently cooled by helium in a superfluid state at 1.8 Kelvin (-271.35°C). The magnetic field of 11.7 T is a world record in the field of MRI for such a volume, and an absolute record with this type of superconductor material.
With a resolution of 400 microns in three dimensions, the images of the cucurbit prefigure the prowess that the scientific and technical teams of the CEA and their partners will be able to achieve in order to probe the human brain, for the benefit of fundamental research, cognitive sciences and in understanding brain pathologies. These images are the culmination of 20 years of research that have enabled the researchers, engineers and scientists to apply innovative technological developments.
“The development of the Iseult project magnet has been an exceptional human, technological and industrial adventure. To see it come to fruition with the achievement of the magnet nominal field strength - 11.7 T - followed by these first high-resolution images, which are so promising, is a real source of pride for all of us,” said Anne-Isabelle Etienvre, director of CEA-Irfu.
“Thanks to this extraordinary MRI, our researchers are looking forward to studying the anatomical and structural organization of the brain in greater detail. This work will undoubtedly lead to major clinical applications,” added Stanislas Dehaene, director of NeuroSpin, the neuroimaging platform at CEA-Paris-Saclay.
Related Links:
Siemens Healthineers
CEA
Latest MRI News
- Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
- AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
- AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
- New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
- Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
- MRI to Replace Painful Spinal Tap for Faster MS Diagnosis
- MRI Scans Can Identify Cardiovascular Disease Ten Years in Advance
- Simple Brain Scan Diagnoses Parkinson's Disease Years Before It Becomes Untreatable
- Cutting-Edge MRI Technology to Revolutionize Diagnosis of Common Heart Problem
- New MRI Technique Reveals True Heart Age to Prevent Attacks and Strokes
- AI Tool Predicts Relapse of Pediatric Brain Cancer from Brain MRI Scans
- AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
- Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
- AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
- Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
- First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
Chronological age does not always reflect how fast the body is truly aging, and current biological age tests often rely on DNA-based markers that may miss early organ-level decline. Detecting subtle, age-related... Read more
X-Ray Breakthrough Captures Three Image-Contrast Types in Single Shot
Detecting early-stage cancer or subtle changes deep inside tissues has long challenged conventional X-ray systems, which rely only on how structures absorb radiation. This limitation keeps many microstructural... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Wearable Ultrasound Imaging System to Enable Real-Time Disease Monitoring
Chronic conditions such as hypertension and heart failure require close monitoring, yet today’s ultrasound imaging is largely confined to hospitals and short, episodic scans. This reactive model limits... Read more
Ultrasound Technique Visualizes Deep Blood Vessels in 3D Without Contrast Agents
Producing clear 3D images of deep blood vessels has long been difficult without relying on contrast agents, CT scans, or MRI. Standard ultrasound typically provides only 2D cross-sections, limiting clinicians’... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
PET Imaging of Inflammation Predicts Recovery and Guides Therapy After Heart Attack
Acute myocardial infarction can trigger lasting heart damage, yet clinicians still lack reliable tools to identify which patients will regain function and which may develop heart failure.... Read more
Radiotheranostic Approach Detects, Kills and Reprograms Aggressive Cancers
Aggressive cancers such as osteosarcoma and glioblastoma often resist standard therapies, thrive in hostile tumor environments, and recur despite surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy. These tumors also... Read more
New Imaging Solution Improves Survival for Patients with Recurring Prostate Cancer
Detecting recurrent prostate cancer remains one of the most difficult challenges in oncology, as standard imaging methods such as bone scans and CT scans often fail to accurately locate small or early-stage tumors.... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI-Based Tool Accelerates Detection of Kidney Cancer
Diagnosing kidney cancer depends on computed tomography scans, often using contrast agents to reveal abnormalities in kidney structure. Tumors are not always searched for deliberately, as many scans are... Read more
New Algorithm Dramatically Speeds Up Stroke Detection Scans
When patients arrive at emergency rooms with stroke symptoms, clinicians must rapidly determine whether the cause is a blood clot or a brain bleed, as treatment decisions depend on this distinction.... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more