New Imaging Technology Detects Gastric Lymphomas
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 13 Oct 2021 |
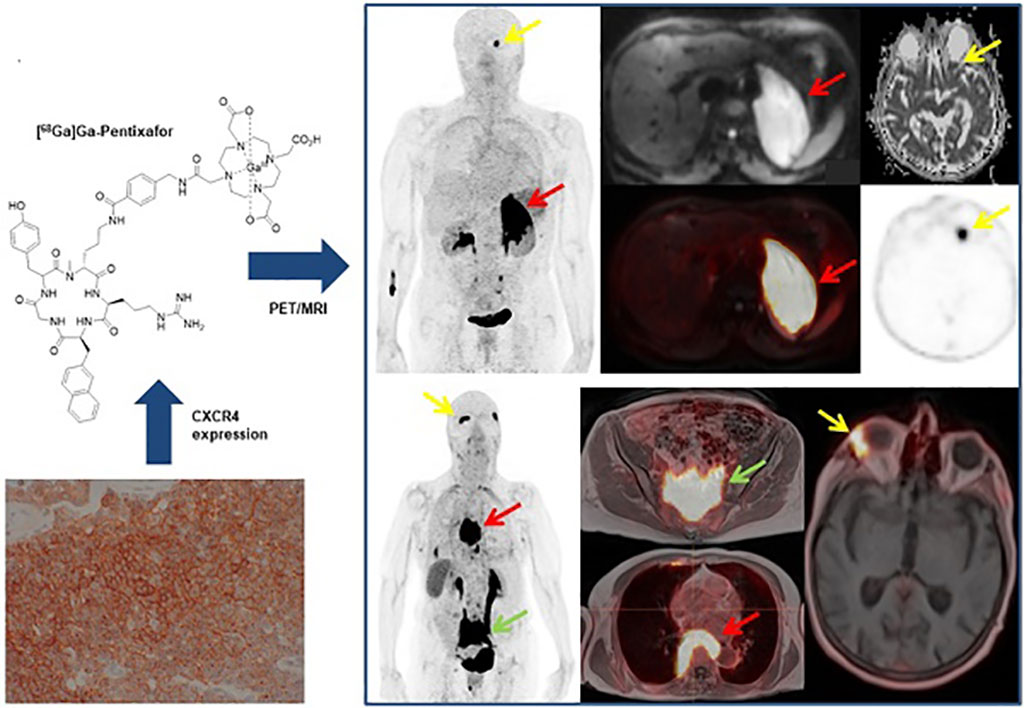
Image: MALT lymphomas express the chemokine receptor CXCR4 (Photo courtesy of MedUni)
A new imaging technique for the detection of gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphomas could reduce invasive gastroscopy biopsies, according to a new study.
The study, by researchers at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC; New York, NY, USA), the Medical University of Vienna (MedUni; Austria), and other institutions, explored if [68Ga]Pentixafor, a positron emission tomography (PET) tracer that targets the chemokine receptor CXCR4 (which is overexpressed in MALT lymphoma), could serve as a potential alternative to follow-up biopsies for assessment of residual disease following first-line H. pylori eradication.
The study, which included [68Ga]Pentixafor-PET and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans in 26 gastric MALT lymphoma patients and 20 control group patients without lymphoma, showed that accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive value of [68Ga]Pentixafor-PET for detection of residual gastric MALT lymphoma at follow-up were 97%, 95%, 100%, 100%, and 92.9%, respectively. Maximum and mean PET standardized uptake values also showed correlation with immunohistochemistry-based CXCR4 cell counts. The study was published on September 15, 2021, in Blood.
“Post-treatment evaluation of gastric MALT currently relies on esophagogastroduodenoscopy with histological assessment of biopsies,” concluded lead author Marius Mayerhöfer, PhD, of the MedUni department of biomedical imaging and image-guided therapy, and colleagues. “If a sufficiently high CXCR4 expression is detected at the initial diagnosis of MALT lymphoma, the new imaging could replace repeated gastroscopies in the course of the disease in the future, or at least increase the time intervals between gastroscopies.”
CXCR4 is an alpha-chemokine receptor specific for stromal-derived-factor-1 (SDF-1), a molecule with potent chemotactic activity for lymphocytes. After attachment to SDF-1, the CXCR4 protein activates signaling pathways inside the cell that help regulate cell growth and proliferation. CXCR4 is also involved in cell migration cells, especially hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow.
Related Links:
Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center
Medical University of Vienna
The study, by researchers at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC; New York, NY, USA), the Medical University of Vienna (MedUni; Austria), and other institutions, explored if [68Ga]Pentixafor, a positron emission tomography (PET) tracer that targets the chemokine receptor CXCR4 (which is overexpressed in MALT lymphoma), could serve as a potential alternative to follow-up biopsies for assessment of residual disease following first-line H. pylori eradication.
The study, which included [68Ga]Pentixafor-PET and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans in 26 gastric MALT lymphoma patients and 20 control group patients without lymphoma, showed that accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive value of [68Ga]Pentixafor-PET for detection of residual gastric MALT lymphoma at follow-up were 97%, 95%, 100%, 100%, and 92.9%, respectively. Maximum and mean PET standardized uptake values also showed correlation with immunohistochemistry-based CXCR4 cell counts. The study was published on September 15, 2021, in Blood.
“Post-treatment evaluation of gastric MALT currently relies on esophagogastroduodenoscopy with histological assessment of biopsies,” concluded lead author Marius Mayerhöfer, PhD, of the MedUni department of biomedical imaging and image-guided therapy, and colleagues. “If a sufficiently high CXCR4 expression is detected at the initial diagnosis of MALT lymphoma, the new imaging could replace repeated gastroscopies in the course of the disease in the future, or at least increase the time intervals between gastroscopies.”
CXCR4 is an alpha-chemokine receptor specific for stromal-derived-factor-1 (SDF-1), a molecule with potent chemotactic activity for lymphocytes. After attachment to SDF-1, the CXCR4 protein activates signaling pathways inside the cell that help regulate cell growth and proliferation. CXCR4 is also involved in cell migration cells, especially hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow.
Related Links:
Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center
Medical University of Vienna
Latest General/Advanced Imaging News
- AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
- New 3D Imaging System Addresses MRI, CT and Ultrasound Limitations
- AI-Based Tool Predicts Future Cardiovascular Events in Angina Patients
- AI-Based Tool Accelerates Detection of Kidney Cancer
- New Algorithm Dramatically Speeds Up Stroke Detection Scans
- 3D Scanning Approach Enables Ultra-Precise Brain Surgery
- AI Tool Improves Medical Imaging Process by 90%
- New Ultrasmall, Light-Sensitive Nanoparticles Could Serve as Contrast Agents
- AI Algorithm Accurately Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis Using Routine CT Images
- Cutting-Edge Angio-CT Solution Offers New Therapeutic Possibilities
- Extending CT Imaging Detects Hidden Blood Clots in Stroke Patients
- Groundbreaking AI Model Accurately Segments Liver Tumors from CT Scans
- New CT-Based Indicator Helps Predict Life-Threatening Postpartum Bleeding Cases
- CT Colonography Beats Stool DNA Testing for Colon Cancer Screening
- First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
- AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read more
AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
Chronological age does not always reflect how fast the body is truly aging, and current biological age tests often rely on DNA-based markers that may miss early organ-level decline. Detecting subtle, age-related... Read moreMRI
view channel
New Material Boosts MRI Image Quality
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a cornerstone of modern diagnostics, yet certain deep or anatomically complex tissues, including delicate structures of the eye and orbit, remain difficult to visualize clearly.... Read more
AI Model Reads and Diagnoses Brain MRI in Seconds
Brain MRI scans are critical for diagnosing strokes, hemorrhages, and other neurological disorders, but interpreting them can take hours or even days due to growing demand and limited specialist availability.... Read moreMRI Scan Breakthrough to Help Avoid Risky Invasive Tests for Heart Patients
Heart failure patients often require right heart catheterization to assess how severely their heart is struggling to pump blood, a procedure that involves inserting a tube into the heart to measure blood... Read more
MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
Recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies widely, with some patients regaining full function while others are left with lasting disabilities. Prognosis is especially difficult to assess in patients... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
AI Model Accurately Detects Placenta Accreta in Pregnancy Before Delivery
Placenta accreta spectrum (PAS) is a life-threatening pregnancy complication in which the placenta abnormally attaches to the uterine wall. The condition is a leading cause of maternal mortality and morbidity... Read more
Portable Ultrasound Sensor to Enable Earlier Breast Cancer Detection
Breast cancer screening relies heavily on annual mammograms, but aggressive tumors can develop between scans, accounting for up to 30 percent of cases. These interval cancers are often diagnosed later,... Read more
Portable Imaging Scanner to Diagnose Lymphatic Disease in Real Time
Lymphatic disorders affect hundreds of millions of people worldwide and are linked to conditions ranging from limb swelling and organ dysfunction to birth defects and cancer-related complications.... Read more
Imaging Technique Generates Simultaneous 3D Color Images of Soft-Tissue Structure and Vasculature
Medical imaging tools often force clinicians to choose between speed, structural detail, and functional insight. Ultrasound is fast and affordable but typically limited to two-dimensional anatomy, while... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
Targeted cancer therapies only work when tumor cells express the specific molecular structures they are designed to attack. In urothelial carcinoma, a common form of bladder cancer, the cell surface protein... Read more
Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
Targeted cancer therapies can be highly effective, but only when a patient’s tumor expresses the specific protein the treatment is designed to attack. Determining this usually requires biopsies or advanced... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Nuclear Medicine Set for Continued Growth Driven by Demand for Precision Diagnostics
Clinical imaging services face rising demand for precise molecular diagnostics and targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy as cancer and chronic disease rates climb. A new market analysis projects rapid expansion... Read more



















