POC MRI Helps Evaluate Intracerebral Hemorrhage
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 09 Sep 2021 |
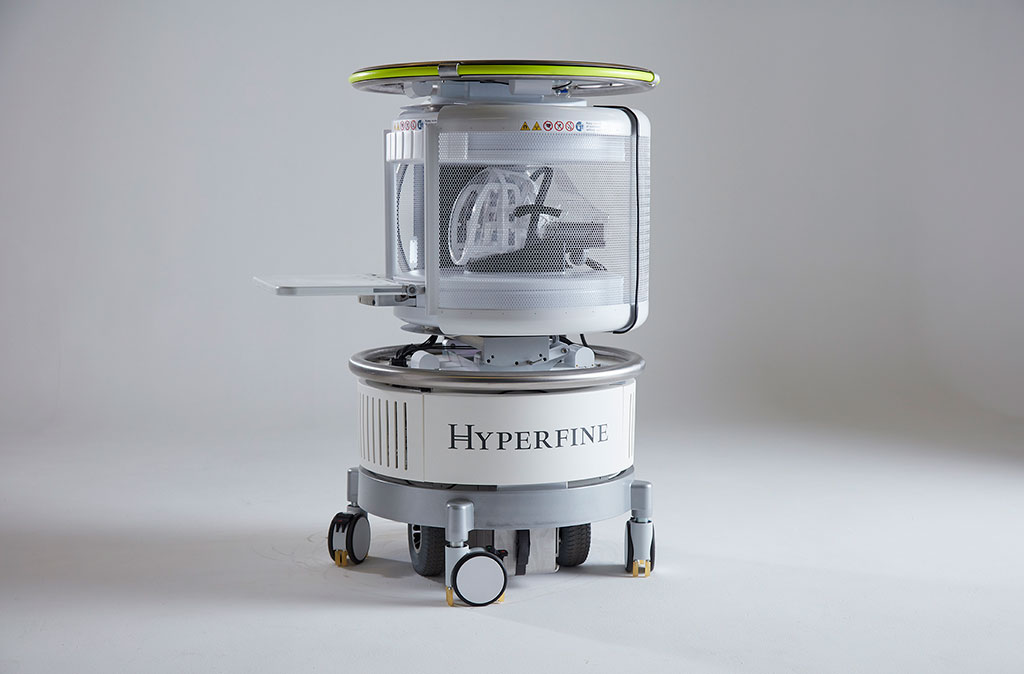

Image: The Swoop low-field pMRI device (Photo courtesy of HyperFine Research)
A new study confirms that portable magnetic resonance imaging (pMRI) can scan for intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) at the point-of-care (POC).
Researchers at Yale School of Medicine (New Haven, CT, USA) and Yale New Haven Hospital (YNHH; CT, USA) conducted a study involving 144 pMRI examinations (56 ICH, 48 acute ischemic stroke, 40 healthy controls) taken at the bedside at YNHH from July 2018 to November 2020, and compared them to traditional neuroimaging scans (non-contrast computerized tomography (CT) or 1.5/3 T MRI) to examine the efficacy of the Hyperfine Research (Guilford, CT, USA) Swoop low-field (0.064 T) pMRI device.
Two neuroradiologists evaluated all pMRI scans, with one ICH imaging core lab researcher reviewing the cases of disagreement. The raters correctly detected ICH in 45 of 56 cases (80.4%), and blood-negative cases were correctly identified in 85 of 88 cases (96.6%). Manually segmented hematoma volumes and ABC/2 formula for estimated volumes on pMRI correlated with conventional imaging volumes. Hematoma volumes measured on pMRI at discharge also correlated with manual and ABC/2 volumes. The study was published on August 25, 2021, in Nature Communications.
“There is no question this device can help save lives in resource-limited settings, such as rural hospitals or developing countries,” said senior author professor of neurology and neurosurgery Kevin Sheth, MD, of Yale School of Medicine. “There is also now a path to see how it can help in modern settings. It is of critical importance to continue to collect more data across a range of stroke characteristics so that we can maximize the potential benefit of this approach.”
The Swoop pMRI is a low-field system that features standard permanent magnets that require no power or cooling systems, producing an image using low-power radio waves and magnetic fields instead. The Swoop is controlled via a tablet device, using sequences and protocols selected from a playlist. As a result, the system is 10X lower in weight than current fixed conventional MRI systems, costs a fraction of the price, is highly portable, and plugs directly into a standard electrical wall outlet, with 35X lower power consumption.
Related Links:
Yale School of Medicine
Yale New Haven Hospital
Hyperfine Research
Researchers at Yale School of Medicine (New Haven, CT, USA) and Yale New Haven Hospital (YNHH; CT, USA) conducted a study involving 144 pMRI examinations (56 ICH, 48 acute ischemic stroke, 40 healthy controls) taken at the bedside at YNHH from July 2018 to November 2020, and compared them to traditional neuroimaging scans (non-contrast computerized tomography (CT) or 1.5/3 T MRI) to examine the efficacy of the Hyperfine Research (Guilford, CT, USA) Swoop low-field (0.064 T) pMRI device.
Two neuroradiologists evaluated all pMRI scans, with one ICH imaging core lab researcher reviewing the cases of disagreement. The raters correctly detected ICH in 45 of 56 cases (80.4%), and blood-negative cases were correctly identified in 85 of 88 cases (96.6%). Manually segmented hematoma volumes and ABC/2 formula for estimated volumes on pMRI correlated with conventional imaging volumes. Hematoma volumes measured on pMRI at discharge also correlated with manual and ABC/2 volumes. The study was published on August 25, 2021, in Nature Communications.
“There is no question this device can help save lives in resource-limited settings, such as rural hospitals or developing countries,” said senior author professor of neurology and neurosurgery Kevin Sheth, MD, of Yale School of Medicine. “There is also now a path to see how it can help in modern settings. It is of critical importance to continue to collect more data across a range of stroke characteristics so that we can maximize the potential benefit of this approach.”
The Swoop pMRI is a low-field system that features standard permanent magnets that require no power or cooling systems, producing an image using low-power radio waves and magnetic fields instead. The Swoop is controlled via a tablet device, using sequences and protocols selected from a playlist. As a result, the system is 10X lower in weight than current fixed conventional MRI systems, costs a fraction of the price, is highly portable, and plugs directly into a standard electrical wall outlet, with 35X lower power consumption.
Related Links:
Yale School of Medicine
Yale New Haven Hospital
Hyperfine Research
Latest MRI News
- New Material Boosts MRI Image Quality
- AI Model Reads and Diagnoses Brain MRI in Seconds
- MRI Scan Breakthrough to Help Avoid Risky Invasive Tests for Heart Patients
- MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
- Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
- AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
- AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
- New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
- Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
- MRI to Replace Painful Spinal Tap for Faster MS Diagnosis
- MRI Scans Can Identify Cardiovascular Disease Ten Years in Advance
- Simple Brain Scan Diagnoses Parkinson's Disease Years Before It Becomes Untreatable
- Cutting-Edge MRI Technology to Revolutionize Diagnosis of Common Heart Problem
- New MRI Technique Reveals True Heart Age to Prevent Attacks and Strokes
- AI Tool Predicts Relapse of Pediatric Brain Cancer from Brain MRI Scans
- AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read more
AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
Chronological age does not always reflect how fast the body is truly aging, and current biological age tests often rely on DNA-based markers that may miss early organ-level decline. Detecting subtle, age-related... Read moreMRI
view channel
New Material Boosts MRI Image Quality
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a cornerstone of modern diagnostics, yet certain deep or anatomically complex tissues, including delicate structures of the eye and orbit, remain difficult to visualize clearly.... Read more
AI Model Reads and Diagnoses Brain MRI in Seconds
Brain MRI scans are critical for diagnosing strokes, hemorrhages, and other neurological disorders, but interpreting them can take hours or even days due to growing demand and limited specialist availability.... Read moreMRI Scan Breakthrough to Help Avoid Risky Invasive Tests for Heart Patients
Heart failure patients often require right heart catheterization to assess how severely their heart is struggling to pump blood, a procedure that involves inserting a tube into the heart to measure blood... Read more
MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
Recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies widely, with some patients regaining full function while others are left with lasting disabilities. Prognosis is especially difficult to assess in patients... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Reusable Gel Pad Made from Tamarind Seed Could Transform Ultrasound Examinations
Ultrasound imaging depends on a conductive gel to eliminate air between the probe and the skin so sound waves can pass clearly into the body. While the imaging technology is fast, safe, and noninvasive,... Read more
AI Model Accurately Detects Placenta Accreta in Pregnancy Before Delivery
Placenta accreta spectrum (PAS) is a life-threatening pregnancy complication in which the placenta abnormally attaches to the uterine wall. The condition is a leading cause of maternal mortality and morbidity... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
Targeted cancer therapies only work when tumor cells express the specific molecular structures they are designed to attack. In urothelial carcinoma, a common form of bladder cancer, the cell surface protein... Read more
Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
Targeted cancer therapies can be highly effective, but only when a patient’s tumor expresses the specific protein the treatment is designed to attack. Determining this usually requires biopsies or advanced... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer is a form of head and neck cancer that can spread through lymph nodes, significantly affecting survival and treatment decisions. Current therapies often involve combinations of surgery,... Read more
New 3D Imaging System Addresses MRI, CT and Ultrasound Limitations
Medical imaging is central to diagnosing and managing injuries, cancer, infections, and chronic diseases, yet existing tools each come with trade-offs. Ultrasound, X-ray, CT, and MRI can be costly, time-consuming,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Nuclear Medicine Set for Continued Growth Driven by Demand for Precision Diagnostics
Clinical imaging services face rising demand for precise molecular diagnostics and targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy as cancer and chronic disease rates climb. A new market analysis projects rapid expansion... Read more























