AI Tool Improves Diagnosis of Joint Cartilage Defects
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 03 Aug 2021 |
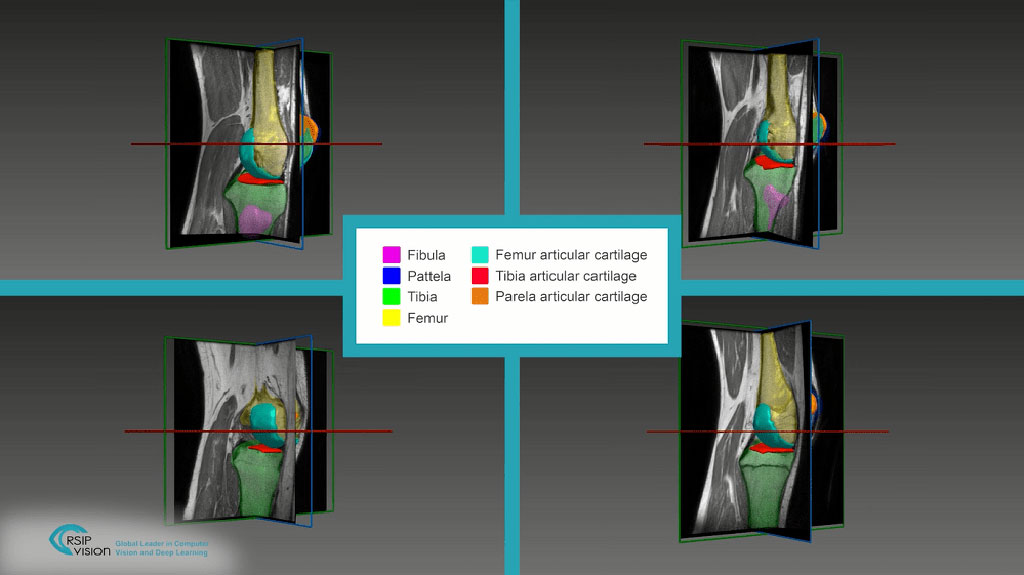
A novel AI tool aids articular cartilage segmentation (Photo courtesy of RSIP Vision)
New artificial intelligence (AI) software provides fully automated precise segmentation and robust assessment of chondral lesions, including location, diameter, shape, and boundaries.
The RSIP Vision (Jerusalem, Israel) articular cartilage segmentation tool is an AI algorithm designed to deliver accurate, non-invasive and automatic assessment of chondral lesions in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of the hips, knees, and ankles. The algorithm provides an accurate measurement of the location, geometry, and boundaries of osteochondral lesions, enabling physicians to evaluate the extent of the damage, select the appropriate treatment approach, and assess its efficacy.
The segmentation is carried out by classifying image pixels (or voxels, in 3D cases) using random forest classifiers, which delineate the boundaries between points in feature space belonging to different classes. The random forest is composed of an ensemble of decision trees, trained to assign membership value to either the lesion or the background group. To construct each tree, a different bootstrap subset of the training data is chosen at random. Since trees are uncorrelated, the overall decision in random forest is consistent by using a majority vote of trees with different structure.
“Our new segmentation tool makes it easier to pinpoint specific points and boundaries in images, which in turn leads to greater accuracy during surgeries without being dependent on the capability and experience of a specific individual,” said Ron Soferman, founder & CEO of RSIP Vision. “RSIP Vision will continue to drive innovation in image analysis across the medical verticals through custom software, advanced algorithm development and custom technologies.”
“Analyzing the parameters of the lesion and its boundaries allows the surgeon, along with the patient, to choose the ideal cartilage repair technique,” said orthopedic surgeon Shai Factor, MD, of Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center (Israel). “Additionally, in cases where cartilage transfer is the chosen option, this technology will make it possible to map the donor cartilage area as well and plan the surgery in the best way that will lead to better outcomes.”
Chondral lesions are prevalent among young and active patients, and due to the avascular nature of articular cartilage, healing potential is limited. In many cases, chondral lesions limit the athlete’s ability to participate in sports and even affect their daily activities. Cartilage segmentation is a crucial tool that aids the physician in choosing optimal treatment for the patient, including mosaicplasty, micro-fracture, osteochondral autograft transfer system (OATS), or autologous chondrocyte implantation.
Related Links:
RSIP Vision
The RSIP Vision (Jerusalem, Israel) articular cartilage segmentation tool is an AI algorithm designed to deliver accurate, non-invasive and automatic assessment of chondral lesions in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of the hips, knees, and ankles. The algorithm provides an accurate measurement of the location, geometry, and boundaries of osteochondral lesions, enabling physicians to evaluate the extent of the damage, select the appropriate treatment approach, and assess its efficacy.
The segmentation is carried out by classifying image pixels (or voxels, in 3D cases) using random forest classifiers, which delineate the boundaries between points in feature space belonging to different classes. The random forest is composed of an ensemble of decision trees, trained to assign membership value to either the lesion or the background group. To construct each tree, a different bootstrap subset of the training data is chosen at random. Since trees are uncorrelated, the overall decision in random forest is consistent by using a majority vote of trees with different structure.
“Our new segmentation tool makes it easier to pinpoint specific points and boundaries in images, which in turn leads to greater accuracy during surgeries without being dependent on the capability and experience of a specific individual,” said Ron Soferman, founder & CEO of RSIP Vision. “RSIP Vision will continue to drive innovation in image analysis across the medical verticals through custom software, advanced algorithm development and custom technologies.”
“Analyzing the parameters of the lesion and its boundaries allows the surgeon, along with the patient, to choose the ideal cartilage repair technique,” said orthopedic surgeon Shai Factor, MD, of Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center (Israel). “Additionally, in cases where cartilage transfer is the chosen option, this technology will make it possible to map the donor cartilage area as well and plan the surgery in the best way that will lead to better outcomes.”
Chondral lesions are prevalent among young and active patients, and due to the avascular nature of articular cartilage, healing potential is limited. In many cases, chondral lesions limit the athlete’s ability to participate in sports and even affect their daily activities. Cartilage segmentation is a crucial tool that aids the physician in choosing optimal treatment for the patient, including mosaicplasty, micro-fracture, osteochondral autograft transfer system (OATS), or autologous chondrocyte implantation.
Related Links:
RSIP Vision
Latest Imaging IT News
- New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
- Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
- AI-Based Mammography Triage Software Helps Dramatically Improve Interpretation Process
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Program Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk from CT Images
- Image Management Platform Streamlines Treatment Plans
- AI-Based Technology for Ultrasound Image Analysis Receives FDA Approval
- AI Technology for Detecting Breast Cancer Receives CE Mark Approval
- Digital Pathology Software Improves Workflow Efficiency
- Patient-Centric Portal Facilitates Direct Imaging Access
- New Workstation Supports Customer-Driven Imaging Workflow
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI Detects Fatty Liver Disease from Chest X-Rays
Fatty liver disease, which results from excess fat accumulation in the liver, is believed to impact approximately one in four individuals globally. If not addressed in time, it can progress to severe conditions... Read more
AI Detects Hidden Heart Disease in Existing CT Chest Scans
Coronary artery calcium (CAC) is a major indicator of cardiovascular risk, but its assessment typically requires a specialized “gated” CT scan that synchronizes with the heartbeat. In contrast, most chest... Read moreUltrasound
view channel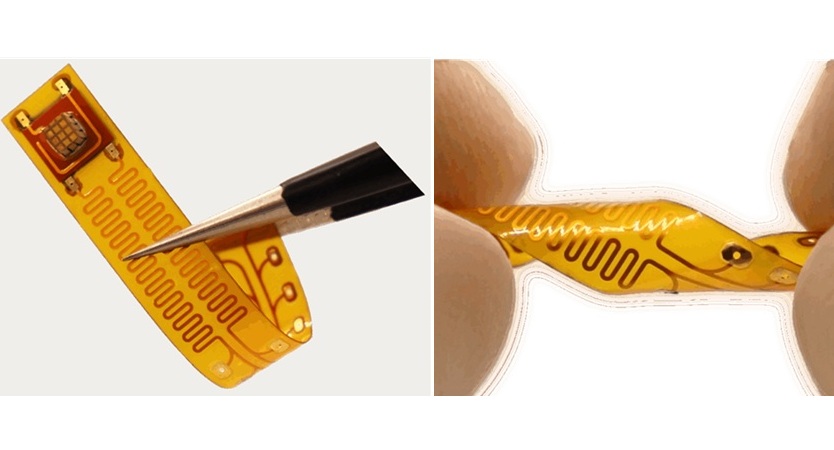
Wireless Chronic Pain Management Device to Reduce Need for Painkillers and Surgery
Chronic pain affects millions of people globally, often leading to long-term disability and dependence on opioid medications, which carry significant risks of side effects and addiction.... Read more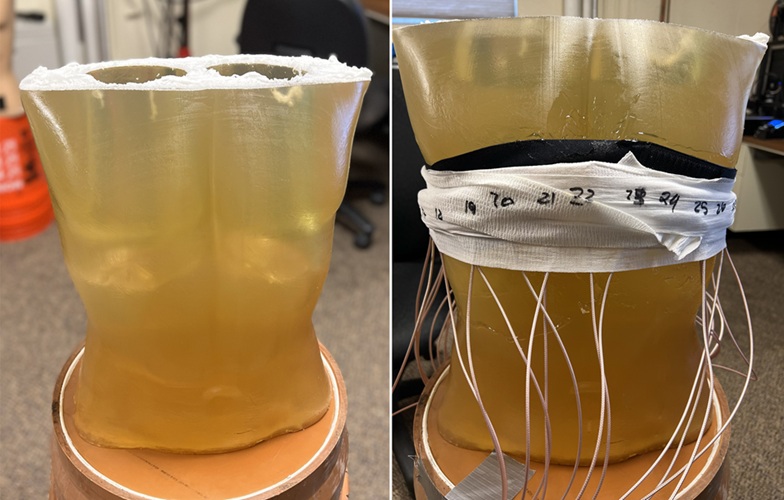
New Medical Ultrasound Imaging Technique Enables ICU Bedside Monitoring
Ultrasound computed tomography (USCT) presents a safer alternative to imaging techniques like X-ray computed tomography (commonly known as CT or “CAT” scans) because it does not produce ionizing radiation.... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Novel Bacteria-Specific PET Imaging Approach Detects Hard-To-Diagnose Lung Infections
Mycobacteroides abscessus is a rapidly growing mycobacteria that primarily affects immunocompromised patients and those with underlying lung diseases, such as cystic fibrosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary... Read more
New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the second leading cause of cancer-related death among men in the United States. However, the majority of older men diagnosed with prostate cancer have slow-growing, low-risk forms of... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel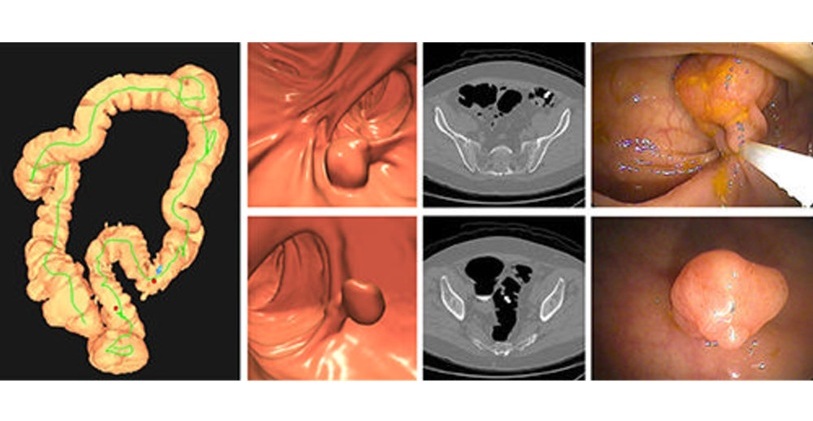
CT Colonography Beats Stool DNA Testing for Colon Cancer Screening
As colorectal cancer remains the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, early detection through screening is vital to reduce advanced-stage treatments and associated costs.... Read more
First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
Currently, patients with conditions such as heart failure, pneumonia, or respiratory distress often require multiple imaging procedures that are intermittent, disruptive, and involve high levels of radiation.... Read more
AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
Radioligand therapy, a form of targeted nuclear medicine, has recently gained attention for its potential in treating specific types of tumors. However, one of the potential side effects of this therapy... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more










 Guided Devices.jpg)


.jpeg)




