Pediatric Ultrasound-Guided Central Venous Access Shown Safe
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 13 Jan 2021 |
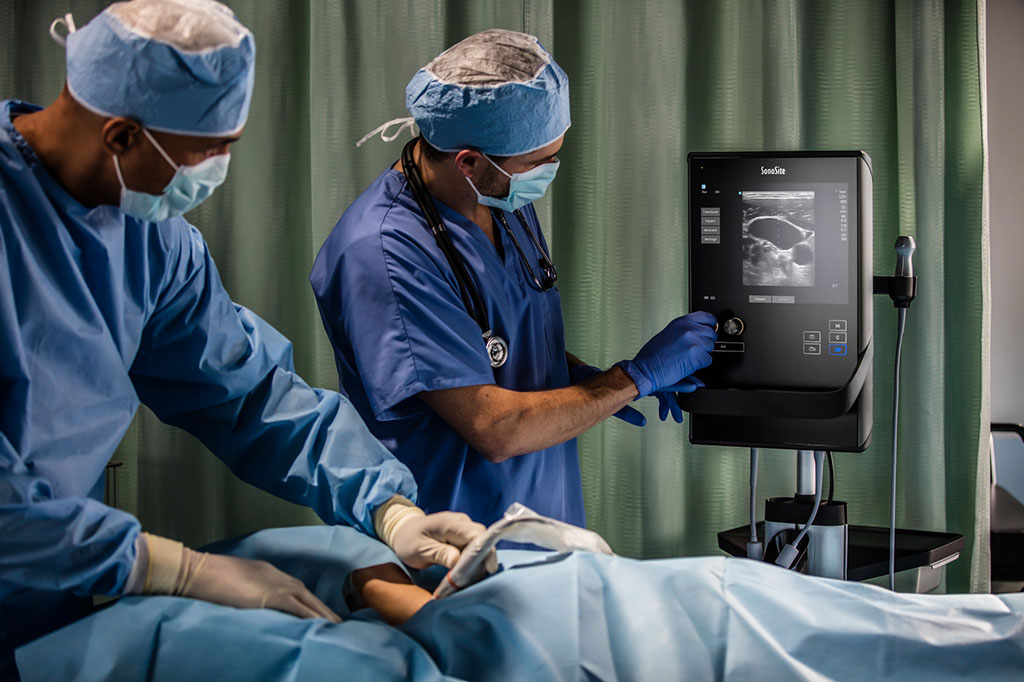
Image: Portable ultrasound facilitates central line placement (Photo courtesy of Fujifilm SonoSite)
A new study puts to rest any lingering concerns over the use ultrasound-guided percutaneous tunneled central line placement in children.
Researchers at the University of Sydney (US; Australia), The Children's Hospital at Westmead (CHW; Sydney, Australia), and Tung Wah College (Hong Kong) conducted a prospective randomized trial involving 108 children (64 male) to compare ultrasound-guided central venous access to open insertion. The researchers used the Fujifilm SonoSite (Bothell, WA, USA) M-Turbo system with an intraoperative linear array probe, passing the needle perpendicular to the transducer axis and in line with the internal jugular vein (IJV) to perform vein puncture.
The primary outcome was complication (both immediate and late), with secondary outcomes being time taken to complete procedure, conversion rates, and duration of line use. The results showed more than one needle puncture was needed in 22%, and 12 patients needed more than one insertion to achieve optimal position of the tip; 11 patients experienced immediate/late complications. Operating time was 20% shorter with percutaneous access, with no conversions, and children in the ultrasound group had significantly larger vein size after removal, despite having similar vein sizes before insertion. The study was published on December 24, 2020, in Journal of Surgical Research.
“The study as it was performed was reflective of real-life practice, and showed ultrasound-guided percutaneous lines were safe to perform, but there was no dedicated radiology technician present in the operating room at the time of the procedure, which meant our times were longer than they should be,” concluded lead author Soundappan Soundappan, MD, of the CHW department of surgery. “However, even with a shortage of radiology team members, the ultrasound-guided placement provided its worth in the trial.”
Researchers at the University of Sydney (US; Australia), The Children's Hospital at Westmead (CHW; Sydney, Australia), and Tung Wah College (Hong Kong) conducted a prospective randomized trial involving 108 children (64 male) to compare ultrasound-guided central venous access to open insertion. The researchers used the Fujifilm SonoSite (Bothell, WA, USA) M-Turbo system with an intraoperative linear array probe, passing the needle perpendicular to the transducer axis and in line with the internal jugular vein (IJV) to perform vein puncture.
The primary outcome was complication (both immediate and late), with secondary outcomes being time taken to complete procedure, conversion rates, and duration of line use. The results showed more than one needle puncture was needed in 22%, and 12 patients needed more than one insertion to achieve optimal position of the tip; 11 patients experienced immediate/late complications. Operating time was 20% shorter with percutaneous access, with no conversions, and children in the ultrasound group had significantly larger vein size after removal, despite having similar vein sizes before insertion. The study was published on December 24, 2020, in Journal of Surgical Research.
“The study as it was performed was reflective of real-life practice, and showed ultrasound-guided percutaneous lines were safe to perform, but there was no dedicated radiology technician present in the operating room at the time of the procedure, which meant our times were longer than they should be,” concluded lead author Soundappan Soundappan, MD, of the CHW department of surgery. “However, even with a shortage of radiology team members, the ultrasound-guided placement provided its worth in the trial.”
Latest Ultrasound News
- Imaging Technique Generates Simultaneous 3D Color Images of Soft-Tissue Structure and Vasculature
- Wearable Ultrasound Imaging System to Enable Real-Time Disease Monitoring
- Ultrasound Technique Visualizes Deep Blood Vessels in 3D Without Contrast Agents
- Ultrasound Probe Images Entire Organ in 4D

- Disposable Ultrasound Patch Performs Better Than Existing Devices
- Non-Invasive Ultrasound-Based Tool Accurately Detects Infant Meningitis
- Breakthrough Deep Learning Model Enhances Handheld 3D Medical Imaging
- Pain-Free Breast Imaging System Performs One Minute Cancer Scan
- Wireless Chronic Pain Management Device to Reduce Need for Painkillers and Surgery
- New Medical Ultrasound Imaging Technique Enables ICU Bedside Monitoring
- New Incision-Free Technique Halts Growth of Debilitating Brain Lesions
- AI-Powered Lung Ultrasound Outperforms Human Experts in Tuberculosis Diagnosis
- AI Identifies Heart Valve Disease from Common Imaging Test
- Novel Imaging Method Enables Early Diagnosis and Treatment Monitoring of Type 2 Diabetes
- Ultrasound-Based Microscopy Technique to Help Diagnose Small Vessel Diseases
- Smart Ultrasound-Activated Immune Cells Destroy Cancer Cells for Extended Periods
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read more
AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
Chronological age does not always reflect how fast the body is truly aging, and current biological age tests often rely on DNA-based markers that may miss early organ-level decline. Detecting subtle, age-related... Read moreMRI
view channel
MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
Recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies widely, with some patients regaining full function while others are left with lasting disabilities. Prognosis is especially difficult to assess in patients... Read more
Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
Vascular dysfunction in the spinal cord contributes to multiple neurological conditions, including traumatic injuries and degenerative cervical myelopathy, where reduced blood flow can lead to progressive... Read more
AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
A cardiac MRI can reveal critical information about the heart’s function and any abnormalities, but traditional scans take 30 to 90 minutes and often suffer from poor image quality due to patient movement.... Read more
AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is one of the most common inherited heart conditions and a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young individuals and athletes. While many patients live normal lives, some... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
Targeted cancer therapies only work when tumor cells express the specific molecular structures they are designed to attack. In urothelial carcinoma, a common form of bladder cancer, the cell surface protein... Read more
Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
Targeted cancer therapies can be highly effective, but only when a patient’s tumor expresses the specific protein the treatment is designed to attack. Determining this usually requires biopsies or advanced... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer is a form of head and neck cancer that can spread through lymph nodes, significantly affecting survival and treatment decisions. Current therapies often involve combinations of surgery,... Read more
New 3D Imaging System Addresses MRI, CT and Ultrasound Limitations
Medical imaging is central to diagnosing and managing injuries, cancer, infections, and chronic diseases, yet existing tools each come with trade-offs. Ultrasound, X-ray, CT, and MRI can be costly, time-consuming,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more


















