Novel AI Algorithm for Mammography Interpretation Can Successfully Spot Breast Cancer Years Before Radiologists
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 13 Jan 2021 |
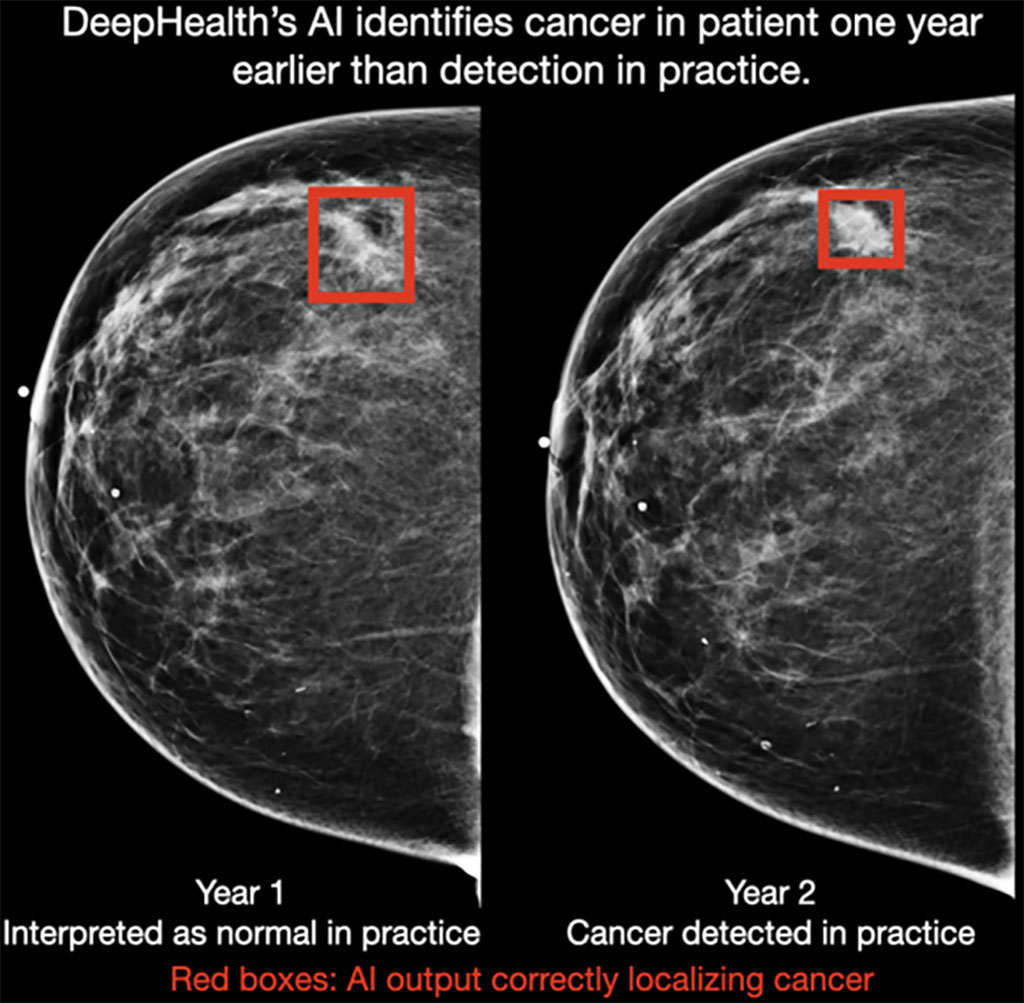
Image: DeepHealth`s AI identifies cancer in a patient one year earlier than detected in practice (Photo courtesy of DeepHealth)
A novel artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm for mammography interpretation has demonstrated the ability to detect breast cancer a year or more earlier than current practice.
DeepHealth (Cambridge, MA, USA), a wholly owned subsidiary of RadNet, Inc. (Los Angeles, CA, USA), compared its AI to five full-time, breast-fellowship-trained expert radiologists reading the same screening mammograms. The software exhibited higher performance than all five radiologists, and the results suggest that the AI could help detect cancer one to two years earlier than standard interpretation in many cases.
Additionally, the software showed promising generalization capabilities, demonstrating strong performance when tested across clinical sites and populations that were not directly involved in training the AI algorithms. While AI holds tremendous promise for improving screening mammography interpretation, there remain substantial challenges in developing expert-level AI. The new study by DeepHealth demonstrates progress in resolving these challenges.
“Reaching world-class performance requires a new way of building AI,” said Gregory Sorensen, M.D., CEO, and co-founder of DeepHealth. “The brute-force methods that have worked so well in other domains, such as self-driving cars or game playing, where data is plentiful, have not translated effectively to many parts of medicine, where human data is often scarce. For example, to train the technology for better detection, AI algorithms must be developed from annotated data where the cancer status is known. Such data can be difficult to obtain. Then, to validate performance, the AI should be tested across different clinical sites and patient populations in different scenarios.”
“We have developed an approach that mimics how humans often learn by progressively training the AI models on more difficult tasks. By leveraging prior information learned in each successive training stage, this strategy results in AI that detects cancer accurately while also relying less on highly-annotated data,” said lead author Bill Lotter, Ph.D., CTO, and co-founder of DeepHealth. “Our approach and validation extend to 3D mammography, which is particularly important given its growing use and the significant challenges it presents for AI.”
Related Links:
DeepHealth
RadNet, Inc.
DeepHealth (Cambridge, MA, USA), a wholly owned subsidiary of RadNet, Inc. (Los Angeles, CA, USA), compared its AI to five full-time, breast-fellowship-trained expert radiologists reading the same screening mammograms. The software exhibited higher performance than all five radiologists, and the results suggest that the AI could help detect cancer one to two years earlier than standard interpretation in many cases.
Additionally, the software showed promising generalization capabilities, demonstrating strong performance when tested across clinical sites and populations that were not directly involved in training the AI algorithms. While AI holds tremendous promise for improving screening mammography interpretation, there remain substantial challenges in developing expert-level AI. The new study by DeepHealth demonstrates progress in resolving these challenges.
“Reaching world-class performance requires a new way of building AI,” said Gregory Sorensen, M.D., CEO, and co-founder of DeepHealth. “The brute-force methods that have worked so well in other domains, such as self-driving cars or game playing, where data is plentiful, have not translated effectively to many parts of medicine, where human data is often scarce. For example, to train the technology for better detection, AI algorithms must be developed from annotated data where the cancer status is known. Such data can be difficult to obtain. Then, to validate performance, the AI should be tested across different clinical sites and patient populations in different scenarios.”
“We have developed an approach that mimics how humans often learn by progressively training the AI models on more difficult tasks. By leveraging prior information learned in each successive training stage, this strategy results in AI that detects cancer accurately while also relying less on highly-annotated data,” said lead author Bill Lotter, Ph.D., CTO, and co-founder of DeepHealth. “Our approach and validation extend to 3D mammography, which is particularly important given its growing use and the significant challenges it presents for AI.”
Related Links:
DeepHealth
RadNet, Inc.
Latest Industry News News
- Nuclear Medicine Set for Continued Growth Driven by Demand for Precision Diagnostics
- GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
- Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
- Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
- Bracco Diagnostics and ColoWatch Partner to Expand Availability CRC Screening Tests Using Virtual Colonoscopy
- Mindray Partners with TeleRay to Streamline Ultrasound Delivery
- Philips and Medtronic Partner on Stroke Care
- Siemens and Medtronic Enter into Global Partnership for Advancing Spine Care Imaging Technologies
- RSNA 2024 Technical Exhibits to Showcase Latest Advances in Radiology
- Bracco Collaborates with Arrayus on Microbubble-Assisted Focused Ultrasound Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer
- Innovative Collaboration to Enhance Ischemic Stroke Detection and Elevate Standards in Diagnostic Imaging
- RSNA 2024 Registration Opens
- Microsoft collaborates with Leading Academic Medical Systems to Advance AI in Medical Imaging
- GE HealthCare Acquires Intelligent Ultrasound Group’s Clinical Artificial Intelligence Business
- Bayer and Rad AI Collaborate on Expanding Use of Cutting Edge AI Radiology Operational Solutions
- Polish Med-Tech Company BrainScan to Expand Extensively into Foreign Markets
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read more
AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
Chronological age does not always reflect how fast the body is truly aging, and current biological age tests often rely on DNA-based markers that may miss early organ-level decline. Detecting subtle, age-related... Read moreMRI
view channel
New Material Boosts MRI Image Quality
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a cornerstone of modern diagnostics, yet certain deep or anatomically complex tissues, including delicate structures of the eye and orbit, remain difficult to visualize clearly.... Read more
AI Model Reads and Diagnoses Brain MRI in Seconds
Brain MRI scans are critical for diagnosing strokes, hemorrhages, and other neurological disorders, but interpreting them can take hours or even days due to growing demand and limited specialist availability.... Read moreMRI Scan Breakthrough to Help Avoid Risky Invasive Tests for Heart Patients
Heart failure patients often require right heart catheterization to assess how severely their heart is struggling to pump blood, a procedure that involves inserting a tube into the heart to measure blood... Read more
MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
Recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies widely, with some patients regaining full function while others are left with lasting disabilities. Prognosis is especially difficult to assess in patients... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Reusable Gel Pad Made from Tamarind Seed Could Transform Ultrasound Examinations
Ultrasound imaging depends on a conductive gel to eliminate air between the probe and the skin so sound waves can pass clearly into the body. While the imaging technology is fast, safe, and noninvasive,... Read more
AI Model Accurately Detects Placenta Accreta in Pregnancy Before Delivery
Placenta accreta spectrum (PAS) is a life-threatening pregnancy complication in which the placenta abnormally attaches to the uterine wall. The condition is a leading cause of maternal mortality and morbidity... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
Targeted cancer therapies only work when tumor cells express the specific molecular structures they are designed to attack. In urothelial carcinoma, a common form of bladder cancer, the cell surface protein... Read more
Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
Targeted cancer therapies can be highly effective, but only when a patient’s tumor expresses the specific protein the treatment is designed to attack. Determining this usually requires biopsies or advanced... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Tool Predicts Side Effects from Lung Cancer Treatment
Radiation therapy is a central treatment for lung cancer, but even carefully targeted radiation can affect surrounding healthy tissue. Patients may develop side effects such as lung inflammation, coughing,... Read more
AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer is a form of head and neck cancer that can spread through lymph nodes, significantly affecting survival and treatment decisions. Current therapies often involve combinations of surgery,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more





















