Novel MRI Contrast Agent Swiftly Eliminated from Body
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 12 Jan 2021 |
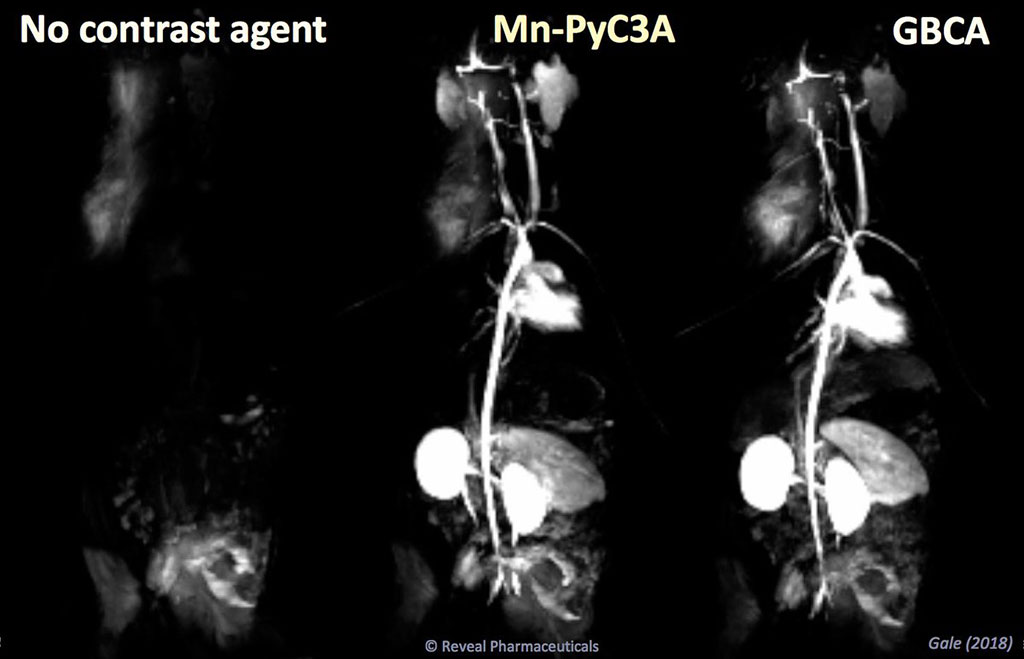
Image: MRI manganese-based contrast agents are as efficient as gadolinium, but less toxic (Photo courtesy of Eric Gale/ MGH)
A new study suggests that a manganese (Mn) based magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agent could soon replace gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) as a non-toxic alternative.
Researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH; Boston, USA) and Harvard Medical School (HMS; Boston, MA, USA) conducted a study to compare the new contrast agent, Mn-PyC3A, to the older Mn-based contrast agent mangafodipir (Mn-DPDP), and to the GBCA gadoterate (Gd-DOTA). For the study, the researchers used simultaneous positron emission tomography (PET) and MRI (PET-MRI) to compare pharmacokinetics, in-vivo biodistribution, and whole-body elimination in a rat model.
The results revealed that while both Mn-PyC3A and Mn-DPDP are eliminated via mixed hepatobiliary and renal routes, a greater fraction of the Mn-PyC3A contrast agent was eliminated by renal filtration. Whole-body PET images showed that Mn-PyC3A was efficiently eliminated, whereas Mn-DPDP was retained throughout the body. The experimental data also showed significantly more efficient whole-body elimination of Mn-PyC3A than Gd-DOTA both one day and one week after injection. The study was published on October 30, 2020, in Investigative Radiology.
“This manganese-based contrast agent does everything a GBCA would do; this is obviously important for patients with chronic kidney disease and other forms of renal insufficiency that might require careful risk/benefit analysis before undergoing a GBCA-enhanced MRI,” said senior author biomedical engineer Eric Gale, PhD, of MGH and HMS, co-inventor of Mn-PyC3A. “But we can also envision giving Mn-PyC3A to any patient requiring a contrast-enhanced MRI. There are patients who require many GBCA-enhanced MRI examinations over the course of years for disease surveillance or screening.”
Efficient elimination of a contrast agent is critical for tissue health. Since Gadolinium is eliminated only from the kidneys, retention from GBCAs can cause nephrogenic systemic fibrosis, and it is also retained in the brain, bones, skin and other organs, even in patients with normal kidney function. Mn-PyC3A, on the other hand, is also eliminated from the liver, compensating for diminished renal function in kidney patients and ensuring a more rapid and complete elimination.
Related Links:
Massachusetts General Hospital
Harvard Medical School
Researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH; Boston, USA) and Harvard Medical School (HMS; Boston, MA, USA) conducted a study to compare the new contrast agent, Mn-PyC3A, to the older Mn-based contrast agent mangafodipir (Mn-DPDP), and to the GBCA gadoterate (Gd-DOTA). For the study, the researchers used simultaneous positron emission tomography (PET) and MRI (PET-MRI) to compare pharmacokinetics, in-vivo biodistribution, and whole-body elimination in a rat model.
The results revealed that while both Mn-PyC3A and Mn-DPDP are eliminated via mixed hepatobiliary and renal routes, a greater fraction of the Mn-PyC3A contrast agent was eliminated by renal filtration. Whole-body PET images showed that Mn-PyC3A was efficiently eliminated, whereas Mn-DPDP was retained throughout the body. The experimental data also showed significantly more efficient whole-body elimination of Mn-PyC3A than Gd-DOTA both one day and one week after injection. The study was published on October 30, 2020, in Investigative Radiology.
“This manganese-based contrast agent does everything a GBCA would do; this is obviously important for patients with chronic kidney disease and other forms of renal insufficiency that might require careful risk/benefit analysis before undergoing a GBCA-enhanced MRI,” said senior author biomedical engineer Eric Gale, PhD, of MGH and HMS, co-inventor of Mn-PyC3A. “But we can also envision giving Mn-PyC3A to any patient requiring a contrast-enhanced MRI. There are patients who require many GBCA-enhanced MRI examinations over the course of years for disease surveillance or screening.”
Efficient elimination of a contrast agent is critical for tissue health. Since Gadolinium is eliminated only from the kidneys, retention from GBCAs can cause nephrogenic systemic fibrosis, and it is also retained in the brain, bones, skin and other organs, even in patients with normal kidney function. Mn-PyC3A, on the other hand, is also eliminated from the liver, compensating for diminished renal function in kidney patients and ensuring a more rapid and complete elimination.
Related Links:
Massachusetts General Hospital
Harvard Medical School
Latest MRI News
- New Material Boosts MRI Image Quality
- AI Model Reads and Diagnoses Brain MRI in Seconds
- MRI Scan Breakthrough to Help Avoid Risky Invasive Tests for Heart Patients
- MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
- Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
- AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
- AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
- New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
- Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
- MRI to Replace Painful Spinal Tap for Faster MS Diagnosis
- MRI Scans Can Identify Cardiovascular Disease Ten Years in Advance
- Simple Brain Scan Diagnoses Parkinson's Disease Years Before It Becomes Untreatable
- Cutting-Edge MRI Technology to Revolutionize Diagnosis of Common Heart Problem
- New MRI Technique Reveals True Heart Age to Prevent Attacks and Strokes
- AI Tool Predicts Relapse of Pediatric Brain Cancer from Brain MRI Scans
- AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read more
AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
Chronological age does not always reflect how fast the body is truly aging, and current biological age tests often rely on DNA-based markers that may miss early organ-level decline. Detecting subtle, age-related... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
AI Model Accurately Detects Placenta Accreta in Pregnancy Before Delivery
Placenta accreta spectrum (PAS) is a life-threatening pregnancy complication in which the placenta abnormally attaches to the uterine wall. The condition is a leading cause of maternal mortality and morbidity... Read more
Portable Ultrasound Sensor to Enable Earlier Breast Cancer Detection
Breast cancer screening relies heavily on annual mammograms, but aggressive tumors can develop between scans, accounting for up to 30 percent of cases. These interval cancers are often diagnosed later,... Read more
Portable Imaging Scanner to Diagnose Lymphatic Disease in Real Time
Lymphatic disorders affect hundreds of millions of people worldwide and are linked to conditions ranging from limb swelling and organ dysfunction to birth defects and cancer-related complications.... Read more
Imaging Technique Generates Simultaneous 3D Color Images of Soft-Tissue Structure and Vasculature
Medical imaging tools often force clinicians to choose between speed, structural detail, and functional insight. Ultrasound is fast and affordable but typically limited to two-dimensional anatomy, while... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
Targeted cancer therapies only work when tumor cells express the specific molecular structures they are designed to attack. In urothelial carcinoma, a common form of bladder cancer, the cell surface protein... Read more
Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
Targeted cancer therapies can be highly effective, but only when a patient’s tumor expresses the specific protein the treatment is designed to attack. Determining this usually requires biopsies or advanced... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer is a form of head and neck cancer that can spread through lymph nodes, significantly affecting survival and treatment decisions. Current therapies often involve combinations of surgery,... Read more
New 3D Imaging System Addresses MRI, CT and Ultrasound Limitations
Medical imaging is central to diagnosing and managing injuries, cancer, infections, and chronic diseases, yet existing tools each come with trade-offs. Ultrasound, X-ray, CT, and MRI can be costly, time-consuming,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Nuclear Medicine Set for Continued Growth Driven by Demand for Precision Diagnostics
Clinical imaging services face rising demand for precise molecular diagnostics and targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy as cancer and chronic disease rates climb. A new market analysis projects rapid expansion... Read more




















