Portable MRI Scanner Increases Access to Neuroimaging
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 23 Dec 2020 |
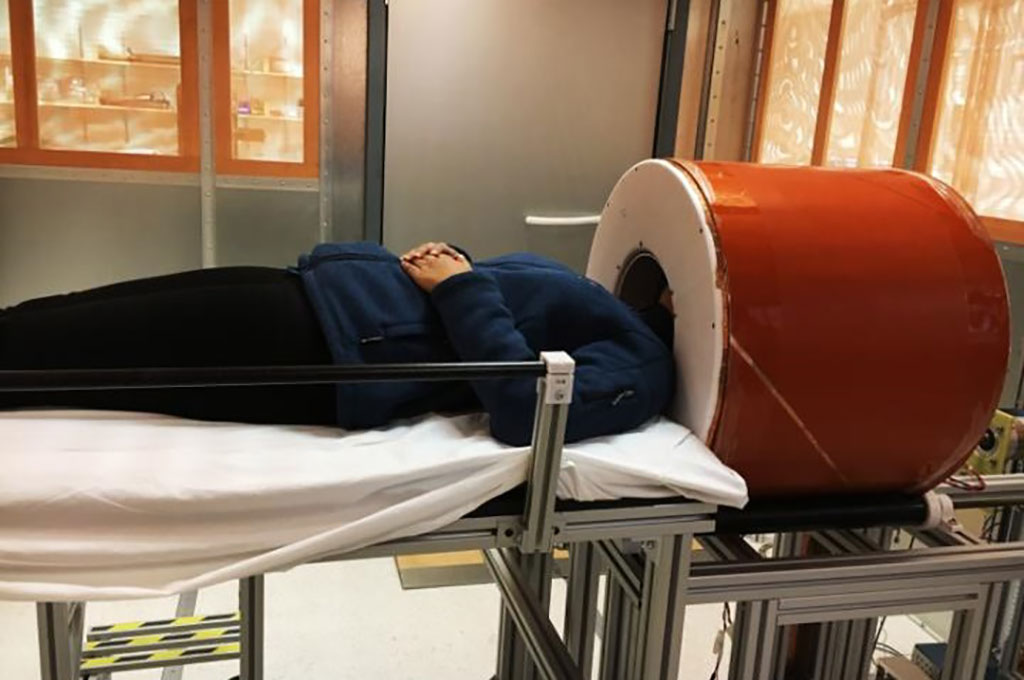
Image: A low-cost, low-power brain MRI device could scan brains at the POC (Photo courtesy of MGH)
A portable magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner based on a compact, lightweight, permanent magnet could expand enable point-of-care (POC) diagnostics for neurological emergencies.
Developed at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH; Boston, USA) and Harvard Medical School (HMS; Boston, MA, USA), the prototype brain MRI system uses an array of neodymium (NdFeB) rare-earth magnets that generate a low (80 mT) magnetic field with a built-in readout gradient. The configuration reduces reliance on high-power gradient drivers, lowers the overall requirements for power and cooling, and reduces acoustic noise. Imperfections in the encoding fields are mitigated with a generalized iterative image reconstruction technique.
A Halbach cylinder design creates a transverse field inside the magnet and zero field outside the magnet that results in a minimal stray field that requires neither cryogenics nor external power; the intrinsic self-shielding is thus ideal for portable applications where stray fields could pose safety hazards. The scanner can generate T1-weighted, T2-weighted, and proton density-weighted brain images with a spatial resolution of 2.2 × 1.3 × 6.8 mm3. The study was published on November 23, 2020, in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
“Although the scanner’s spatial resolution and sensitivity are both lower than that of a high-field MRI, its performance is sufficient to detect and characterize serious intracranial processes, such as hemorrhage, hydrocephalus, infarction, and mass lesions,” concluded lead author Clarissa Cooley, PhD, of the MGH department of radiology, and colleagues. “Our preliminary work also suggests that diffusion-weighted imaging, which is critical to applications such as acute stroke detection, should also be possible.”
A neodymium rare-earth magnet is made from an alloy of neodymium, iron, and boron formed into a tetragonal crystalline structure that has a magnetic energy value about 18 times greater than ferrite magnets (by volume) and 12 times (by mass). The strength and magnetic field homogeneity of such neodymium magnets has led to their introduction in MRI scanners as an alternative to superconducting magnets.
Related Links:
Massachusetts General Hospital
Harvard Medical School
Developed at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH; Boston, USA) and Harvard Medical School (HMS; Boston, MA, USA), the prototype brain MRI system uses an array of neodymium (NdFeB) rare-earth magnets that generate a low (80 mT) magnetic field with a built-in readout gradient. The configuration reduces reliance on high-power gradient drivers, lowers the overall requirements for power and cooling, and reduces acoustic noise. Imperfections in the encoding fields are mitigated with a generalized iterative image reconstruction technique.
A Halbach cylinder design creates a transverse field inside the magnet and zero field outside the magnet that results in a minimal stray field that requires neither cryogenics nor external power; the intrinsic self-shielding is thus ideal for portable applications where stray fields could pose safety hazards. The scanner can generate T1-weighted, T2-weighted, and proton density-weighted brain images with a spatial resolution of 2.2 × 1.3 × 6.8 mm3. The study was published on November 23, 2020, in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
“Although the scanner’s spatial resolution and sensitivity are both lower than that of a high-field MRI, its performance is sufficient to detect and characterize serious intracranial processes, such as hemorrhage, hydrocephalus, infarction, and mass lesions,” concluded lead author Clarissa Cooley, PhD, of the MGH department of radiology, and colleagues. “Our preliminary work also suggests that diffusion-weighted imaging, which is critical to applications such as acute stroke detection, should also be possible.”
A neodymium rare-earth magnet is made from an alloy of neodymium, iron, and boron formed into a tetragonal crystalline structure that has a magnetic energy value about 18 times greater than ferrite magnets (by volume) and 12 times (by mass). The strength and magnetic field homogeneity of such neodymium magnets has led to their introduction in MRI scanners as an alternative to superconducting magnets.
Related Links:
Massachusetts General Hospital
Harvard Medical School
Latest MRI News
- AI Model Reads and Diagnoses Brain MRI in Seconds
- MRI Scan Breakthrough to Help Avoid Risky Invasive Tests for Heart Patients
- MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
- Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
- AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
- AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
- New MRI Technique Reveals Hidden Heart Issues
- Shorter MRI Exam Effectively Detects Cancer in Dense Breasts
- MRI to Replace Painful Spinal Tap for Faster MS Diagnosis
- MRI Scans Can Identify Cardiovascular Disease Ten Years in Advance
- Simple Brain Scan Diagnoses Parkinson's Disease Years Before It Becomes Untreatable
- Cutting-Edge MRI Technology to Revolutionize Diagnosis of Common Heart Problem
- New MRI Technique Reveals True Heart Age to Prevent Attacks and Strokes
- AI Tool Predicts Relapse of Pediatric Brain Cancer from Brain MRI Scans
- AI Tool Tracks Effectiveness of Multiple Sclerosis Treatments Using Brain MRI Scans
- Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read more
AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
Chronological age does not always reflect how fast the body is truly aging, and current biological age tests often rely on DNA-based markers that may miss early organ-level decline. Detecting subtle, age-related... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Portable Ultrasound Sensor to Enable Earlier Breast Cancer Detection
Breast cancer screening relies heavily on annual mammograms, but aggressive tumors can develop between scans, accounting for up to 30 percent of cases. These interval cancers are often diagnosed later,... Read more
Portable Imaging Scanner to Diagnose Lymphatic Disease in Real Time
Lymphatic disorders affect hundreds of millions of people worldwide and are linked to conditions ranging from limb swelling and organ dysfunction to birth defects and cancer-related complications.... Read more
Imaging Technique Generates Simultaneous 3D Color Images of Soft-Tissue Structure and Vasculature
Medical imaging tools often force clinicians to choose between speed, structural detail, and functional insight. Ultrasound is fast and affordable but typically limited to two-dimensional anatomy, while... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
Targeted cancer therapies only work when tumor cells express the specific molecular structures they are designed to attack. In urothelial carcinoma, a common form of bladder cancer, the cell surface protein... Read more
Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
Targeted cancer therapies can be highly effective, but only when a patient’s tumor expresses the specific protein the treatment is designed to attack. Determining this usually requires biopsies or advanced... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer is a form of head and neck cancer that can spread through lymph nodes, significantly affecting survival and treatment decisions. Current therapies often involve combinations of surgery,... Read more
New 3D Imaging System Addresses MRI, CT and Ultrasound Limitations
Medical imaging is central to diagnosing and managing injuries, cancer, infections, and chronic diseases, yet existing tools each come with trade-offs. Ultrasound, X-ray, CT, and MRI can be costly, time-consuming,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Nuclear Medicine Set for Continued Growth Driven by Demand for Precision Diagnostics
Clinical imaging services face rising demand for precise molecular diagnostics and targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy as cancer and chronic disease rates climb. A new market analysis projects rapid expansion... Read more









 Guided Devices.jpg)











