Endoscopic Ultrasound Gastroscopes Match Clinical Needs
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 28 Sep 2020 |
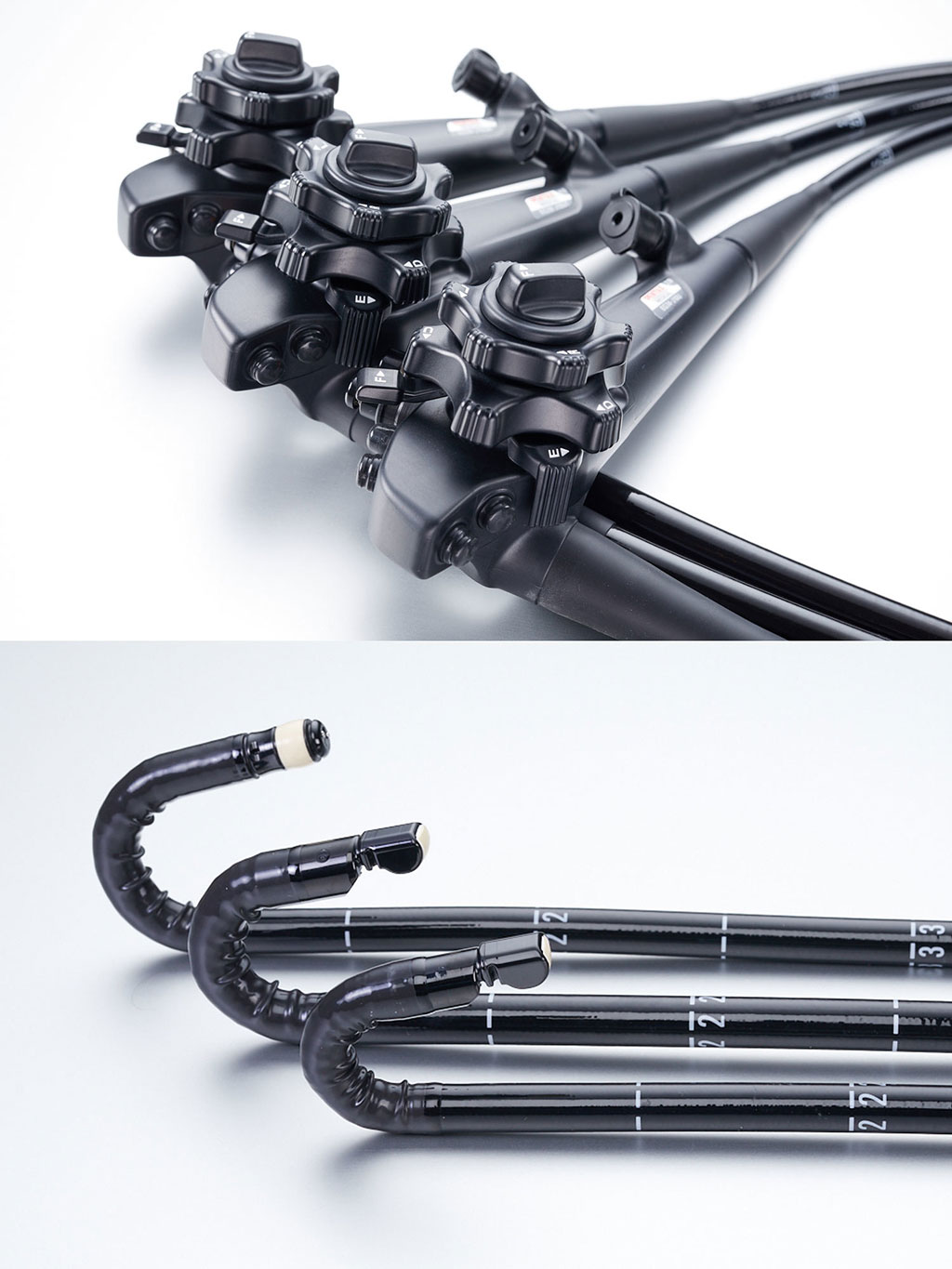

Image: The EG36-J10UR, the EG34-J10U, and EG38-J10UT EUS video gastroscopes (Photo courtesy of Pentax Medical)
A new series of endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) video gastroscopes offer ergonomic design, superior image quality, and enhanced maneuverability.
The Pentax Medical (Tokyo, Japan) J10 Series ultrasound video gastroscopes are designed for optimal procedural efficiency in EUS, providing a lightweight and ergonomic control body that ensures stability and ease of intubation, while reducing hand fatigue. Maneuvering, device control, and instrument compatibility are augmented with shorter rigid distal section lengths, increased tip deflection, smaller bending radius, increased angulations and an enlarged working channel that optimize access to the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
The J10 Series includes the EG36-J10UR, the EG34-J10U, and the EG38-J10UT devices. Common features include an increased linear scope scan angle of 150° for broader imaging, 13MHz frequency scans for near-field exploration, a depth of field range of 3-100mm, and sealed elevator wire channels to help reduce risk of cross-contamination. The EG38-J10UT also has an enlarged instrument channel width of four mm, expanding the therapeutic capabilities of EUS-guided interventions while providing full control of the procedure.
“Endoscopic Ultrasound is the gold standard for tumor staging and diagnosis and rapidly advancing into therapy. With our newest innovative solution, we have demonstrated a clear commitment in providing enhanced procedural efficiency and optimized patient care,” said Gerald Bottero, global president of PENTAX Medical. “The J10 Series provides an innovative solution for performing endoscopic evaluations, increasing diagnostic capabilities, and determining pathways for effective patient management.”
EUS is a minimally invasive procedure to assess GI and lung diseases, using high-frequency sound waves to produce detailed images of the lining and walls of the GI tract and chest, nearby organs such as the pancreas and liver, and lymph nodes. When combined with fine-needle aspiration (FNS), EUS allows biopsy fluid and tissue samples to be collected as a minimally invasive alternative to exploratory surgery.
The Pentax Medical (Tokyo, Japan) J10 Series ultrasound video gastroscopes are designed for optimal procedural efficiency in EUS, providing a lightweight and ergonomic control body that ensures stability and ease of intubation, while reducing hand fatigue. Maneuvering, device control, and instrument compatibility are augmented with shorter rigid distal section lengths, increased tip deflection, smaller bending radius, increased angulations and an enlarged working channel that optimize access to the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
The J10 Series includes the EG36-J10UR, the EG34-J10U, and the EG38-J10UT devices. Common features include an increased linear scope scan angle of 150° for broader imaging, 13MHz frequency scans for near-field exploration, a depth of field range of 3-100mm, and sealed elevator wire channels to help reduce risk of cross-contamination. The EG38-J10UT also has an enlarged instrument channel width of four mm, expanding the therapeutic capabilities of EUS-guided interventions while providing full control of the procedure.
“Endoscopic Ultrasound is the gold standard for tumor staging and diagnosis and rapidly advancing into therapy. With our newest innovative solution, we have demonstrated a clear commitment in providing enhanced procedural efficiency and optimized patient care,” said Gerald Bottero, global president of PENTAX Medical. “The J10 Series provides an innovative solution for performing endoscopic evaluations, increasing diagnostic capabilities, and determining pathways for effective patient management.”
EUS is a minimally invasive procedure to assess GI and lung diseases, using high-frequency sound waves to produce detailed images of the lining and walls of the GI tract and chest, nearby organs such as the pancreas and liver, and lymph nodes. When combined with fine-needle aspiration (FNS), EUS allows biopsy fluid and tissue samples to be collected as a minimally invasive alternative to exploratory surgery.
Latest Ultrasound News
- Reusable Gel Pad Made from Tamarind Seed Could Transform Ultrasound Examinations
- AI Model Accurately Detects Placenta Accreta in Pregnancy Before Delivery
- Portable Ultrasound Sensor to Enable Earlier Breast Cancer Detection
- Portable Imaging Scanner to Diagnose Lymphatic Disease in Real Time
- Imaging Technique Generates Simultaneous 3D Color Images of Soft-Tissue Structure and Vasculature
- Wearable Ultrasound Imaging System to Enable Real-Time Disease Monitoring
- Ultrasound Technique Visualizes Deep Blood Vessels in 3D Without Contrast Agents
- Ultrasound Probe Images Entire Organ in 4D

- Disposable Ultrasound Patch Performs Better Than Existing Devices
- Non-Invasive Ultrasound-Based Tool Accurately Detects Infant Meningitis
- Breakthrough Deep Learning Model Enhances Handheld 3D Medical Imaging
- Pain-Free Breast Imaging System Performs One Minute Cancer Scan
- Wireless Chronic Pain Management Device to Reduce Need for Painkillers and Surgery
- New Medical Ultrasound Imaging Technique Enables ICU Bedside Monitoring
- New Incision-Free Technique Halts Growth of Debilitating Brain Lesions
- AI-Powered Lung Ultrasound Outperforms Human Experts in Tuberculosis Diagnosis
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read more
AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
Chronological age does not always reflect how fast the body is truly aging, and current biological age tests often rely on DNA-based markers that may miss early organ-level decline. Detecting subtle, age-related... Read moreMRI
view channel
New Material Boosts MRI Image Quality
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a cornerstone of modern diagnostics, yet certain deep or anatomically complex tissues, including delicate structures of the eye and orbit, remain difficult to visualize clearly.... Read more
AI Model Reads and Diagnoses Brain MRI in Seconds
Brain MRI scans are critical for diagnosing strokes, hemorrhages, and other neurological disorders, but interpreting them can take hours or even days due to growing demand and limited specialist availability.... Read moreMRI Scan Breakthrough to Help Avoid Risky Invasive Tests for Heart Patients
Heart failure patients often require right heart catheterization to assess how severely their heart is struggling to pump blood, a procedure that involves inserting a tube into the heart to measure blood... Read more
MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
Recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies widely, with some patients regaining full function while others are left with lasting disabilities. Prognosis is especially difficult to assess in patients... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
Targeted cancer therapies only work when tumor cells express the specific molecular structures they are designed to attack. In urothelial carcinoma, a common form of bladder cancer, the cell surface protein... Read more
Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
Targeted cancer therapies can be highly effective, but only when a patient’s tumor expresses the specific protein the treatment is designed to attack. Determining this usually requires biopsies or advanced... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer is a form of head and neck cancer that can spread through lymph nodes, significantly affecting survival and treatment decisions. Current therapies often involve combinations of surgery,... Read more
New 3D Imaging System Addresses MRI, CT and Ultrasound Limitations
Medical imaging is central to diagnosing and managing injuries, cancer, infections, and chronic diseases, yet existing tools each come with trade-offs. Ultrasound, X-ray, CT, and MRI can be costly, time-consuming,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Nuclear Medicine Set for Continued Growth Driven by Demand for Precision Diagnostics
Clinical imaging services face rising demand for precise molecular diagnostics and targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy as cancer and chronic disease rates climb. A new market analysis projects rapid expansion... Read more





















