Tau Radiotracer Aids Alzheimer's Disease Diagnosis
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 11 Jun 2020 |
A novel diagnostic radiotracer can help estimate the density and distribution of aggregated tau neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) in adults being evaluated for Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
Developed by Avid Radiopharmaceuticals (Philadelphia, PA, USA), a wholly owned subsidiary of Eli Lilly (Indianapolis, IN, USA), Tauvid (flortaucipir 18F) radiotracer is a small-molecule selective positron emission tomography (PET) imaging agent that binds to aggregated tau protein, which in the brains of patients with AD, combine to form NFTs, one of the two components required for the neuropathological diagnosis of AD. The safety and effectiveness of the tau tracer were demonstrated in two clinical studies.
The first study included 156 terminally ill patients who agreed to undergo Tauvid PET imaging and to donate their brains after death; 64 died within nine months of brain scanning. Five evaluators' readings were then compared to post mortem readings from independent pathologists, who were blinded to the PET scan results. The results showed that the five evaluator’s readings had a high probability of correctly evaluating patients with tau pathology and had an average-to-high probability of correctly evaluating patients without tau pathology.
The second study included the same patients with terminal illness that participated in the first study, but with an additional 18 patients with terminal illness and 159 patients with cognitive impairment who were being evaluated for AD. In this second study, reader agreement was 0.87 across all 241 patients. In a separate subgroup analysis that included the 82 terminally ill patients who were diagnosed after death and the 159 patients with cognitive impairment, reader agreement was 0.90 for the AD patients and 0.82 in the terminally ill patients.
“The fight against Alzheimer’s disease requires precise and reliable assessments of the two key pathologies of the disease, because clinical assessments alone are limited in their ability to accurately diagnose patients,” said Mark Mintun, MD, vice president of Lilly's pain and neurodegeneration research and development. “Lilly and Avid Radiopharmaceuticals are committed to bringing innovative AD diagnostics to the patients who need them most.”
“Diagnostic imaging can help patients and their families plan for the future and make informed choices about their health and well-being, in addition to facilitating appropriate patient management for physicians,” said professor of neurology Reisa Sperling, MD, of Harvard Medical School (Boston, MA, USA). “Determining the anatomic distribution and density of tau NFTs in the brain was previously possible only at autopsy. Now we have a way to obtain this important information in patients.”
18F is a fluorine radioisotope that decays by positron emission 97% of the time, and electron capture 3% of the time; both modes of decay yield stable oxygen-18 (18O). 18F is an important radioisotope as a result of both its short half-life and the emission of positrons when decaying. It is primarily synthesized into fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) for use in PET scans.
Related Links:
Avid Radiopharmaceuticals
Eli Lilly
Developed by Avid Radiopharmaceuticals (Philadelphia, PA, USA), a wholly owned subsidiary of Eli Lilly (Indianapolis, IN, USA), Tauvid (flortaucipir 18F) radiotracer is a small-molecule selective positron emission tomography (PET) imaging agent that binds to aggregated tau protein, which in the brains of patients with AD, combine to form NFTs, one of the two components required for the neuropathological diagnosis of AD. The safety and effectiveness of the tau tracer were demonstrated in two clinical studies.
The first study included 156 terminally ill patients who agreed to undergo Tauvid PET imaging and to donate their brains after death; 64 died within nine months of brain scanning. Five evaluators' readings were then compared to post mortem readings from independent pathologists, who were blinded to the PET scan results. The results showed that the five evaluator’s readings had a high probability of correctly evaluating patients with tau pathology and had an average-to-high probability of correctly evaluating patients without tau pathology.
The second study included the same patients with terminal illness that participated in the first study, but with an additional 18 patients with terminal illness and 159 patients with cognitive impairment who were being evaluated for AD. In this second study, reader agreement was 0.87 across all 241 patients. In a separate subgroup analysis that included the 82 terminally ill patients who were diagnosed after death and the 159 patients with cognitive impairment, reader agreement was 0.90 for the AD patients and 0.82 in the terminally ill patients.
“The fight against Alzheimer’s disease requires precise and reliable assessments of the two key pathologies of the disease, because clinical assessments alone are limited in their ability to accurately diagnose patients,” said Mark Mintun, MD, vice president of Lilly's pain and neurodegeneration research and development. “Lilly and Avid Radiopharmaceuticals are committed to bringing innovative AD diagnostics to the patients who need them most.”
“Diagnostic imaging can help patients and their families plan for the future and make informed choices about their health and well-being, in addition to facilitating appropriate patient management for physicians,” said professor of neurology Reisa Sperling, MD, of Harvard Medical School (Boston, MA, USA). “Determining the anatomic distribution and density of tau NFTs in the brain was previously possible only at autopsy. Now we have a way to obtain this important information in patients.”
18F is a fluorine radioisotope that decays by positron emission 97% of the time, and electron capture 3% of the time; both modes of decay yield stable oxygen-18 (18O). 18F is an important radioisotope as a result of both its short half-life and the emission of positrons when decaying. It is primarily synthesized into fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) for use in PET scans.
Related Links:
Avid Radiopharmaceuticals
Eli Lilly
Latest Nuclear Medicine News
- Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
- Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
- PET Imaging of Inflammation Predicts Recovery and Guides Therapy After Heart Attack
- Radiotheranostic Approach Detects, Kills and Reprograms Aggressive Cancers
- New Imaging Solution Improves Survival for Patients with Recurring Prostate Cancer
- PET Tracer Enables Same-Day Imaging of Triple-Negative Breast and Urothelial Cancers
- New Camera Sees Inside Human Body for Enhanced Scanning and Diagnosis
- Novel Bacteria-Specific PET Imaging Approach Detects Hard-To-Diagnose Lung Infections
- New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
- Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
- Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
- Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
- New Molecular Imaging Test to Improve Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- Novel PET Technique Visualizes Spinal Cord Injuries to Predict Recovery
- Next-Gen Tau Radiotracers Outperform FDA-Approved Imaging Agents in Detecting Alzheimer’s
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI Tool Predicts Breast Cancer Risk Years Ahead Using Routine Mammograms
Breast cancer screening saves lives but still relies largely on uniform schedules despite wide differences in individual risk. This one-size-fits-all approach can miss cancers in higher-risk women while... Read more
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read moreMRI
view channel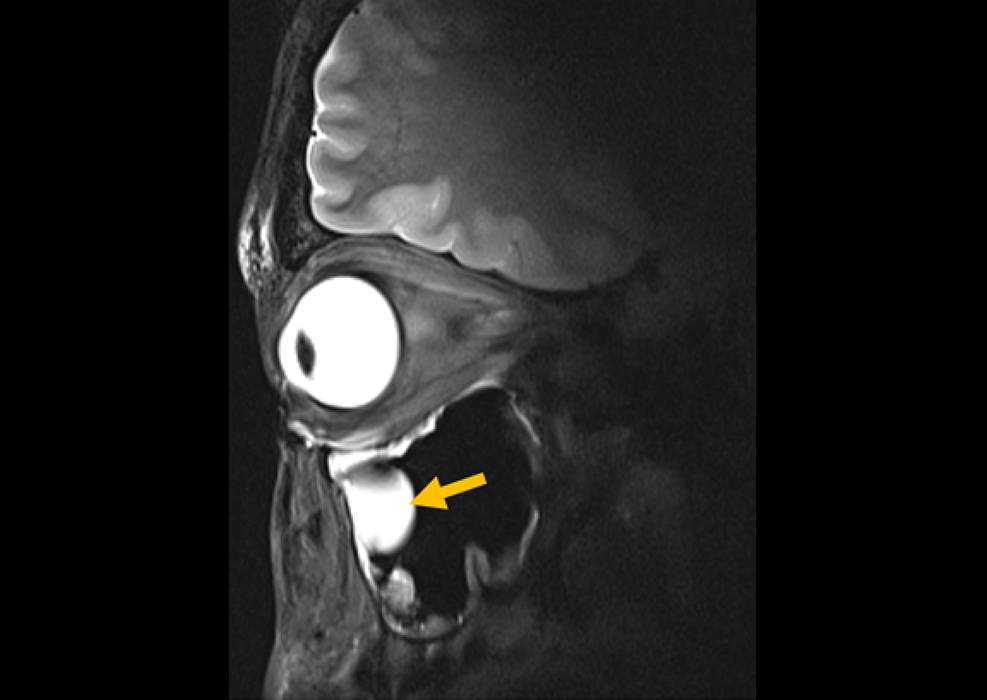
New Material Boosts MRI Image Quality
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a cornerstone of modern diagnostics, yet certain deep or anatomically complex tissues, including delicate structures of the eye and orbit, remain difficult to visualize clearly.... Read more
AI Model Reads and Diagnoses Brain MRI in Seconds
Brain MRI scans are critical for diagnosing strokes, hemorrhages, and other neurological disorders, but interpreting them can take hours or even days due to growing demand and limited specialist availability.... Read moreMRI Scan Breakthrough to Help Avoid Risky Invasive Tests for Heart Patients
Heart failure patients often require right heart catheterization to assess how severely their heart is struggling to pump blood, a procedure that involves inserting a tube into the heart to measure blood... Read more
MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
Recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies widely, with some patients regaining full function while others are left with lasting disabilities. Prognosis is especially difficult to assess in patients... Read moreUltrasound
view channel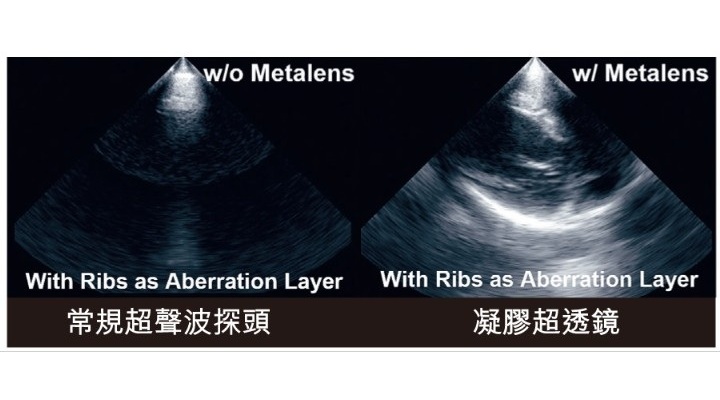
Groundbreaking Technology to Enhance Precision in Emergency and Critical Care
Rapid and accurate imaging is essential for diagnosing life-threatening conditions such as myocardial infarction, heart failure, and pulmonary embolism. However, conventional ultrasound imaging of the... Read more
Reusable Gel Pad Made from Tamarind Seed Could Transform Ultrasound Examinations
Ultrasound imaging depends on a conductive gel to eliminate air between the probe and the skin so sound waves can pass clearly into the body. While the imaging technology is fast, safe, and noninvasive,... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Tool Predicts Side Effects from Lung Cancer Treatment
Radiation therapy is a central treatment for lung cancer, but even carefully targeted radiation can affect surrounding healthy tissue. Patients may develop side effects such as lung inflammation, coughing,... Read more
AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer is a form of head and neck cancer that can spread through lymph nodes, significantly affecting survival and treatment decisions. Current therapies often involve combinations of surgery,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Nuclear Medicine Set for Continued Growth Driven by Demand for Precision Diagnostics
Clinical imaging services face rising demand for precise molecular diagnostics and targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy as cancer and chronic disease rates climb. A new market analysis projects rapid expansion... Read more





















