Mobile Devices Prove Reliable for Acute Stroke Diagnosis
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 25 Feb 2020 |
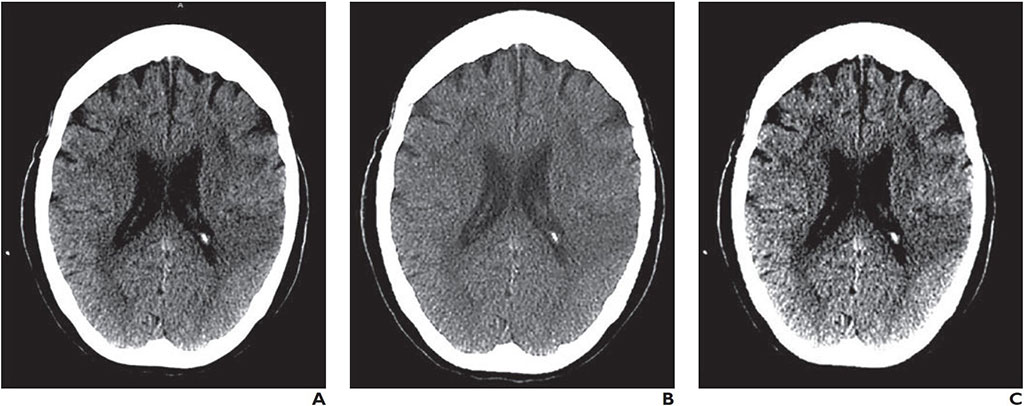
Image: A CT image as seen on a Barco E-2620 monitor (A), Samsung Galaxy S8 Plus smartphone (B), and a Lenovo ThinkPad T460s laptop (C) (Photo courtesy of AJR)
A new study shows that interpretation of a computerized tomography (CT) scan on a smartphone or laptop is reliable prior to IV thrombolysis administration in acute stroke patients.
Researchers at the University of Los Andes (UniAndes; Bogotá, Colombia), Hospital Fundación Santa Fe de Bogotá (Colombia), and the Baptist Neurological Institute (Jacksonville, FL, USA) conducted a retrospective study of 2,256 CT interpretations to evaluate the reliability of head CT images displayed on smartphone or laptop reading systems in 880 patients with symptoms of acute stroke, compared with those made after interpretation of images displayed on a medical workstation monitor.
The CT interpretations on all three systems, conducted by four neuroradiologists, were then analyzed to calculate intra-observer and inter-observer agreements using the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) and interpretation variables that included hemorrhagic lesions; infarct size assessment; stroke dating (acute, subacute, and chronic); intraaxial neoplasm; and hyperdense arteries. In addition, accuracy equivalence tests were performed on recommendations for IV thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (tPA).
The results showed that good or very good intra-observer agreements were shown for all the variables, and specifically for those variables required to establish contraindications for IV thrombolysis, where the agreements were ranked as very good. The tPA IV thrombolysis recommendation showed very good inter-observer agreements, with AUC values and sensitivities equivalent among all the reading systems at a 5% equivalent threshold. The study was published on January 28, 2020, in the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR).
“Our study found that mobile devices are reliable and accurate to help stroke teams to decide whether to administer IV thrombolysis in patients with acute stroke,” concluded lead author Antonio Salazar, PhD, of the UniAndes Laboratory of Telemedicine and Electrophysiology, and colleagues. “These results constitute a strong foundation for the development of mobile-based telestroke services, because they increase neuroradiologist availability and the possibility of using reperfusion therapies in resource-limited countries.”
Mobile phone screen resolution has been significantly increased over the years, from the incipient QCIF (176 × 144 pixel) standard to the current Quad HD (2560 × 1440 pixel) or even Ultra HD (3840 × 2160 pixel) resolutions. At the same time, screen size has also been enlarged, from smaller than one inch to seven inches, or even larger. But the most important features for accurate medical grade images is the number of colors on grey scale images, contrast modulation, viewing angle, and calibration.
Related Links:
University of Los Andes
Hospital Fundación Santa Fe de Bogotá
Baptist Neurological Institute
Researchers at the University of Los Andes (UniAndes; Bogotá, Colombia), Hospital Fundación Santa Fe de Bogotá (Colombia), and the Baptist Neurological Institute (Jacksonville, FL, USA) conducted a retrospective study of 2,256 CT interpretations to evaluate the reliability of head CT images displayed on smartphone or laptop reading systems in 880 patients with symptoms of acute stroke, compared with those made after interpretation of images displayed on a medical workstation monitor.
The CT interpretations on all three systems, conducted by four neuroradiologists, were then analyzed to calculate intra-observer and inter-observer agreements using the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) and interpretation variables that included hemorrhagic lesions; infarct size assessment; stroke dating (acute, subacute, and chronic); intraaxial neoplasm; and hyperdense arteries. In addition, accuracy equivalence tests were performed on recommendations for IV thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (tPA).
The results showed that good or very good intra-observer agreements were shown for all the variables, and specifically for those variables required to establish contraindications for IV thrombolysis, where the agreements were ranked as very good. The tPA IV thrombolysis recommendation showed very good inter-observer agreements, with AUC values and sensitivities equivalent among all the reading systems at a 5% equivalent threshold. The study was published on January 28, 2020, in the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR).
“Our study found that mobile devices are reliable and accurate to help stroke teams to decide whether to administer IV thrombolysis in patients with acute stroke,” concluded lead author Antonio Salazar, PhD, of the UniAndes Laboratory of Telemedicine and Electrophysiology, and colleagues. “These results constitute a strong foundation for the development of mobile-based telestroke services, because they increase neuroradiologist availability and the possibility of using reperfusion therapies in resource-limited countries.”
Mobile phone screen resolution has been significantly increased over the years, from the incipient QCIF (176 × 144 pixel) standard to the current Quad HD (2560 × 1440 pixel) or even Ultra HD (3840 × 2160 pixel) resolutions. At the same time, screen size has also been enlarged, from smaller than one inch to seven inches, or even larger. But the most important features for accurate medical grade images is the number of colors on grey scale images, contrast modulation, viewing angle, and calibration.
Related Links:
University of Los Andes
Hospital Fundación Santa Fe de Bogotá
Baptist Neurological Institute
Latest General/Advanced Imaging News
- AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
- New 3D Imaging System Addresses MRI, CT and Ultrasound Limitations
- AI-Based Tool Predicts Future Cardiovascular Events in Angina Patients
- AI-Based Tool Accelerates Detection of Kidney Cancer
- New Algorithm Dramatically Speeds Up Stroke Detection Scans
- 3D Scanning Approach Enables Ultra-Precise Brain Surgery
- AI Tool Improves Medical Imaging Process by 90%
- New Ultrasmall, Light-Sensitive Nanoparticles Could Serve as Contrast Agents
- AI Algorithm Accurately Predicts Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis Using Routine CT Images
- Cutting-Edge Angio-CT Solution Offers New Therapeutic Possibilities
- Extending CT Imaging Detects Hidden Blood Clots in Stroke Patients
- Groundbreaking AI Model Accurately Segments Liver Tumors from CT Scans
- New CT-Based Indicator Helps Predict Life-Threatening Postpartum Bleeding Cases
- CT Colonography Beats Stool DNA Testing for Colon Cancer Screening
- First-Of-Its-Kind Wearable Device Offers Revolutionary Alternative to CT Scans
- AI-Based CT Scan Analysis Predicts Early-Stage Kidney Damage Due to Cancer Treatments
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read more
AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
Chronological age does not always reflect how fast the body is truly aging, and current biological age tests often rely on DNA-based markers that may miss early organ-level decline. Detecting subtle, age-related... Read moreMRI
view channel
New Material Boosts MRI Image Quality
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a cornerstone of modern diagnostics, yet certain deep or anatomically complex tissues, including delicate structures of the eye and orbit, remain difficult to visualize clearly.... Read more
AI Model Reads and Diagnoses Brain MRI in Seconds
Brain MRI scans are critical for diagnosing strokes, hemorrhages, and other neurological disorders, but interpreting them can take hours or even days due to growing demand and limited specialist availability.... Read moreMRI Scan Breakthrough to Help Avoid Risky Invasive Tests for Heart Patients
Heart failure patients often require right heart catheterization to assess how severely their heart is struggling to pump blood, a procedure that involves inserting a tube into the heart to measure blood... Read more
MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
Recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies widely, with some patients regaining full function while others are left with lasting disabilities. Prognosis is especially difficult to assess in patients... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Reusable Gel Pad Made from Tamarind Seed Could Transform Ultrasound Examinations
Ultrasound imaging depends on a conductive gel to eliminate air between the probe and the skin so sound waves can pass clearly into the body. While the imaging technology is fast, safe, and noninvasive,... Read more
AI Model Accurately Detects Placenta Accreta in Pregnancy Before Delivery
Placenta accreta spectrum (PAS) is a life-threatening pregnancy complication in which the placenta abnormally attaches to the uterine wall. The condition is a leading cause of maternal mortality and morbidity... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
Targeted cancer therapies only work when tumor cells express the specific molecular structures they are designed to attack. In urothelial carcinoma, a common form of bladder cancer, the cell surface protein... Read more
Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
Targeted cancer therapies can be highly effective, but only when a patient’s tumor expresses the specific protein the treatment is designed to attack. Determining this usually requires biopsies or advanced... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Nuclear Medicine Set for Continued Growth Driven by Demand for Precision Diagnostics
Clinical imaging services face rising demand for precise molecular diagnostics and targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy as cancer and chronic disease rates climb. A new market analysis projects rapid expansion... Read more





















