AI Outperforms Radiologists in Detecting Tiny Brain Hemorrhages on CT Scans
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 02 Jan 2020 |
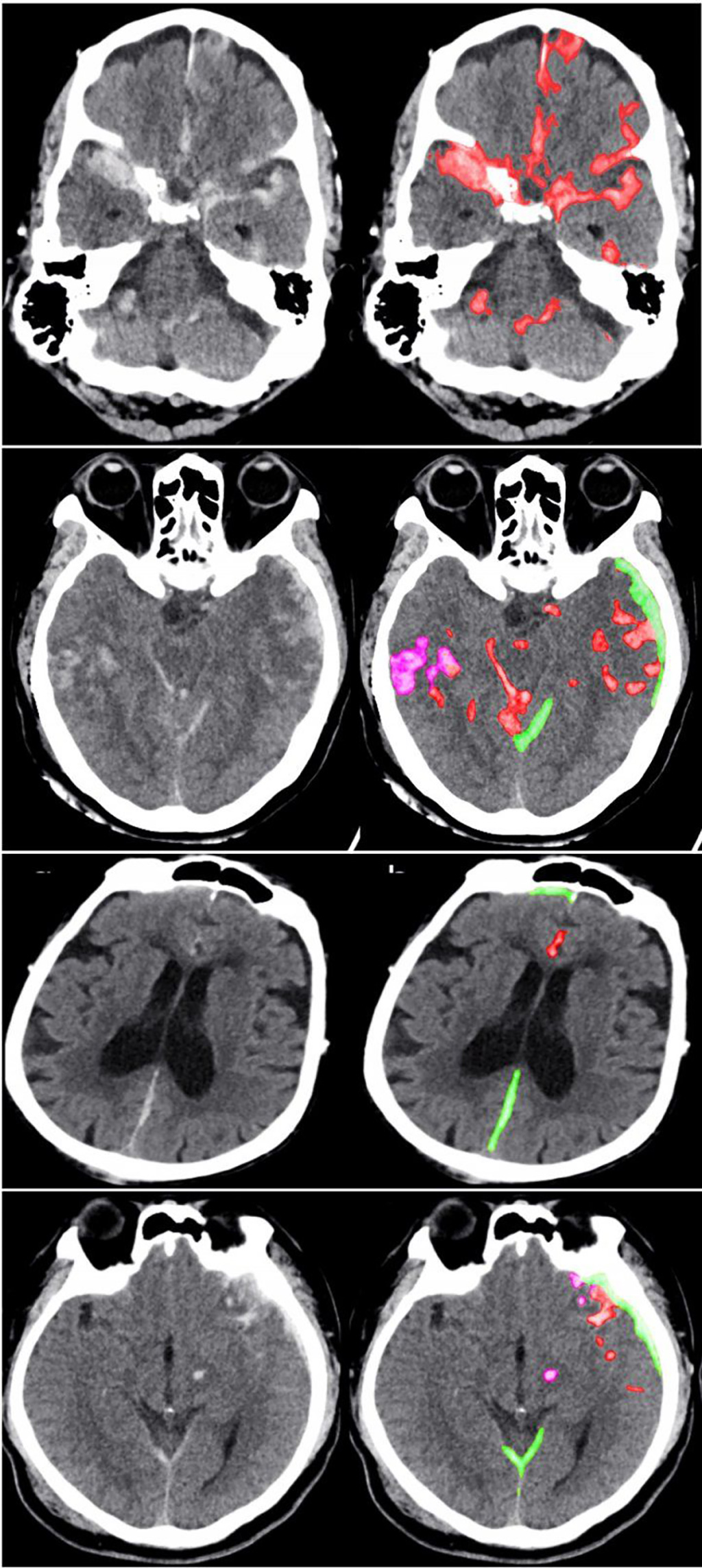
Image: CT scans of the head (Photo courtesy of UC San Francisco)
Scientists at UC San Francisco (San Francisco, CA, USA) and UC Berkeley (Berkeley, CA, USA) have developed an algorithm that performed better than two out of four expert radiologists in finding tiny brain hemorrhages in head scans. The algorithm could help doctors treat patients with traumatic brain injuries (TBI), strokes and aneurysms.
Radiologists have to look at thousands of images each day, searching for tiny abnormalities that can signal life-threatening emergencies. Some spots may be on the order of 100 pixels in size, in a 3D stack of images containing over a million of them, and even expert radiologists sometimes miss them, with potentially grave consequences. However, radiologists could be much more efficient and accurate if artificial intelligence (AI) technology can pick out the images with significant abnormalities, so they can be examined more closely.
The algorithm developed the UCSF researchers took just one second to determine whether an entire head scan contained any signs of hemorrhage. It also traced the detailed outlines of the abnormalities it found – demonstrating their location within the brain’s 3D structure. The algorithm found some small abnormalities that the experts missed. It also noted their location within the brain, and classified them according to subtype, information that physicians need to determine the best treatment. Notably the algorithm provided all of this information with an acceptable level of false positives – minimizing the amount of time that physicians would need to spend reviewing its results. The radiology experts said the algorithm’s ability to find very small abnormalities and demonstrate their location in the brain was a substantial advance.
“The hemorrhage can be tiny and still be significant,” said Pratik Mukherjee, MD, PhD, professor of radiology at UCSF. “That’s what makes a radiologist’s job so hard, and that’s why these things occasionally get missed. If a patient has an aneurysm, and it’s starting to bleed, and you send them home, they can die."
Related Links:
UC San Francisco
UC Berkeley
Radiologists have to look at thousands of images each day, searching for tiny abnormalities that can signal life-threatening emergencies. Some spots may be on the order of 100 pixels in size, in a 3D stack of images containing over a million of them, and even expert radiologists sometimes miss them, with potentially grave consequences. However, radiologists could be much more efficient and accurate if artificial intelligence (AI) technology can pick out the images with significant abnormalities, so they can be examined more closely.
The algorithm developed the UCSF researchers took just one second to determine whether an entire head scan contained any signs of hemorrhage. It also traced the detailed outlines of the abnormalities it found – demonstrating their location within the brain’s 3D structure. The algorithm found some small abnormalities that the experts missed. It also noted their location within the brain, and classified them according to subtype, information that physicians need to determine the best treatment. Notably the algorithm provided all of this information with an acceptable level of false positives – minimizing the amount of time that physicians would need to spend reviewing its results. The radiology experts said the algorithm’s ability to find very small abnormalities and demonstrate their location in the brain was a substantial advance.
“The hemorrhage can be tiny and still be significant,” said Pratik Mukherjee, MD, PhD, professor of radiology at UCSF. “That’s what makes a radiologist’s job so hard, and that’s why these things occasionally get missed. If a patient has an aneurysm, and it’s starting to bleed, and you send them home, they can die."
Related Links:
UC San Francisco
UC Berkeley
Latest Industry News News
- GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
- Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
- Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
- Bracco Diagnostics and ColoWatch Partner to Expand Availability CRC Screening Tests Using Virtual Colonoscopy
- Mindray Partners with TeleRay to Streamline Ultrasound Delivery
- Philips and Medtronic Partner on Stroke Care
- Siemens and Medtronic Enter into Global Partnership for Advancing Spine Care Imaging Technologies
- RSNA 2024 Technical Exhibits to Showcase Latest Advances in Radiology
- Bracco Collaborates with Arrayus on Microbubble-Assisted Focused Ultrasound Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer
- Innovative Collaboration to Enhance Ischemic Stroke Detection and Elevate Standards in Diagnostic Imaging
- RSNA 2024 Registration Opens
- Microsoft collaborates with Leading Academic Medical Systems to Advance AI in Medical Imaging
- GE HealthCare Acquires Intelligent Ultrasound Group’s Clinical Artificial Intelligence Business
- Bayer and Rad AI Collaborate on Expanding Use of Cutting Edge AI Radiology Operational Solutions
- Polish Med-Tech Company BrainScan to Expand Extensively into Foreign Markets
- Hologic Acquires UK-Based Breast Surgical Guidance Company Endomagnetics Ltd.
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read more
AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
Chronological age does not always reflect how fast the body is truly aging, and current biological age tests often rely on DNA-based markers that may miss early organ-level decline. Detecting subtle, age-related... Read moreMRI
view channel
MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
Recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies widely, with some patients regaining full function while others are left with lasting disabilities. Prognosis is especially difficult to assess in patients... Read more
Novel Imaging Approach to Improve Treatment for Spinal Cord Injuries
Vascular dysfunction in the spinal cord contributes to multiple neurological conditions, including traumatic injuries and degenerative cervical myelopathy, where reduced blood flow can lead to progressive... Read more
AI-Assisted Model Enhances MRI Heart Scans
A cardiac MRI can reveal critical information about the heart’s function and any abnormalities, but traditional scans take 30 to 90 minutes and often suffer from poor image quality due to patient movement.... Read more
AI Model Outperforms Doctors at Identifying Patients Most At-Risk of Cardiac Arrest
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is one of the most common inherited heart conditions and a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young individuals and athletes. While many patients live normal lives, some... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Wearable Ultrasound Imaging System to Enable Real-Time Disease Monitoring
Chronic conditions such as hypertension and heart failure require close monitoring, yet today’s ultrasound imaging is largely confined to hospitals and short, episodic scans. This reactive model limits... Read more
Ultrasound Technique Visualizes Deep Blood Vessels in 3D Without Contrast Agents
Producing clear 3D images of deep blood vessels has long been difficult without relying on contrast agents, CT scans, or MRI. Standard ultrasound typically provides only 2D cross-sections, limiting clinicians’... Read moreNuclear Medicine
view channel
PET Imaging of Inflammation Predicts Recovery and Guides Therapy After Heart Attack
Acute myocardial infarction can trigger lasting heart damage, yet clinicians still lack reliable tools to identify which patients will regain function and which may develop heart failure.... Read more
Radiotheranostic Approach Detects, Kills and Reprograms Aggressive Cancers
Aggressive cancers such as osteosarcoma and glioblastoma often resist standard therapies, thrive in hostile tumor environments, and recur despite surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy. These tumors also... Read more
New Imaging Solution Improves Survival for Patients with Recurring Prostate Cancer
Detecting recurrent prostate cancer remains one of the most difficult challenges in oncology, as standard imaging methods such as bone scans and CT scans often fail to accurately locate small or early-stage tumors.... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI-Based Tool Accelerates Detection of Kidney Cancer
Diagnosing kidney cancer depends on computed tomography scans, often using contrast agents to reveal abnormalities in kidney structure. Tumors are not always searched for deliberately, as many scans are... Read more
New Algorithm Dramatically Speeds Up Stroke Detection Scans
When patients arrive at emergency rooms with stroke symptoms, clinicians must rapidly determine whether the cause is a blood clot or a brain bleed, as treatment decisions depend on this distinction.... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more