Proton Therapy System Available in Multi-Room Configuration
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 02 Oct 2019 |
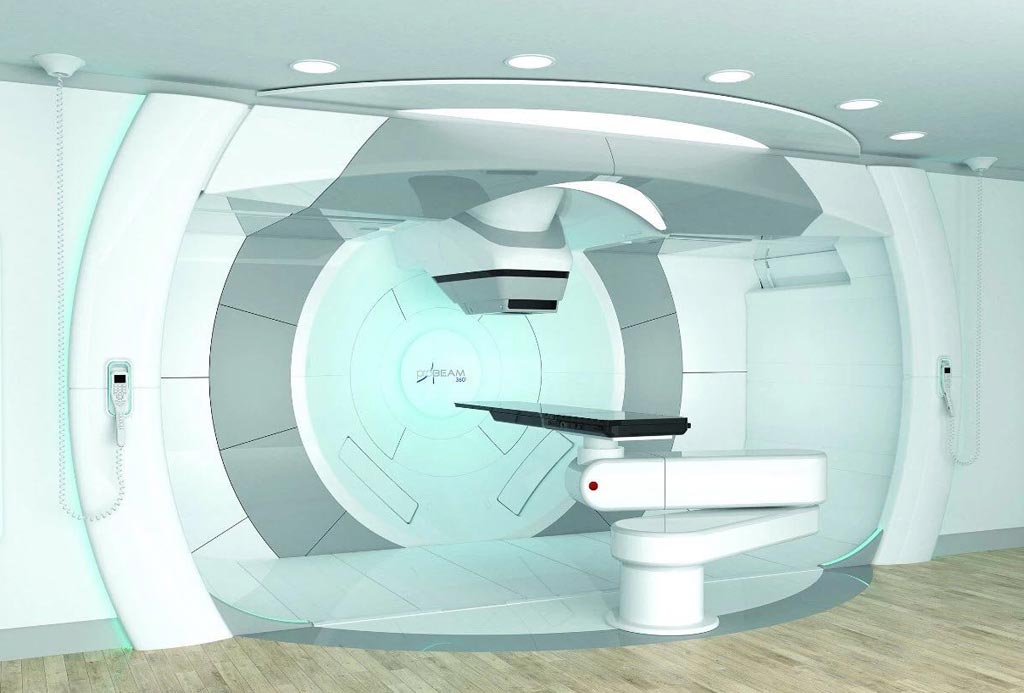
Image: The ProBeam 360° system is now available in multi-room configurations (Photo courtesy of Varian Medical Systems).
The Varian Medical Systems (Varian, Palo Alto, CA, USA) ProBeam 360° system is now available in a multi-room (one to five treatment or research rooms) configuration, which allows cancer centers to tailor the system to meet clinical, research, and capacity needs. Treatment room options include rotating gantries, fixed beam rooms, or eye treatment rooms. Research rooms are available for non-clinical proton beam applications.
The ProBeam 360° system features an extremely powerful cyclotron accelerator, iterative cone-beam computerized tomography (CT) imaging, and high-definition pencil-beam scanning. The 360° rotating gantry enables efficient intensity-modulated proton therapy (IMPT) and faster treatment times by minimizing the need for patient repositioning, thus allowing high-quality cone-beam CT (CBCT) imaging from most angles. RapidScan technology simplifies the process of motion management by delivering each field in a single breath-hold, a capability that increases the number of patients who can comply with breath-hold treatments.
The high-definition pencil-beam scanning technology gives clinicians the ability to deliver dose precisely within the contours of a tumor, minimizing dose to healthy tissue. An iterative CBCT capability enables adaptive precision radiation therapy (RT) during a course of treatment. The system also offers clinicians a viable path to potential next-generation treatments such as Flash therapy. In addition, the ProBeam 360° System offers a 50% smaller volume, a 30% smaller footprint, and 25% lower vault construction cost than Varian’s previous multi-room solution.
“Proton therapy plays an important role in the fight against cancer. The multi-room configuration of ProBeam 360° system provides clinics the flexibility to meet their treatment needs, while also increasing access for patients to proton therapy,” said Kolleen Kennedy, chief growth officer and president of Proton Therapy Solutions at Varian. “Increasing access to advanced treatments like proton therapy is an important step towards achieving our vision of a world without fear of cancer.”
Protons are generated by accelerators in the range of 70 to 250 MeV; by adjusting the energy of the protons during application of treatment, the cell damage due to the proton beam is maximized within the tumor itself. And due to their relatively large mass, protons also have little lateral side scatter in the tissue, staying focused on the tumor. Tissues closer to the surface of the body than the tumor receive reduced radiation, while tissues deeper within the body receive very few protons, so that the dosage becomes immeasurably small.
The ProBeam 360° system features an extremely powerful cyclotron accelerator, iterative cone-beam computerized tomography (CT) imaging, and high-definition pencil-beam scanning. The 360° rotating gantry enables efficient intensity-modulated proton therapy (IMPT) and faster treatment times by minimizing the need for patient repositioning, thus allowing high-quality cone-beam CT (CBCT) imaging from most angles. RapidScan technology simplifies the process of motion management by delivering each field in a single breath-hold, a capability that increases the number of patients who can comply with breath-hold treatments.
The high-definition pencil-beam scanning technology gives clinicians the ability to deliver dose precisely within the contours of a tumor, minimizing dose to healthy tissue. An iterative CBCT capability enables adaptive precision radiation therapy (RT) during a course of treatment. The system also offers clinicians a viable path to potential next-generation treatments such as Flash therapy. In addition, the ProBeam 360° System offers a 50% smaller volume, a 30% smaller footprint, and 25% lower vault construction cost than Varian’s previous multi-room solution.
“Proton therapy plays an important role in the fight against cancer. The multi-room configuration of ProBeam 360° system provides clinics the flexibility to meet their treatment needs, while also increasing access for patients to proton therapy,” said Kolleen Kennedy, chief growth officer and president of Proton Therapy Solutions at Varian. “Increasing access to advanced treatments like proton therapy is an important step towards achieving our vision of a world without fear of cancer.”
Protons are generated by accelerators in the range of 70 to 250 MeV; by adjusting the energy of the protons during application of treatment, the cell damage due to the proton beam is maximized within the tumor itself. And due to their relatively large mass, protons also have little lateral side scatter in the tissue, staying focused on the tumor. Tissues closer to the surface of the body than the tumor receive reduced radiation, while tissues deeper within the body receive very few protons, so that the dosage becomes immeasurably small.
Latest Nuclear Medicine News
- Radiopharmaceutical Molecule Marker to Improve Choice of Bladder Cancer Therapies
- Cancer “Flashlight” Shows Who Can Benefit from Targeted Treatments
- PET Imaging of Inflammation Predicts Recovery and Guides Therapy After Heart Attack
- Radiotheranostic Approach Detects, Kills and Reprograms Aggressive Cancers
- New Imaging Solution Improves Survival for Patients with Recurring Prostate Cancer
- PET Tracer Enables Same-Day Imaging of Triple-Negative Breast and Urothelial Cancers
- New Camera Sees Inside Human Body for Enhanced Scanning and Diagnosis
- Novel Bacteria-Specific PET Imaging Approach Detects Hard-To-Diagnose Lung Infections
- New Imaging Approach Could Reduce Need for Biopsies to Monitor Prostate Cancer
- Novel Radiolabeled Antibody Improves Diagnosis and Treatment of Solid Tumors
- Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
- Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
- New Molecular Imaging Test to Improve Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- Novel PET Technique Visualizes Spinal Cord Injuries to Predict Recovery
- Next-Gen Tau Radiotracers Outperform FDA-Approved Imaging Agents in Detecting Alzheimer’s
Channels
Radiography
view channel
Routine Mammograms Could Predict Future Cardiovascular Disease in Women
Mammograms are widely used to screen for breast cancer, but they may also contain overlooked clues about cardiovascular health. Calcium deposits in the arteries of the breast signal stiffening blood vessels,... Read more
AI Detects Early Signs of Aging from Chest X-Rays
Chronological age does not always reflect how fast the body is truly aging, and current biological age tests often rely on DNA-based markers that may miss early organ-level decline. Detecting subtle, age-related... Read moreMRI
view channel
New Material Boosts MRI Image Quality
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a cornerstone of modern diagnostics, yet certain deep or anatomically complex tissues, including delicate structures of the eye and orbit, remain difficult to visualize clearly.... Read more
AI Model Reads and Diagnoses Brain MRI in Seconds
Brain MRI scans are critical for diagnosing strokes, hemorrhages, and other neurological disorders, but interpreting them can take hours or even days due to growing demand and limited specialist availability.... Read moreMRI Scan Breakthrough to Help Avoid Risky Invasive Tests for Heart Patients
Heart failure patients often require right heart catheterization to assess how severely their heart is struggling to pump blood, a procedure that involves inserting a tube into the heart to measure blood... Read more
MRI Scans Reveal Signature Patterns of Brain Activity to Predict Recovery from TBI
Recovery after traumatic brain injury (TBI) varies widely, with some patients regaining full function while others are left with lasting disabilities. Prognosis is especially difficult to assess in patients... Read moreUltrasound
view channel
Reusable Gel Pad Made from Tamarind Seed Could Transform Ultrasound Examinations
Ultrasound imaging depends on a conductive gel to eliminate air between the probe and the skin so sound waves can pass clearly into the body. While the imaging technology is fast, safe, and noninvasive,... Read more
AI Model Accurately Detects Placenta Accreta in Pregnancy Before Delivery
Placenta accreta spectrum (PAS) is a life-threatening pregnancy complication in which the placenta abnormally attaches to the uterine wall. The condition is a leading cause of maternal mortality and morbidity... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI Tool Predicts Side Effects from Lung Cancer Treatment
Radiation therapy is a central treatment for lung cancer, but even carefully targeted radiation can affect surrounding healthy tissue. Patients may develop side effects such as lung inflammation, coughing,... Read more
AI Tool Offers Prognosis for Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Oropharyngeal cancer is a form of head and neck cancer that can spread through lymph nodes, significantly affecting survival and treatment decisions. Current therapies often involve combinations of surgery,... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
Nuclear Medicine Set for Continued Growth Driven by Demand for Precision Diagnostics
Clinical imaging services face rising demand for precise molecular diagnostics and targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy as cancer and chronic disease rates climb. A new market analysis projects rapid expansion... Read more





















