Superficial RT System Treats Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer
|
By MedImaging International staff writers Posted on 08 May 2019 |
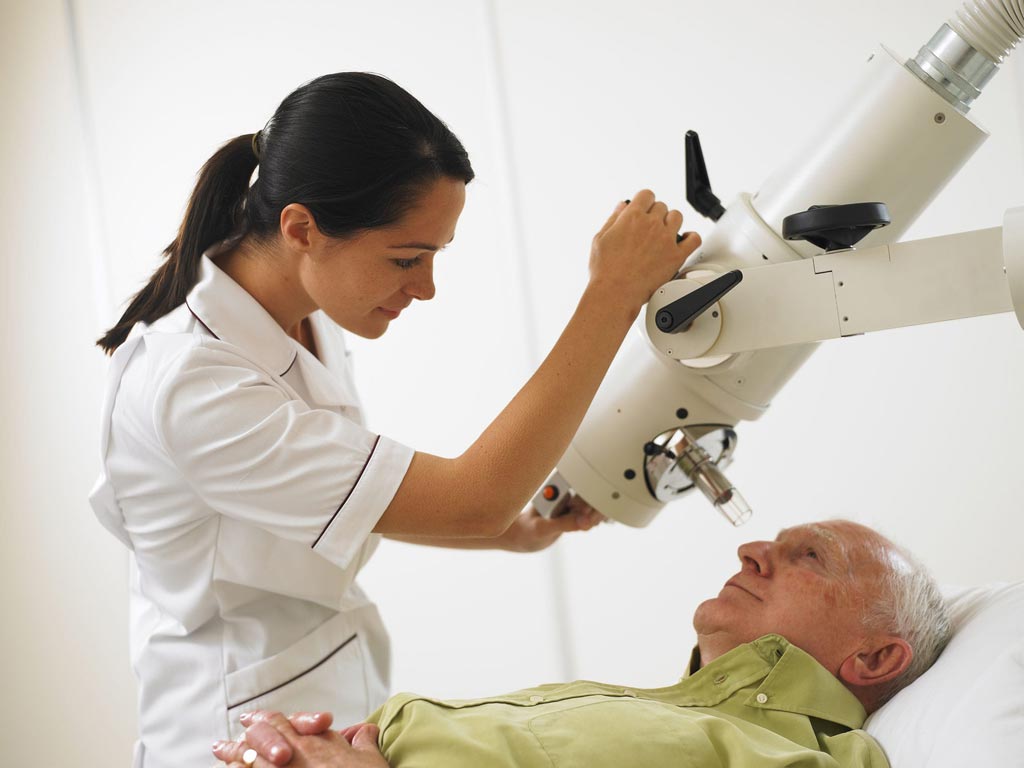
Image: The Xstrahl 150 system is designed to treat superficial skin lesions (Photo courtesy of Xstrahl).
A comprehensive superficial radiotherapy (RT) system offers clinicians the ability to treat the full range of non-melanoma skin cancer cases with optimum dose control.
The Xstrahl Medical (Camberley, United Kingdom) 150 X-ray system delivers an adaptable energy range of up to 150kV, allowing treatment of superficial lesions that range from keloid scars and dermatological conditions such as psoriasis to benign plaques, and up to basal cell carcinoma. With built-in low energy dosimetry control, filter and applicator recognition, and suitability with oval applicators, treatment is pain-free and with pinpoint accuracy, so that healthy skin is not affected and surgical scarring is avoided. Fast treatment times result in a large reduction in time and impact on the patient’s day-to-day life.
The Xstrahl 150 is supplied with eight open-ended clinical applicators of 15 cm and 25 cm focus to skin distance (FSD). The applicators are interlocked into the head of the treatment machine, ensuring that RT exposure may only be delivered with the correct applicator attached. Made from stainless steel and with clear Perspex viewing ends, radiographers can accurately position the applicators prior to treatment so as to achieve optimal skin apposition Additional focal spot applicators, standardized applicators, oval applicators, and bespoke applicators are available upon request.
The Xstrahl 150 can be floor or ceiling mounted, making it easy to install alongside other equipment and adaptable where space is restricted. The intuitive machine controls have been ergonomically designed to provide the operator with smooth, controlled movements at all times, allowing the RT therapist to easily position the unit, with smooth fine adjustments easy set up for each treatment field, ensuring patient comfort. The unit’s low energy and short exposure times also mean that the treatment room requires less shielding compared to a high energy linear accelerator (Linac).
The system is controlled via proprietary Concerto and Fisica software. Concerto, the clinical interface, provides an intuitive workflow for treatments and creates a unique and detailed clinical record for each patient, including treatment images that are linked to each treatment field, providing a clinical record of the delivered exposure. For patients with multiple fields, Concerto provides a simple and easy method to recall and create new treatment fields. Fisica, the interface between the physicist and the system hardware, is a highly customizable user level app that enables configuration of the Xstrahl system.
“We've re-engineered the capabilities of our 150kV offering for skin cancer treatments,” said Adrian Treverton, CEO of Xstrahl. “The result is a one-stop-shop for all non-melanoma skin cancer cases, with optimum levels of dose control.”
Related Links:
Xstrahl Medical
The Xstrahl Medical (Camberley, United Kingdom) 150 X-ray system delivers an adaptable energy range of up to 150kV, allowing treatment of superficial lesions that range from keloid scars and dermatological conditions such as psoriasis to benign plaques, and up to basal cell carcinoma. With built-in low energy dosimetry control, filter and applicator recognition, and suitability with oval applicators, treatment is pain-free and with pinpoint accuracy, so that healthy skin is not affected and surgical scarring is avoided. Fast treatment times result in a large reduction in time and impact on the patient’s day-to-day life.
The Xstrahl 150 is supplied with eight open-ended clinical applicators of 15 cm and 25 cm focus to skin distance (FSD). The applicators are interlocked into the head of the treatment machine, ensuring that RT exposure may only be delivered with the correct applicator attached. Made from stainless steel and with clear Perspex viewing ends, radiographers can accurately position the applicators prior to treatment so as to achieve optimal skin apposition Additional focal spot applicators, standardized applicators, oval applicators, and bespoke applicators are available upon request.
The Xstrahl 150 can be floor or ceiling mounted, making it easy to install alongside other equipment and adaptable where space is restricted. The intuitive machine controls have been ergonomically designed to provide the operator with smooth, controlled movements at all times, allowing the RT therapist to easily position the unit, with smooth fine adjustments easy set up for each treatment field, ensuring patient comfort. The unit’s low energy and short exposure times also mean that the treatment room requires less shielding compared to a high energy linear accelerator (Linac).
The system is controlled via proprietary Concerto and Fisica software. Concerto, the clinical interface, provides an intuitive workflow for treatments and creates a unique and detailed clinical record for each patient, including treatment images that are linked to each treatment field, providing a clinical record of the delivered exposure. For patients with multiple fields, Concerto provides a simple and easy method to recall and create new treatment fields. Fisica, the interface between the physicist and the system hardware, is a highly customizable user level app that enables configuration of the Xstrahl system.
“We've re-engineered the capabilities of our 150kV offering for skin cancer treatments,” said Adrian Treverton, CEO of Xstrahl. “The result is a one-stop-shop for all non-melanoma skin cancer cases, with optimum levels of dose control.”
Related Links:
Xstrahl Medical
Latest Nuclear Medicine News
- Novel PET Imaging Approach Offers Never-Before-Seen View of Neuroinflammation
- Novel Radiotracer Identifies Biomarker for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
- Innovative PET Imaging Technique to Help Diagnose Neurodegeneration
- New Molecular Imaging Test to Improve Lung Cancer Diagnosis
- Novel PET Technique Visualizes Spinal Cord Injuries to Predict Recovery
- Next-Gen Tau Radiotracers Outperform FDA-Approved Imaging Agents in Detecting Alzheimer’s
- Breakthrough Method Detects Inflammation in Body Using PET Imaging
- Advanced Imaging Reveals Hidden Metastases in High-Risk Prostate Cancer Patients
- Combining Advanced Imaging Technologies Offers Breakthrough in Glioblastoma Treatment
- New Molecular Imaging Agent Accurately Identifies Crucial Cancer Biomarker
- New Scans Light Up Aggressive Tumors for Better Treatment
- AI Stroke Brain Scan Readings Twice as Accurate as Current Method
- AI Analysis of PET/CT Images Predicts Side Effects of Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer
- New Imaging Agent to Drive Step-Change for Brain Cancer Imaging
- Portable PET Scanner to Detect Earliest Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease
- New Immuno-PET Imaging Technique Identifies Glioblastoma Patients Who Would Benefit from Immunotherapy
Channels
Radiography
view channel
AI-Powered Imaging Technique Shows Promise in Evaluating Patients for PCI
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), also known as coronary angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure where small metal tubes called stents are inserted into partially blocked coronary arteries... Read more
Higher Chest X-Ray Usage Catches Lung Cancer Earlier and Improves Survival
Lung cancer continues to be the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. While advanced technologies like CT scanners play a crucial role in detecting lung cancer, more accessible and affordable... Read moreMRI
view channel
Ultra-Powerful MRI Scans Enable Life-Changing Surgery in Treatment-Resistant Epileptic Patients
Approximately 360,000 individuals in the UK suffer from focal epilepsy, a condition in which seizures spread from one part of the brain. Around a third of these patients experience persistent seizures... Read more
AI-Powered MRI Technology Improves Parkinson’s Diagnoses
Current research shows that the accuracy of diagnosing Parkinson’s disease typically ranges from 55% to 78% within the first five years of assessment. This is partly due to the similarities shared by Parkinson’s... Read more
Biparametric MRI Combined with AI Enhances Detection of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer
Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are transforming the way medical images are analyzed, offering unprecedented capabilities in quantitatively extracting features that go beyond traditional visual... Read more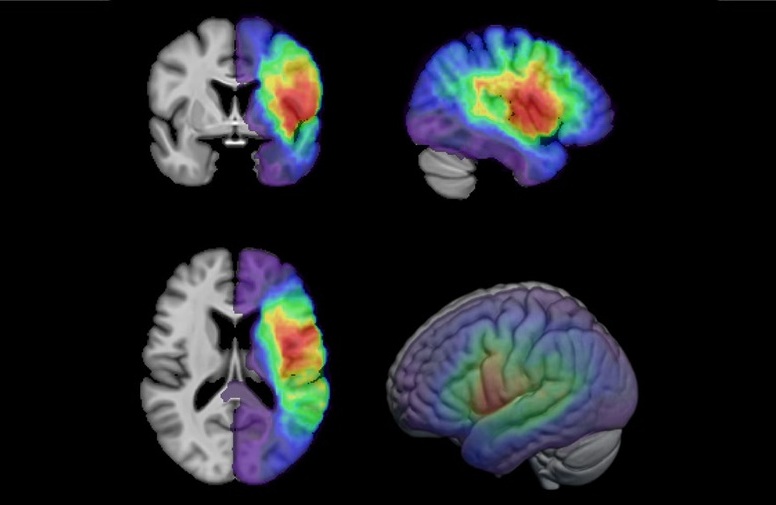
First-Of-Its-Kind AI-Driven Brain Imaging Platform to Better Guide Stroke Treatment Options
Each year, approximately 800,000 people in the U.S. experience strokes, with marginalized and minoritized groups being disproportionately affected. Strokes vary in terms of size and location within the... Read moreUltrasound
view channel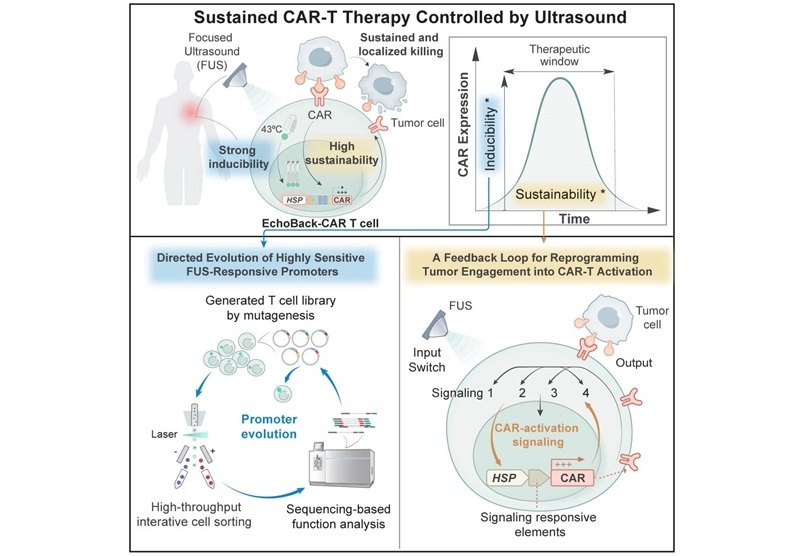
Smart Ultrasound-Activated Immune Cells Destroy Cancer Cells for Extended Periods
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has emerged as a highly promising cancer treatment, especially for bloodborne cancers like leukemia. This highly personalized therapy involves extracting... Read more
Tiny Magnetic Robot Takes 3D Scans from Deep Within Body
Colorectal cancer ranks as one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide. However, when detected early, it is highly treatable. Now, a new minimally invasive technique could significantly... Read more
High Resolution Ultrasound Speeds Up Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
Each year, approximately one million prostate cancer biopsies are conducted across Europe, with similar numbers in the USA and around 100,000 in Canada. Most of these biopsies are performed using MRI images... Read more
World's First Wireless, Handheld, Whole-Body Ultrasound with Single PZT Transducer Makes Imaging More Accessible
Ultrasound devices play a vital role in the medical field, routinely used to examine the body's internal tissues and structures. While advancements have steadily improved ultrasound image quality and processing... Read moreGeneral/Advanced Imaging
view channel
AI-Powered Imaging System Improves Lung Cancer Diagnosis
Given the need to detect lung cancer at earlier stages, there is an increasing need for a definitive diagnostic pathway for patients with suspicious pulmonary nodules. However, obtaining tissue samples... Read more
AI Model Significantly Enhances Low-Dose CT Capabilities
Lung cancer remains one of the most challenging diseases, making early diagnosis vital for effective treatment. Fortunately, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing lung cancer... Read moreImaging IT
view channel
New Google Cloud Medical Imaging Suite Makes Imaging Healthcare Data More Accessible
Medical imaging is a critical tool used to diagnose patients, and there are billions of medical images scanned globally each year. Imaging data accounts for about 90% of all healthcare data1 and, until... Read more
Global AI in Medical Diagnostics Market to Be Driven by Demand for Image Recognition in Radiology
The global artificial intelligence (AI) in medical diagnostics market is expanding with early disease detection being one of its key applications and image recognition becoming a compelling consumer proposition... Read moreIndustry News
view channel
GE HealthCare and NVIDIA Collaboration to Reimagine Diagnostic Imaging
GE HealthCare (Chicago, IL, USA) has entered into a collaboration with NVIDIA (Santa Clara, CA, USA), expanding the existing relationship between the two companies to focus on pioneering innovation in... Read more
Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Phantoms Transform CT Imaging
New research has highlighted how anatomically precise, patient-specific 3D-printed phantoms are proving to be scalable, cost-effective, and efficient tools in the development of new CT scan algorithms... Read more
Siemens and Sectra Collaborate on Enhancing Radiology Workflows
Siemens Healthineers (Forchheim, Germany) and Sectra (Linköping, Sweden) have entered into a collaboration aimed at enhancing radiologists' diagnostic capabilities and, in turn, improving patient care... Read more